Formal and informal communication refers to two different styles of communication that people use in various contexts. Formal communication is more structured, and professional, and follows specific rules and conventions, whereas informal communication is more relaxed, casual, and spontaneous.
Understanding the differences between these two styles of communication is important as it can affect how people perceive and respond to your message, depending on the context and audience.
Overview of formal vs informal communication
Differentiator Factor | Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
Setting | Used in professional or official settings | Used in personal or casual settings |
Rules and Procedures | Follows established rules and procedures | Has no set rules or procedures |
Structure | Generally structured, organized and planned | Can be spontaneous and unplanned |
Language | Uses proper grammar and vocabulary | May use slang, colloquial language or jargon |
Information Delivery | Uses proper grammar and vocabulary | |
Mode of Communication | Often written, such as in emails or memos | Often spoken, such as in conversations or phone calls |
Greetings and Sign-Offs | Uses formal greetings and sign-offs (e.g., "Dear Sir/Madam" and "Sincerely") | Uses casual greetings and sign-offs (e.g., "Hey" and "Take care") |
Personal Topics | Avoids personal topics or opinions | May include personal opinions or experiences |
Tone | Tends to be serious and professional | Tends to be lighthearted and relaxed |
Etiquette and Protocol | Requires attention to etiquette and protocol | Requires little attention to etiquette or protocol |
Detailed explanation on what is the difference between formal and informal communication
Communication can be categorized into two main types: formal and informal. Understanding the differences between these two forms of communication is essential to ensure that the intended message is conveyed accurately and appropriately. In this section, we will explore:
10 Differences between formal and informal communication
1) Setting: Formal communication is used in professional or official settings, such as business meetings, academic conferences, or legal proceedings. Informal communication is typically employed in non-professional or relaxed environments, such as social gatherings with friends or interactions with family members.
2) Rules and Procedures: Formal communication follows established rules and procedures, such as those related to addressing individuals by their formal titles such as Mr. or Dr., using proper grammar and vocabulary, and following established etiquette and protocol. Informal communication has no set rules or procedures and may allow for more flexibility in language use and behavior.
3) Structure: Formal communication is generally structured, organized, and planned. It may involve preparing written documents or presentations in advance, following a specific agenda, or adhering to a strict timeline. Informal communication can be spontaneous and unplanned, with no set structure or agenda.
4) Language: Formal communication uses proper grammar and vocabulary, avoiding slang, colloquial language, or jargon. Informal communication may use more relaxed or casual language, including slang, colloquialisms, or jargon, depending on the context.
5) Information Delivery: Formal communication conveys information clearly and concisely, often prioritizing accuracy and professionalism over a personal connection or entertainment value. Informal communication may use storytelling, humor, or other techniques to convey information, and may prioritize personal connection or entertainment value over accuracy or professionalism.
6) Mode of Communication: Formal communication is often written, such as in emails, business reports, or presented through formal speeches or presentations. Informal communication is often spoken, such as in conversations or phone calls, but can also take written form, such as through text messages or social media.
7) Greetings and Sign-Offs: In formal communication, formal greetings and sign-offs are used, such as “Dear Sir/Madam” and “Sincerely.” In informal communication, casual greetings and sign-offs are used, such as “Hey” or “Take care.”
8) Personal Topics: Formal communication typically avoids personal topics or opinions, focusing on professional or official information. Informal communication may include personal opinions, experiences, or topics unrelated to professional or official matters.
9) Tone: Formal communication tends to be serious and professional, with a focus on conveying information respectfully and objectively. Informal communication tends to be more lighthearted and relaxed, with a focus on personal connection and emotional expression.
10) Etiquette and Protocol: Formal communication requires attention to etiquette and protocol, including adherence to established rules and procedures related to behavior, language use, and other social norms. Informal communication may require little attention to etiquette or protocol and may prioritize personal comfort or spontaneity over strict adherence to social norms.
Similarities between formal and informal communication
Similarities | Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
Aims to convey a message | Yes | Yes |
Involves the use of language | Yes | Yes |
Requires active listening | Yes | Yes |
Can be verbal or nonverbal | Yes | Yes |
Can occur in various settings | Yes | Yes |
Examples of formal and informal communication
Examples of Formal Communication:
- A business meeting in which colleagues discuss company policy and strategy.
- A lecture delivered by a professor to a group of students.
- A press release announcing a new product or service.
- A legal document, such as a contract or a court filing.
- A job interview with a potential employer.
Examples of Informal Communication:
- A conversation between friends discussing their weekend plans.
- A phone call between family members catching up on recent news.
- A text message sent between coworkers about a work-related project.
- A chat over coffee with a neighbor about neighborhood events.
- A post on social media sharing personal experiences or opinions.
