Definition of diagonal communication
“Diagonal communication refers to communication that occurs between individuals or groups at different levels or functions in an organization.” – Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. Organizational behavior.
What is diagonal communication?
Diagonal communication, also known as crosswise communication, is a type of business communication that occurs within an organization between individuals who are not in a direct hierarchical relationship with each other but belong to different departments or teams. In other words, it involves communication that cuts across different levels and departments, forming a diagonal flow in the organizational structure.
Typically, communication in an organization flows vertically (upward and downward) through the formal chain of command and horizontally between individuals or units at the same level. Diagonal communication breaks away from this traditional pattern by allowing individuals from different departments or levels to communicate directly with each other.
Characteristics of diagonal communication
A diagonal communication network has the following characteristics:
1/ Cross-functional Exchange: Diagonal communication enables communication between employees or teams from different departments or functional areas. For instance, it might involve interaction between marketing and finance, or between production and human resources.
2/ Non-hierarchical flow: Unlike vertical communication, which follows the formal chain of command (upward or downward), diagonal communication disregards the hierarchical structure to some extent. It allows employees at different levels to communicate directly without going through formal channels.
3/ Informal nature: Diagonal communication often takes place informally, which means it may not adhere to strict protocols or formalities. It can occur through unplanned conversations, emails, instant messaging, or even during social gatherings.
4/ Middle Management Facilitation: Middle managers often play a vital role in facilitating diagonal communication, as they have connections with various departments and can bridge the gap between different levels of the organization.
5/ Customer-Centric Focus: Diagonal communication in an organization enables different departments, such as marketing, sales, and customer service, to collaborate more effectively to serve customers’ needs. Adopting this customer-centric approach can result in higher customer satisfaction and stronger loyalty.
Purpose of diagonal communication
The purpose of diagonal communication is to facilitate collaboration, coordination, and information exchange across different hierarchical levels and functional areas within an organization. It aims to break down the barriers of traditional vertical communication channels and foster a more interconnected and cross-functional approach.
Diagonal communication promotes a broader understanding of the organization’s goals, enhances problem-solving capabilities, and encourages innovation through the sharing of diverse perspectives and expertise. By facilitating effective communication between different departments or teams, diagonal communication helps to align efforts, improve decision-making, and enhance overall organizational performance.
What are the objectives of diagonal communication?
The main objectives of diagonal communication in an organization are as follows:
1) Collaboration and Coordination: Diagonal communication aims to facilitate collaboration and coordination among individuals or departments at different hierarchical levels and functional areas.
2) Organizational Alignment: Diagonal communication plays a vital role in aligning different parts of the organization toward shared goals and strategies. It helps disseminate information, clarify objectives, and ensure consistent messaging across departments
3) Breakdown of Hierarchical Barriers: Diagonal communication helps break down hierarchical barriers and promotes a more open and transparent organizational culture. It allows for more direct and informal interactions between employees at different levels, enabling a free flow of information, feedback, and suggestions.
4) Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: Encouraging diagonal communication can foster a sense of involvement, ownership, and engagement among employees. It provides opportunities for individuals to contribute their ideas, opinions, and feedback, creating a more inclusive and participative work environment.
The function of diagonal communication
- Improves Cross-Functional Knowledge Sharing: Diagonal communication helps employees gain a better understanding of the different functions within an organization, leading to improved collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Facilitates Conflict Resolution: diagonal relationship can help resolve conflicts by enabling employees to communicate directly with those at different levels or departments.
- Enhances Customer Service: Diagonal communication enables employees to share information about customer needs and preferences across different departments, leading to better customer service.
- Facilitates Change Management: Diagonal communication helps organizations manage change by enabling employees to understand the need for change and providing a platform for feedback and input.
Importance of diagonal communication
Diagonal management is critical for any business or organization as it facilitates the flow of information across different departments and levels, and promotes collaboration and teamwork.
key reasons why diagonal communication is important:
1) Enhances Understanding: Diagonal communication can help individuals to better understand the goals, challenges, and perspectives of other departments or teams within an organization. This can lead to better alignment and coordination across the organization.
2) Increased innovation: Diagonal communication can foster innovation by bringing together individuals from different parts of an organization who may have different backgrounds, expertise, and perspectives.
3) Better decision-making: Diagonal communication ensures that decision-makers have access to all the relevant information and perspectives before making a decision. This helps to avoid biased decision-making and ensures that decisions are made based on objective data and analysis.
4) Fosters cross-functional teamwork: Diagonal communication facilitates cross-functional teamwork by enabling individuals to gain a better understanding of the bigger picture and how their work contributes to the broader organizational goals.
5) Improves organizational culture: Diagonal communication helps to break down silos and create a more open and inclusive organizational culture. When individuals believe they can communicate effectively with others within the organization, they are more likely to experience a sense of value and engagement in their work.
Types of diagonal communication
Diagonal communication is a combination of horizontal and vertical communication, incorporating elements from both. Within an organization, it allows employees to interact with peers at similar levels in different departments or communicate directly with managers outside their own departments.
There are two main types of diagonal communication:
1/ Horizontal Diagonal Communication: This occurs between individuals at different levels of the organization who are not in a direct reporting relationship but collaborate on common projects or tasks. For example, a team leader from the marketing department communicates with a team leader from the production department to coordinate a new product launch.
2/ Vertical Diagonal Communication: This type of communication happens when individuals from different hierarchical levels communicate without strictly following the formal chain of command. For example, a lower-level employee directly communicates with a senior manager or executive to share ideas or concerns.
There are two types of vertical communication:
- Upward communication: Upward communication flows from bottom to top, i.e, from a subordinate to a superior. In relation to diagonal communication, a trainee or subordinate from one department can consult a manager or a higher-ranking employee from another department for assistance.
