Understand the concept of the horizontal flow of communication with examples and types. The guide also includes strategies to improve and implement effective horizontal communication in the workplace.
Definition of Horizontal Communication
“Horizontal communication refers to communication between employees at identical levels of the organisational hierarchy. It usually involves the coordination of information, enabling co-operation and collaboration between employees with a similar ranking or level within the organisation.” (Baden Eunson)
“Horizontal communication refers to communication between individuals not in a hierarchical relationship. Communication horizontally contributes to a high level of satisfaction among the human resource managers.” (Frank Ostroff)
What is horizontal communication?
Horizontal communication is a type of communication that occurs between individuals or groups who hold similar positions within the organizational structure. Instead of following the traditional top-down or bottom-up communication patterns, it allows for direct interactions and information sharing among employees who are on the same level in the hierarchy.
For example, employees from different departments, teams, or functional areas at similar job levels can communicate horizontally.
A horizontal channel of communication is essential for fostering collaboration and teamwork within an organization. It allows employees to share knowledge and ideas freely, fostering a sense of inclusivity. Because horizontal communication bypasses the formal chain of command, information can flow more quickly and reach relevant stakeholders without delays, making decision-making more efficient.
Features of horizontal communication
- Lateral Communication Flow: Horizontal communication involves communication that moves laterally across the organization, rather than vertically up or down the hierarchical structure. It enables employees at the same level to collaborate, share knowledge, coordinate tasks, and address common challenges.
- Informal Nature: While some horizontal communication may occur through formal channels like email or scheduled meetings, it often takes place informally through casual conversations, instant messaging, or water-cooler discussions.
- Reducing Hierarchical Barriers: Horizontal flow of communication helps to break down rigid hierarchical barriers within organizations. It fosters a more inclusive and open communication culture, where ideas can flow freely across different departments or divisions.
- Faster Information Flow: Compared to vertical communication which may need to go through multiple levels of management, horizontal communication allows information to spread more quickly across the organization.
- Conflict Resolution: It provides a platform for conflict resolution and addressing coworker issues effectively. Open communication can help in understanding different perspectives and finding mutually beneficial solutions.
Diagram of horizontal communication
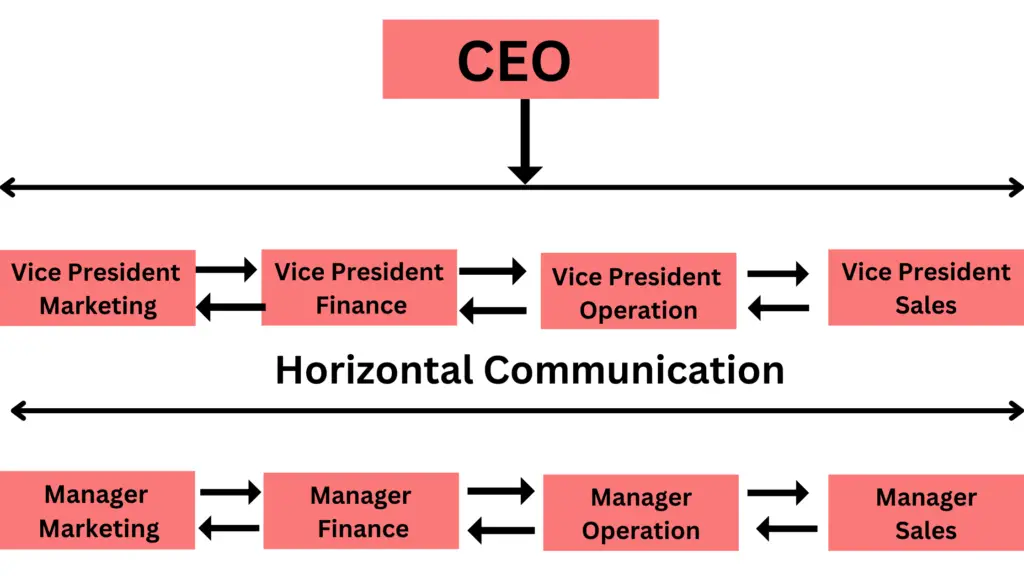
The above diagram represents the flow of horizontal communication among managers and vice presidents between various departments of an organization.