What is formal communication?
Formal communication refers to the use of professional language and structure in conveying information or ideas in an official or professional setting. It involves following established rules and procedures related to language use, behavior, and social norms.
Formal channel of communication often follows a structured format such as in written reports, formal speeches, or presentations. It aims to convey information in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
Check out our detailed guide on What is Formal Communication: Example, Types & Characteristics
Types of formal communication
These types of formal communication channels are important for effective communication in organizations, and understanding them can help individuals communicate more effectively.
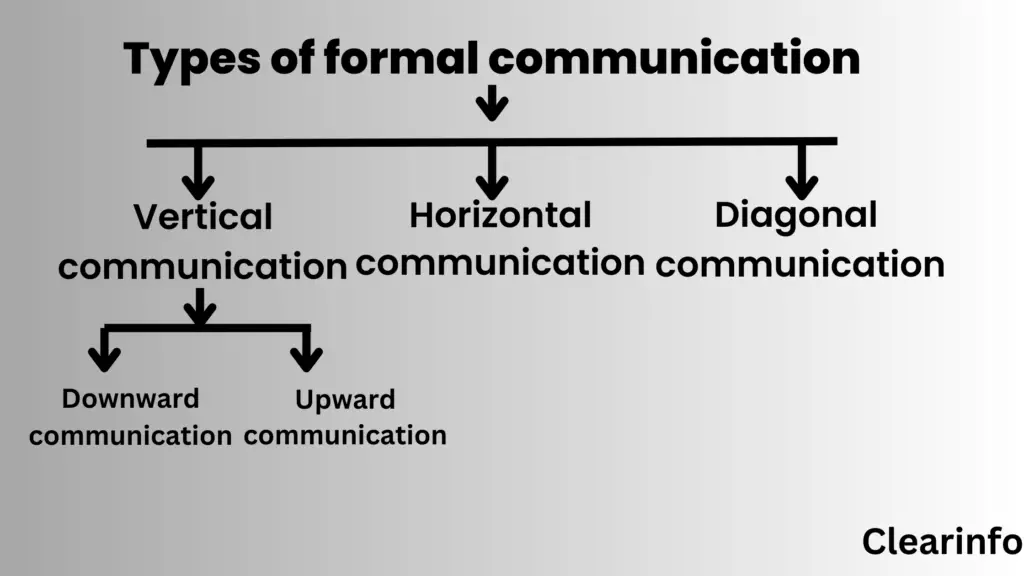
1) Vertical communication: This type of communication occurs between people at different levels of the organizational hierarchy. Information can flow upwards from a lower position to a higher position, or it can flow downwards from a higher position to a lower position.
Check out our detailed guide on What is Vertical Communication: Examples, Types & Importance
2) Upward communication: It refers to the flow of communication from employees in lower positions to those in higher positions. It can be used to provide feedback, make suggestions, or report on progress.
Check out our detailed guide on What is Upward Communication: Examples, Objectives & Methods
Upward Communication: Advantages & Disadvantages With Examples
3) Downward communication: It involves the transmission of information from employees in higher positions to those in lower positions. It can be used to give instructions, provide feedback, or deliver information about company policies and procedures.
Check out our detailed guide on What Is Downward Communication: Examples, Types & Objectives
4) Horizontal communication: This type of communication occurs between people who are at the same level in the organizational hierarchy. It can be used to coordinate work, share information, or solve problems.
Check out our detailed guide on What Is Horizontal Communication: (Examples & Types)
5) Diagonal communication: This is communication that occurs between people who are not in the same hierarchical level or department, but still have a relationship or connection. It can be used to share information, collaborate on projects, or build relationships.
Check out our detailed guide on What Is Diagonal Communication: Examples, Advantages & Features
Advantages and disadvantages of formal communication
Advantages of formal communication:
1. Clarity: Formal communication is structured and precise, making it easier to understand and reducing the chances of misinterpretation.
2. Record-keeping: Formal communication often leaves a paper trail, allowing for easy reference and record-keeping.
Disadvantages of formal communication:
1. Rigidity: Formal communication can be rigid and inflexible, making it difficult to adjust to changing circumstances or respond quickly to new situations.
2. Impersonal: Formal communication can be impersonal and lack the warmth and personal connection of informal communication, making it less effective for building relationships or fostering a positive work culture.
Check out our detailed guide on Advantages And Disadvantages of Formal Communication With Examples
What is the implication of formal communication?
The implication of formal communication is that it sets a professional tone for the exchange of information, ensuring that the message is conveyed in a structured, precise, and official manner. Formal communication can also help to establish a record of communication for future reference or legal purposes.
However, it can also be rigid, inflexible, and impersonal, which can limit its effectiveness in building relationships or fostering a positive work culture.