Diagram of vertical and horizontal communication
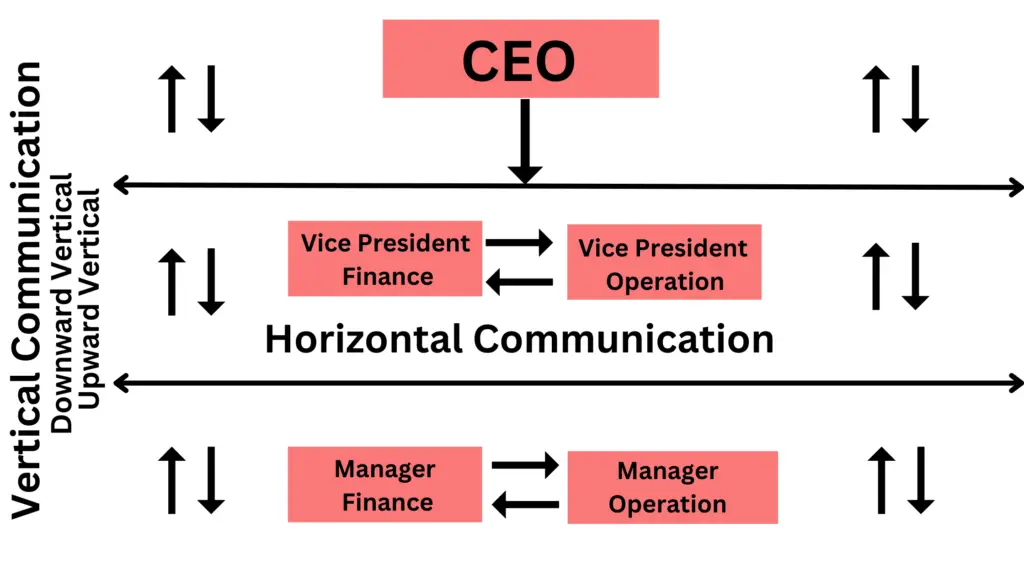
Objectives of horizontal communication
The objectives of horizontal communication are designed to promote effective collaboration and coordination among employees at the same hierarchical level or across different departments. Some key objectives include:
1/ Information Sharing: The primary objective of horizontal communication is to facilitate the exchange of information, knowledge, and data among colleagues or teams. This helps to keep all relevant parties informed about important updates, projects, and organizational developments.
2/ Peer-to-Peer Communication: Horizontal communication flow takes place between individuals or groups who are equals within the organization. This means that there is no formal power or authority difference between them.
3/ Facilitating Feedback: Consistent feedback is crucial for fostering employee growth and development. Horizontal communication provides a platform for giving and receiving feedback among colleagues, which can contribute to individual and team improvement.
4/ Decision-Making Support: Effective horizontal communication facilitates decision-makers’ access to essential information, and input from relevant stakeholders before making important choices. This increases the quality and validity of decisions.
By achieving these objectives, horizontal communication contributes to a more efficient, innovative, and integrated organizational culture, where employees feel valued and connected to the larger mission of the company.
What are the purposes of horizontal communication?
The purposes of horizontal communication serve as specific reasons or intentions for engaging in communication horizontally within an organization. These purposes are aligned with the objectives previously mentioned and include:
1/ Collaboration: Horizontal interactions facilitates collaboration among employees at the same level or across different departments. It allows individuals to work together, share ideas, and collaborate their skills and expertise to accomplish shared objectives.
2/ Building Relationships and Trust: Engaging in horizontal communication builds positive relationships and trust among colleagues. It creates a sense of mutual understanding, leading to a more productive work environment.
3/ Empowerment and Inclusivity: By encouraging horizontal networks, organizations empower employees to express their opinions and ideas freely. It promotes a sense of value, acknowledging individuals as active contributors to the organization’s success.
4/ Conflict Resolution: When conflicts arise between individuals or departments, horizontal communication provides a platform for addressing the issues openly and finding mutually acceptable resolutions.
5/ Cross-Functional Integration: In organizations with multiple departments or teams, a horizontal communication network facilitates integration and consistency across different functions, ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals.
Types of horizontal communication
For an effective flow of communication, horizontal communication in business can be divided into three types including intradepartmental communication, interdepartmental cooperation, and staff advice to line departments. These communication channels contribute to the overall success and efficiency of the organization as a whole. Let’s discuss them in detail:
1/ Intradepartmental Communication: Intradepartmental communication refers to the exchange of information among individuals or teams within the same department or functional unit of an organization. This type of horizontal communication is vital for ensuring smooth internal operations within a department and effective coordination of tasks. It serves several purposes:
- Task Coordination: Intradepartmental communication helps team members coordinate their efforts and align their activities toward achieving common goals.
- Information Sharing: Colleagues within a department share relevant information, data, and knowledge required for their respective roles. This could include sharing market research, customer feedback, or updates on industry trends.
- Feedback and Evaluation: Intradepartmental communication fosters a culture of continuous feedback and evaluation. Team members can offer valuable constructive feedback to each other, supporting individual growth and improvement.
2/ Interdepartmental Cooperation: Interdepartmental cooperation involves communication and collaboration between different departments or functional units within an organization. This type of horizontal communication is crucial for achieving cross-functional goals and maintaining a cohesive organizational strategy. It serves various purposes:
- Cross-Functional Projects: Interdepartmental cooperation is essential when working on projects that require input and resources from multiple departments.
- Resource Sharing: Departments may share resources, such as equipment, data, or expertise, to support one another’s initiatives.
- Strategic Alignment: Departments can align their objectives and strategies through interdepartmental communication. This alignment ensures that all parts of the organization are working cohesively toward the primary mission and vision.
3/ Staff Advice to Line Departments: Staff advice to line departments refers to the communication provided by support or staff functions to operational or line departments. Support functions, such as Human Resources, Finance, or IT, provide expertise and advice to line departments that directly deliver products or services to customers. The purposes of this type of horizontal communication include:
- Expertise and Guidance: Staff functions offer specialized knowledge and expertise to line departments. This guidance ensures that operational decisions align with organizational policies, regulations, and best practices.
- Policy Implementation: Staff functions communicate and explain organizational policies and procedures to line departments. This helps ensure consistent compliance with company guidelines.
- Training and Development: Staff functions offer training and development programs to enhance the skills and capabilities of employees in line departments.
- Resource Allocation: Staff functions, such as Finance or Procurement, communicate information about budgeting, resource allocation, and procurement processes to line departments. This facilitates efficient resource management.
Advantages and disadvantages of horizontal communication
Advantages of horizontal communication
Some of the key merits of horizontal communication include:
1/ Reduce Miscommunication: In a horizontal communication structure, there is less likelihood of messages being distorted or diluted as they do not pass through multiple layers of management. This can help reduce misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
2/ Adapts to Dynamic Environments: Horizontal mode of communication is more adaptable to changes in the business environment. When the organization needs to be flexible and responsive to market shifts, a flat communication structure facilitates quick coordination and adjustment.
3/ Encourages Informal Communication: Horizontal communication often involves informal conversations, which can foster friendships and trust among employees. These personal connections contribute to a more positive organizational culture.
4/ Better Customer Service: When employees from different departments communicate horizontally, they can better understand customer needs and challenges. This shared understanding enables them to provide more holistic and customer-centric solutions.
5/ Efficient Conflict Management: Horizontal communication allows for more direct and open conversations, making it easier to address conflicts and challenges in a timely manner. This promotes a culture of constructive criticism and continuous improvement.
6/ Supports Cross-Functional Projects: Cross-functional projects and initiatives often require seamless collaboration between different departments. Horizontal communication streamlines this process, ensuring smooth cooperation and integration of efforts.
7/ Effective Crisis Management: In times of crises or emergencies, the horizontal flow of information can be vital for swift and coordinated responses. Teams can collaborate seamlessly to address challenges and mitigate risks effectively.
Disadvantages of horizontal communication
Apart from the benefits, there are limitations to horizontal communication as well, which include:
1/ Risk of Bypassing Hierarchical Channels: One of the foremost demerits of horizontal communication is that the frequent horizontal information flow might lead to employees bypassing formal channels of communication, disregarding necessary approvals and protocols.
2/ Potential for Information Overload: Frequent and direct communication between employees can lead to an excess of information circulating within the organization. This may lead to employees overwhelm and make it difficult for them to prioritize essential messages.
3/ Loss of Specialization: Employees in horizontally structured organizations may focus on broader tasks that require collaboration across multiple functions, potentially leading to a loss of expertise in specific areas.
4/ Inefficiency in Large Organizations: As organizations grow larger, horizontal communication can become less effective. It may be challenging to ensure that all relevant parties are included in the communication loop, leading to potential information gaps.