What is informal communication?
Informal communication refers to a form of interaction that takes place between individuals in an informal or social context. It does not follow any structured format or established rules of language use, behavior, or social norms. Informal channel of communication can be verbal or nonverbal and often includes gestures, facial expressions, or body language.
Further Reading: What is informal communication in the workplace
Types of informal communication
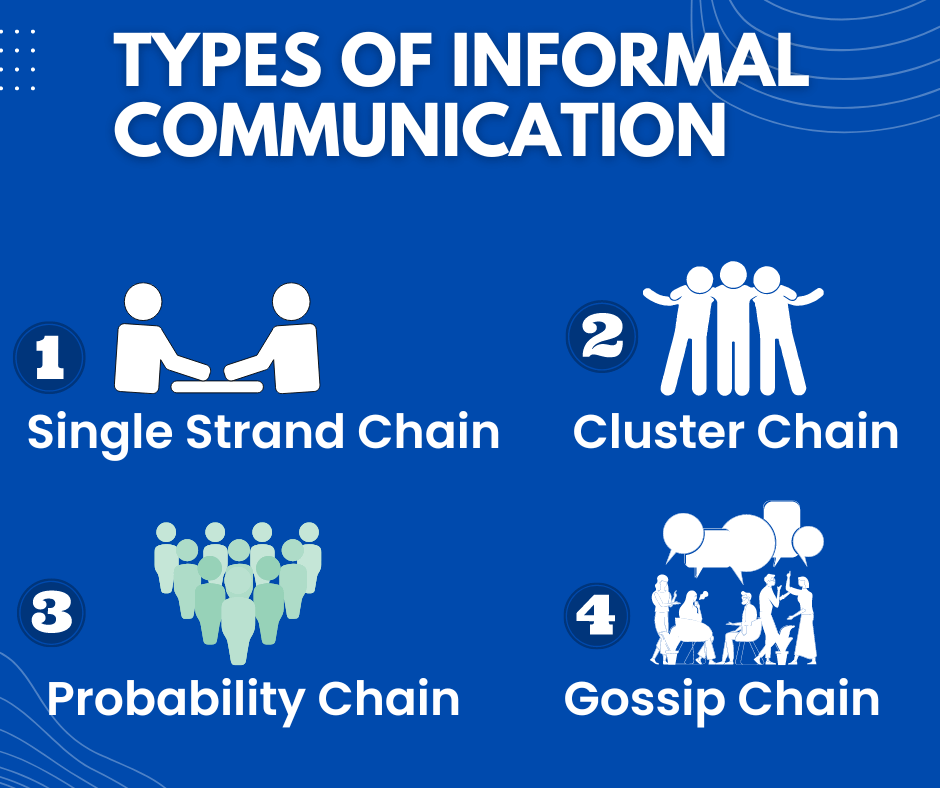
#1 Single Strand Chain: This is a one-to-one form of communication where information is passed from one person to the next in a linear fashion.
#2 Cluster Chain: This is a form of communication method in which information is transmitted from an individual to a network of interconnected people.
#3 Probability Chain: This is a form of communication where information is passed from one person to another at random, and the likelihood of the message being passed on depends on the probability of the next person being receptive to the message.
#4 Gossip Chain: This is a form of communication where information is passed on in a random and unstructured way, often involving multiple people and sometimes resulting in the distortion or exaggeration of the original message.
Advantages and disadvantages of informal communication
Two advantages of informal communication are:
1. Speed: Informal communication can be faster than formal communication since it doesn’t have to go through the organizational hierarchy. It allows information to be quickly disseminated among employees.
2. Flexibility: Compared to formal communication, informal communication is characterized by greater flexibility. It allows employees to communicate in a way that is more comfortable for them, such as using informal language, which can help build stronger relationships and foster collaboration.
Two disadvantages of informal communication are:
1. Inaccuracy: Since informal communication isn’t regulated or controlled, there’s a higher chance that information may be inaccurate, incomplete, or distorted as it is passed along. This can lead to confusion and misunderstandings among employees.
2. Lack of documentation: Informal communication is usually not documented, which can make it difficult to track important decisions or actions taken based on that communication. This can create legal or financial issues for an organization if there’s a need to provide evidence of communication or decisions made.
Check out our detailed guide on Informal Communication Advantages And Disadvantages With Example
What is the implication of informal communication?
Informal communication, whether in personal or organizational settings, can have significant implications for relationships, productivity, and decision-making. While it can facilitate the flow of information and build trust and collaboration, it can also lead to inaccuracies, misunderstandings, and the spread of rumors or gossip, commonly known as the “grapevine”.
To manage the implications of informal communication, individuals, and organizations must strike a balance between the benefits of informal communication and the need for accuracy, accountability, and effective decision-making.