5/ Difficulty in Monitoring and Evaluation: In a horizontally structured organization, it can be more challenging to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of communication processes. This lack of oversight may lead to communication inefficiencies or missed opportunities.
6/ Power Struggles: Horizontal communication can sometimes lead to conflicts and power struggles among employees, particularly if there is ambiguity about roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority.
7/ Challenges in Organizational Alignment: Without a strong vertical communication component, it can be difficult to ensure that the organization’s strategic objectives and vision are effectively communicated and understood throughout all levels of the company.
Example of horizontal communication
Horizontal interactions within the organization play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of management’s initiatives, ultimately leading to improved performance. These interactions trigger the 4C components: Communication, Coordination, Cooperation, and Collaboration among different departments.
For example, let’s consider a scenario where the top management aims to boost production capacity by 25% through economies of scale. To achieve this objective, a cross-departmental team known as the EOS (Economies of Scale) team can be established.
The EOS team will be led by the Sales and Marketing department and will include managers from Finance and Accounting, Human Resources, Information Technology, and Operational Management. This collaboration fosters a horizontal interaction between departments, as illustrated in Figure 1.1 below.
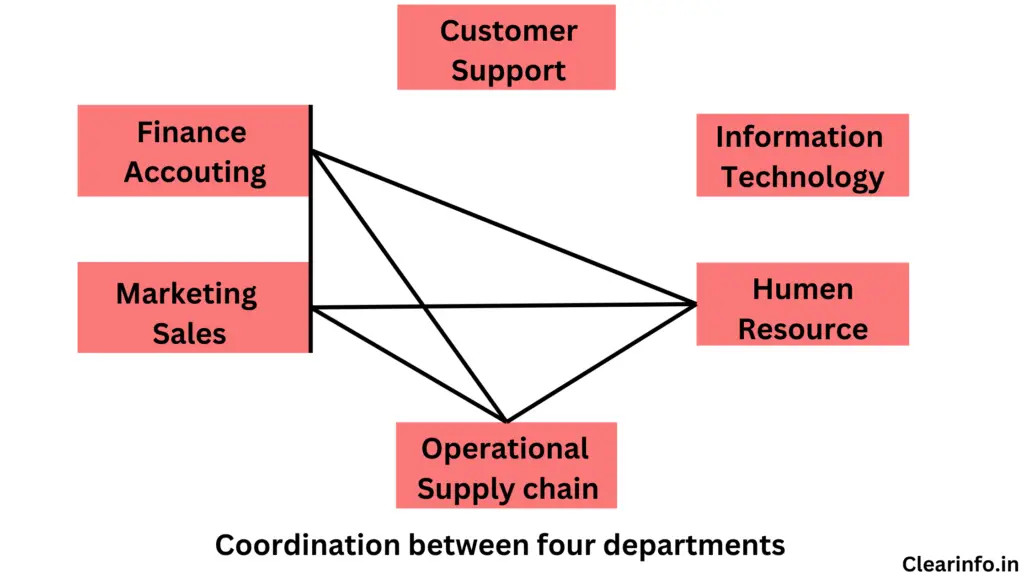
The EOS Team’s primary responsibilities include conducting production research, identifying various strategies, analyzing them, and ultimately selecting the most suitable one from the options available.
Simultaneously, the HR manager can create training manuals to educate employees on the chosen procedure, implement the strategy in production, and measure the resulting percentage change in output with the help of the new EOS strategy.
By fostering cross-departmental horizontal interaction, organizations can optimize resource allocation, leading to enhanced productivity and improved overall performance.
Example of barrier in horizontal communication
In some instances, managers from different departments face challenges in collaborating and cooperating with each other, leading to inefficiencies in horizontal interaction. Figure 2.2 below illustrates conflicts between the Marketing and Finance departments, as well as between the Operational and Information Technology departments. These conflicts can prevent smooth communication and coordination, affecting overall organizational performance.
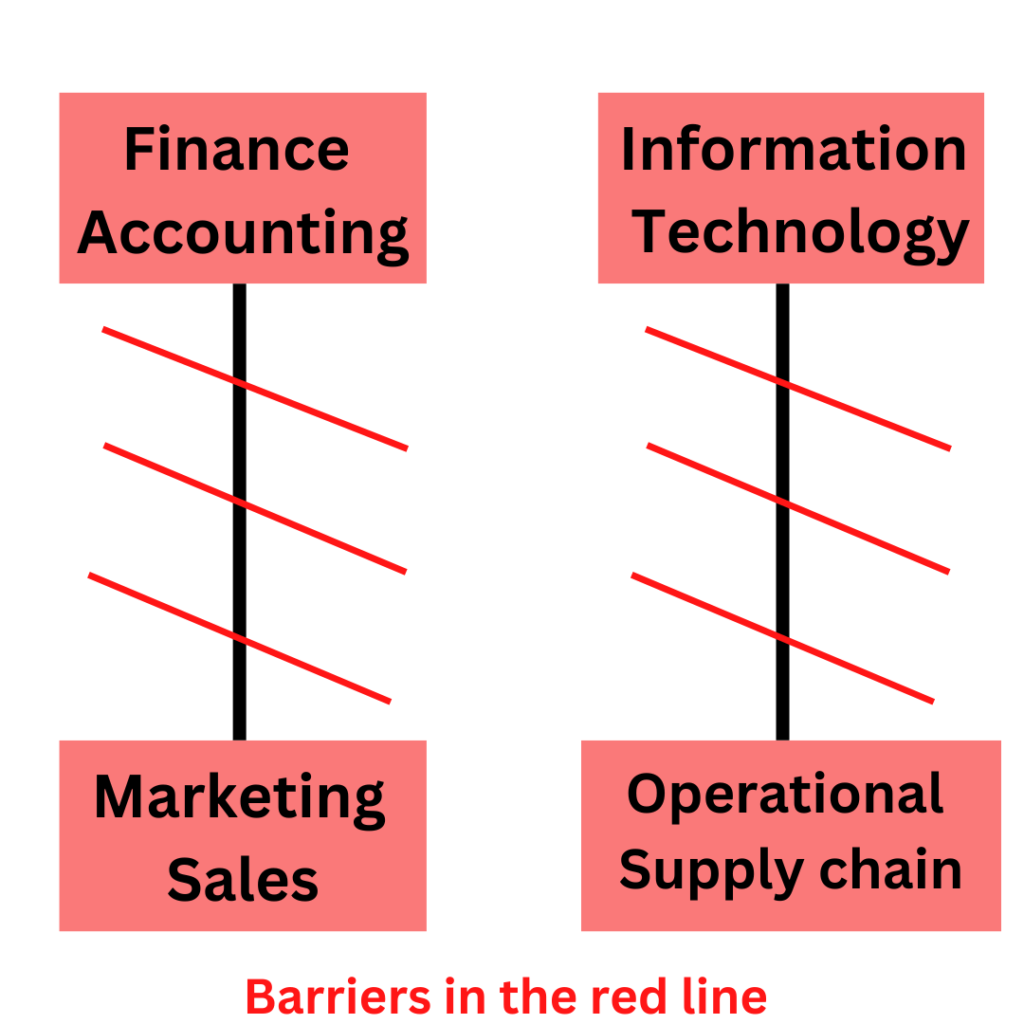
The clashes between departments may arise due to various factors, such as power struggles, physical barriers, resource allocation, a sense of belonging, capital funding, working assets, and more.
For instance, if the Sales and Marketing department fails to collaborate effectively with the Finance team, the organization will face challenges in scaling its production to achieve the economies of scale set.
Similarly, if the Operational and Information Technology departments lack coordination, the organization will encounter difficulties in digitalizing its production procedures and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). This lack of coordination may prevent the organization’s progress in adopting efficient and technologically advanced processes.
Reference for the examples included.
Examples of lateral communication:
1/ Cross-Training Programs: Lateral communication is encouraged when employees participate in cross-training programs, where they learn about the responsibilities and challenges of colleagues in other departments.
2/ Interdepartmental Meetings: When representatives from different departments come together to discuss shared goals, projects, or issues, lateral communication occurs. These meetings ensure a shared understanding among all employees.
3/ Performance reviews and feedback sessions: Regular performance reviews or feedback sessions that involve input from colleagues in other departments provide opportunities for lateral communication and a more holistic evaluation of an employee’s contributions.
These examples demonstrate the importance of lateral communication in promoting a collaborative and efficient work environment within organizations.