Difference between formal and informal communication in management
In management, it’s important to balance the benefits of both formal and informal communication to ensure effective communication and decision-making.
Aspect | Formal Communication in Management | Informal Communication in Management |
Structure | Regulated and follows a specific structure | Not regulated and does not have a defined structure |
Purpose | Used to convey official information, such as policies, procedures, or performance reviews | Used for personal or social purposes |
Channels | Flows through established channels, such as memos, reports, or meetings | Can flow through a variety of channels, such as phone calls, text messages, or social media |
Tone | Professional and respectful | Relaxed and casual |
Documentation | Usually documented for legal and regulatory purposes | Not typically documented |
What is the difference between formal and informal writing
Aspect | Formal Writing | Informal Writing |
Tone | Serious and objective | Conversational and personal |
Structure | Follows a specific structure, such as an introduction, body, and conclusion | More free-form and lacks a set structure |
Vocabulary | Uses complex and technical vocabulary | Uses simple and everyday language |
Audience | Aimed at a professional or academic audience | Intended for personal or social interactions |
Use of contractions and abbreviations | Avoids contractions and abbreviations | May use them for brevity and informality |
Check out detailed article on: Difference between Formal & Informal Writing With Examples
What is the difference between formal and informal conversation
Aspect | Formal Conversation | Informal Conversation |
Tone | Polite and respectful | Casual and relaxed |
Purpose | Typically business or professional | Typically social or personal |
Vocabulary | Uses formal and technical vocabulary | Uses everyday language and slang |
Structure | Follows a specific structure and etiquette | Lacks a specific structure and etiquette |
Use of humor | Limited and usually related to the topic | More frequent and often unrelated to the topic |
Related Reading: Difference between communication and conversation with examples
How can informal communication complement formal communication
Informal communication can complement formal communication by filling in the gaps left by the more structured and regulated nature of formal communication.
While formal communication is important for conveying official information and maintaining the professional reputation of an organization, informal communication can help to create a sense of belonging and build stronger relationships between colleagues.
Informal communication can also provide a more flexible and responsive way of communicating, allowing for faster decision-making and problem-solving.In addition, informal communication can be a useful tool for resolving conflicts between employees.
By discussing issues in an informal setting, employees can often come to a resolution without the need for formal mediation.
Overall, informal communication can complement formal communication by providing additional information, feedback, and insights that can help organizations function more effectively.
Practical tips & strategies for both formal and informal settings
Based on our own experience and expertise below we have drafted three practical tips and strategies for communicating effectively while using formal and informal communication.
Tips for Effective Formal Communication:
1) Prepare ahead of time: Before engaging in formal communication, it’s important to prepare your thoughts and what you want to communicate. This could involve researching the topic, making an outline of your ideas, and reviewing the principles of good communication.
2) Be mindful of your tone: Your tone can impact how your message is received. In formal communication, it’s important to use a professional and respectful tone, even if you’re discussing difficult or contentious topics.
3) Stay focused on the topic: It’s easy to get sidetracked during formal communication, but it’s important to stay focused on the topic at hand. Avoid going off on tangents and bring the conversation back to the main point if it begins to stray.
Tips for Effective Informal Communication:
1) Be personable and approachable: When communicating informally, it’s important to be personable and approachable. This can help to create a relaxed and friendly atmosphere, which can make communication easier and more effective.
2) Listen actively: Effective informal communication requires active listening. Make sure to listen to what the other person is saying and respond appropriately.
3) Be mindful of nonverbal cues: In informal communication, nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and body language can be just as important as spoken words. Pay attention to these cues to better understand the message being conveyed.
By following these tips and strategies, you can communicate effectively in both formal and informal settings, building stronger relationships with your colleagues, friends, and family.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between formal and informal?
Ans: Formal and informal refer to two different styles or approaches to communication. Formal communication is official, and structured, and follows a specific set of rules and conventions. It is used in professional settings or when communicating with people you do not know well. Informal communication, on the other hand, is relaxed, casual, and often unstructured. It is used in social settings or when communicating with friends or colleagues you know well.
Q2: What are the 3 differences between formal and informal communication?
Ans: The three key differences between formal and informal communication are, Tone, Structure, and Audience. Formal communication has a professional tone, and a specific structure, and is usually directed at a wider audience such as clients, or the public. Informal communication has a casual tone, can be unstructured, and is usually directed at a smaller audience such as friends, or colleagues.
Q3: What is the difference between verbal and non-verbal communication?
Ans: Verbal communication refers to the use of words or language to convey a message, either orally or in writing. Nonverbal communication, on the other hand, refers to the use of body language, gestures, facial expressions, and tone of voice to communicate.