Examples of horizontal skills
Horizontal skills, also known as transferable or soft skills, are abilities that are valuable across various professions and industries. These skills are applicable across various jobs and industries but can be applied in a wide range of situations and roles. Here are some examples of horizontal skills:
- Critical Thinking: The capacity to analyze, evaluate, and solve problems by considering all relevant factors and making well-reasoned decisions.
- Time Management: The skill of prioritizing tasks, setting goals, and managing time efficiently to meet deadlines and increase productivity.
- Adaptability/Flexibility: Being able to adjust to changing circumstances, tasks, and environments with a positive attitude.
- Collaboration/Teamwork: Working effectively with others, contributing to group efforts, and being open to diverse perspectives and ideas.
- Leadership: Guiding and motivating others to achieve common goals, providing direction, and leading by example.
How does horizontal communication work?
Horizontal communication in the workplace operates through the exchange of messages between individuals or departments at the same hierarchical level within an organization. It enables colleagues to communicate directly with each other, fostering collaboration and problem-solving. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how horizontal communication works:
- Identifying the Need for Communication: The process of horizontal communication begins when individuals or departments recognize the need to share information or collaborate on a particular task, project, or issue. This need can arise from routine work activities or any situation that requires collective effort.
- Initiating Communication: Once the need for communication is identified, one or more individuals from the relevant departments initiate the communication process. This can be done through various means, such as face-to-face conversations, emails, or virtual meetings.
- Choosing the Communication Channel: The choice of communication channel depends on factors like the urgency of the message, the complexity of the information, and the preferences of the involved parties. In some cases, a quick chat or a phone call may be sufficient, while in others, a more formal meeting or a detailed email might be necessary.
- Sharing Information and Ideas: During the communication process, individuals exchange information, ideas, data, feedback, or any other relevant content.
- Active Listening and Feedback: Effective horizontal communication involves active listening from both parties. Participants must listen attentively to understand the perspectives and concerns of their colleagues.
- Collaboration and Decision-Making: Horizontal communication often leads to collaboration between individuals or departments to reach a consensus, make joint decisions, or jointly work on a task. This collaborative approach harnesses the diverse skills and expertise of team members, leading to more well-rounded outcomes.
- Informal Communication Networks: Horizontal organization communication is not solely limited to formal channels. Informal communication networks, such as watercooler chats, team outings, or virtual social interactions, also play a role in building relationships among colleagues.
- Recording and Documentation: Depending on the nature of the communication and the organization’s practices, relevant information and decisions resulting from horizontal business communication may be recorded and documented for future reference.
- Feedback and Iteration: Feedback is a crucial part of the horizontal communication process. If the initial communication results in a decision or action, participants may provide feedback on the outcomes, leading to further refinement and iteration of ideas.
Note: There are some other uses cases of horizontal system mentioned below
Uses of horizontal communication
Promotes collaboration and teamwork among employees.
Enhances efficiency by streamlining work processes and reducing redundancy.
Fosters innovation and creativity by facilitating the exchange of ideas and information.
Improves decision-making and problem-solving by ensuring access to relevant information.
Builds trust and mutual respect among colleagues.Increases job satisfaction and productivity.
What are the steps to implement an efficient horizontal communication strategy in a company?
Implementing an efficient horizontal communication strategy in a company requires careful planning, active involvement from leadership, and a commitment to fostering a collaborative culture. Here are the steps to guide the implementation process:
1/ Assessment and Understanding:
- Perform a comprehensive evaluation of the company’s existing communication practices to identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential barriers to horizontal communication.
- Understand the organizational structure, departmental workflows, and existing communication channels to determine how information currently flows across different levels and departments.
2/ Leadership Buy-In and Support:
- Gain support from top-level management and key stakeholders for the horizontal communication initiative.
- Explain the benefits of horizontal communication in improving teamwork and overall organizational performance.
3/ Set Clear Objectives:
- Define clear and measurable objectives for the horizontal communication strategy. These objectives should align with the company’s goals and address specific communication challenges or opportunities.
4/ Communication Guidelines and Training:
- Develop clear guidelines for horizontal communication, including preferred communication channels, response times, and the importance of active listening.
- Offer employees training in effective communication, emphasizing active listening skills and resolving conflicts collaboratively.
5/ Encourage Openness and Inclusivity:
- Cultivate a culture that values and encourages open communication, enabling employees to freely express their opinions and ideas.
- Promote inclusivity by ensuring that all team members have equal opportunities to participate and contribute to discussions.
6/ Use Technology Wisely:
- Implement communication tools and technologies that facilitate seamless horizontal communication, such as collaborative workspaces, and video conferencing solutions.
- Ensure that employees are trained on how to use these tools effectively.
7/ Establish Cross-Functional Teams and Projects:
- Foster collaboration between different departments by creating cross-functional teams or assigning employees from different areas to work together on specific projects.
- Encourage regular meetings and check-ins among team members to share progress, challenges, and insights.
8/ Monitor and Evaluate Progress:
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the horizontal communication strategy through feedback from employees, performance indicators, and communication metrics.
- Identify areas of improvement and adjust the strategy as needed to ensure ongoing success.
9/ Promote Learning and Knowledge Sharing:
- Facilitate opportunities for employees to share their expertise and knowledge through workshops, training sessions, or internal knowledge-sharing platforms.
- Encourage mentorship and peer-to-peer learning to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
By following these steps, a company can establish an efficient internal horizontal communication strategy that enhances collaboration and overall organizational performance. The key is to create a supportive communication environment where all employees feel empowered to contribute and participate in achieving common objectives.
How can horizontal communication be improved?
Improving horizontal communication requires a thoughtful approach that addresses barriers, enhances collaboration, and fosters a culture of openness. Here are some effective strategies to improve horizontal communication in an organization:
1/ Establish Clear Communication Channels: Identify and establish appropriate communication channels for horizontal communication. Utilize a mix of methods, including in-person meetings, virtual platforms, instant messaging, and collaborative software, to cater to various communication needs and preferences.
2/ Encourage Regular Team Meetings: Facilitate frequent team meetings, encouraging cross-departmental collaboration to discuss projects, share updates, and address challenges collectively. These meetings promote interaction and alignment among team members.
3/ Create Collaborative Spaces: Design physical and virtual spaces that encourage interaction among employees from different departments. Common areas, online forums, or social platforms can facilitate informal communication and idea sharing.
4/ Encourage Feedback Culture: Establish a feedback culture where employees are encouraged to provide constructive feedback to their peers and colleagues. This can be done through regular feedback sessions or anonymous feedback mechanisms.
5/ Promote a Flat Organizational Structure: Where feasible, adopt a flatter organizational structure that reduces hierarchical barriers and allows for more direct communication among employees at different levels.
6/ Use Visual Communication: Utilize visual aids, such as charts, graphs, and infographics, to present complex information and ideas more effectively. Visual communication can enhance understanding and engagement.
7/ Implement Two-Way Communication: Encourage employees to actively share their perspectives and ideas, and ensure that management is receptive to their input. Establishing a two-way communication flow demonstrates that their voices are valued.
8/ Monitor Communication Effectiveness: Regularly assess the effectiveness of horizontal communication initiatives through surveys, feedback loops, and communication metrics. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and fine-tune communication strategies accordingly.
Enhancing horizontal communication demands continuous effort and commitment across all organizational levels. By implementing these strategies, companies cultivate a more collaborative and engaged work environment that fosters effective horizontal communication.
Importance of horizontal communication in Workplace
Some of the key reasons why horizontal communication is essential:
1/ Efficiency and Productivity: Effective horizontal communication streamlines processes and reduces redundant efforts. Colleagues can share best practices, avoid duplication of work, and make more informed decisions, resulting in improved efficiency and productivity.
2/ Diverse Decision-Making: Engaging in horizontal communication ensures that decisions are not made solely from a top-down approach. Including multiple perspectives from different departments leads to more well-rounded and comprehensive decision-making processes.
3/ Networking and Career Development: Through horizontal communication, employees can expand their professional network within the organization. Building relationships with colleagues from various departments can create new career development opportunities.
4/ Effective Change Management: During times of organizational change, horizontal communication helps manage uncertainties and anxieties by providing accurate and timely information to all employees.
5/ Cross-Training and Skill Sharing: Horizontal communication supports cross-training initiatives, where employees can learn skills from others in different departments. This increases workforce readiness for changes within the organization.
Methods of horizontal communication
Horizontal communication flows through both oral and written channels for business communication. It makes use of several methods of communication such as:
- Memos: Memos are commonly used in business communication as they are short and concise pieces of information exchanged by the members of an organization.
- Letters: Businesses use official letters as a method of horizontal communication to exchange information, build relationships, and spike growth.
- Reports: A company uses different types of business reports such as performance reports, analytic reports, informal business reports, etc. to evaluate performance, research, and solve problems.
- Conference: Conferences are a vital part of business communication in any company. They are used as a means to communicate information, set goals, and research new opportunities for growth.
- Meetings: Meetings are part of internal horizontal communication that are regularly held in a department to discuss important matters. These are a gathering of two or more people either in person or through channels such as video calls, audio conference calls, etc.
- Face-to-face conversations: In-person conversations are the most effective and fastest way employees communicate in a lateral communication model. Face-to-face conversations are an informal and flexible means of communication.
Horizontal Vs Vertical Communication
Vertical and horizontal communication are both important parts of business communication. Both are used to share information and develop a cordial relationship between the sender and receiver of the message. However, there are a few key differences between the two.
The difference between vertical and horizontal communication:
Criteria for comparison | Horizontal Communication | Vertical Communication |
Meaning | Communication between employees of the same rank or managerial status is referred to as horizontal communication. | Communication from a superior to subordinate and vice versa is referred to as vertical communication. |
Direction | Moves laterally. | Moves either upward or downward. |
Flow | Subordinate to subordinate of the same level. | Superior to subordinate or subordinate to superior. |
Nature | Participative and casual. | Directive and authoritative. |
Lateral vs Horizontal communication
The terms “lateral communication” and “horizontal communication” are frequently used as synonyms, however, they hold distinct meanings. Lateral communication specifically denotes communication that takes place among individuals or groups at the same level of hierarchy within an organization.
In other words, it is communication that takes place between colleagues who hold similar positions, such as between two managers in different departments or between two employees at the same level.
In contrast, horizontal communication refers to the exchange of information and messages between individuals or groups at varying levels of hierarchy within an organization. This can include communication between managers and employees, between departments, or between different levels of management.
So, the main difference between lateral and horizontal communication is that lateral communication happens between peers or colleagues at the same level, while horizontal communication happens between individuals or groups at different levels within an organization.
What is vertical communication and why is it important?
Vertical communication is the flow of information between superiors and subordinates. It is authoritative and directive in nature as it follows the organizational chain of command. It includes two types – Downward communication and upward communication.
Upward communication refers to information flow from a superior to a subordinate, whereas, downward communication implies when subordinate reports to a superior.
Related Reading:
Vertical communication is vital to an organization as it establishes a chain of command and direct reporting relationships between managers and employees. This creates a disciplined work environment where all members of the company are held accountable to high standards of work performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is the most common form of horizontal communication?
Ans: Face-to-face conversations and memos are the most common form of horizontal communication in an organization. They are quick, informal, and effective channels of communication.
Q2) Is horizontal communication formal or informal?
Ans: Horizontal communication can be either formal or informal. Formal horizontal communication occurs through established channels of communication within an organization’s hierarchy. Informal horizontal communication, on the other hand, takes place through casual conversations, or phone calls between colleagues at the same organizational level.
Q3) What is the difference between horizontal and diagonal communication?
Ans: Horizontal or lateral communication occurs between subordinates on the same level in the organization, whereas, diagonal or crosswise communication is a form of communication that happens between teams or individuals, not in the same department or employee status.
Q4) What is the difference between downward, upward, and horizontal communication?
Ans: Upward communication flows from bottom to top where subordinates report to superiors while downward communication is an authoritative form of communication where superiors give instructions to subordinates. These differ from horizontal communication as it is a lateral form of communication between employees of equal rank in an organization.
Check out our detailed article on: the difference between upward and downward communication
Q5) What is horizontal communication in business communication?
Ans: Horizontal communication in business communication refers to information exchange between colleagues at the same hierarchical level. It promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation. However, it should complement vertical communication for effective organizational functioning.
Q6) What is horizontal communication called?
Ans: Horizontal communication is also commonly referred to as “lateral communication” or “sideways communication.” These terms are used interchangeably to describe the communication between individuals or groups at the same organizational level.
Q7) What is horizontal communication in an organization?
Ans: Horizontal communication in an organization is direct information exchange between colleagues at the same hierarchical level. It fosters collaboration and teamwork, enhancing efficiency and employee empowerment.