Related Reading:
What Is Upward Communication A Detailed Guide With Examples
Upward Communication: Advantages & Disadvantages With Examples
- Downward communication: Downward communication in an organization has an upward to downward flow. This occurs when superiors communicate with subordinates. This can happen diagonally as well in the form of a manager from one department interacting with a subordinate that directly does not work under them.
Related Reading:
Example of diagonal communication in an organization
Example:1.0
When a supply chain manager in an organization communicates with the finance manager to prepare an audit report of the inventory used within the last financial year.
Example:2.0
To prepare a new sales training program the HR executives interact with Sr. line sales managers from the sales department for training modules and territory requirements.
Example:3.0
The Operations head sends a message to field supervisors for creating a new standard operating procedure (SOP) for the new line of machinery attached.
Example:4.0
The performance marketing analyst from the digital marketing department conducts a meeting with the CFO of the company to discuss the budget for the upcoming quarter’s of marketing camping.
Example:5.0
When a talent acquisition head demands the list of additional manpower requirements from manufacturing department executives.
Diagram of diagonal communication
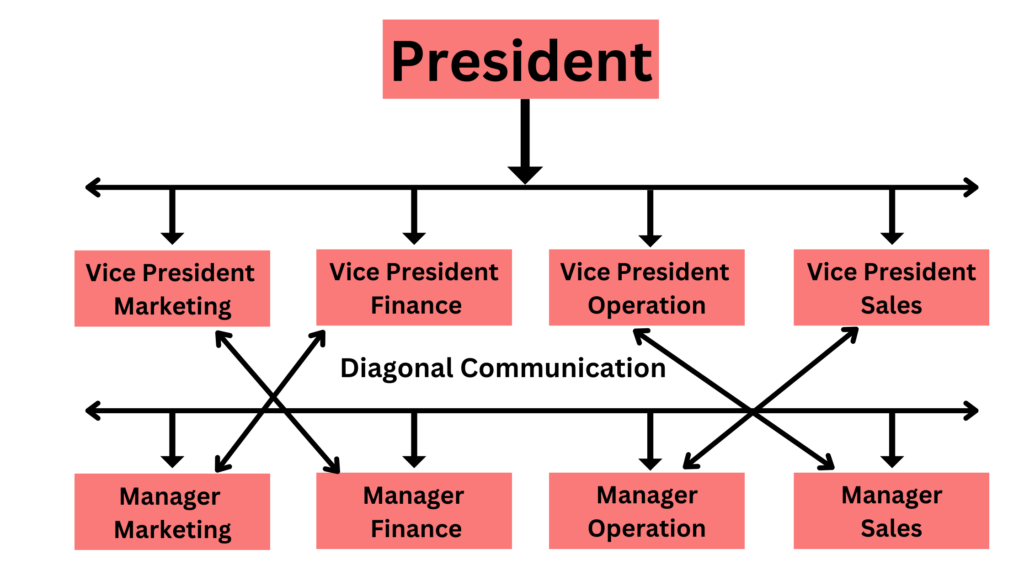
How is diagonal communication applied in an organization?
Diagonal communication is highly beneficial in a large organization as there are multiple departments, each carrying out its own set of tasks. This creates a bigger communication network among managers and teams.
It benefits a company in reaching its goals when there is interdependence between different sectors. This helps in increasing work coordination and achieving tasks faster.
Diagonal communication makes room for assistance on issues and project matters from other departments and capable workers.
For instance, a crosswise communication situation example could be, a sales executive reaching out to a manager or subordinate from the marketing team to seek information in order to come up with an effective sales pitch.
How diagonal communication happens in the workplace
Diagonal communication in the workplace occurs through various channels and interactions that enable information exchange and collaboration across different hierarchical levels and functional areas. Here is a brief analysis of how diagonal communication happens:
- Cross-Departmental Meetings: Diagonal communication often takes place through scheduled meetings where representatives from different departments come together to discuss shared goals, projects, or challenges.
- Project Teams: When employees from different departments or hierarchical levels are brought together to work on a specific project or initiative, diagonal communication naturally occurs.
- Feedback and Performance Reviews: Diagonal communication happens during feedback sessions and performance reviews when supervisors or managers provide guidance, support, and constructive feedback to employees from different departments or hierarchical levels.
- Cross-Functional Training and Workshops: Organizations may arrange cross-functional training sessions or workshops to enhance employees’ knowledge and skills across different functional areas.
Advantages of diagonal communication in an organization
Diagonal communication offers several advantages in organizations. Some of the key advantages include:
1/ Improved Coordination: By enabling direct communication between different parts of the organization, diagonal communication enhances coordination. It reduces delays that may occur when information needs to travel through multiple hierarchical levels.
2/ Employee Empowerment: Allowing employees to communicate diagonally empowers them to take ownership of their tasks and initiatives. It gives them a sense of autonomy and responsibility, leading to increased job satisfaction and motivation.
3/ Breaking Down Silos: Traditional hierarchical communication structures can create silos within an organization, hampering the flow of information and ideas. Diagonal communication helps break down these barriers, encouraging a more open and inclusive work environment.
4/ Personal and Professional Development: When employees engage in diagonal communication, they have the opportunity to learn from others with different skills and expertise. This exposure can contribute to their personal and professional growth.
5/ Increased Transparency: Diagonal communication facilitates transparency within the organization. When information is shared directly between departments and levels, there is a greater sense of openness and trust.
Disadvantages of diagonal communication in an organization
1/ Bypassing Chain of Command: The foremost limitation of diagonal communication is that In some cases it might undermine the established chain of command, leading to confusion about roles, responsibilities, and authority.
2/ Reduced Accountability: Diagonal form of communication may make it challenging to track and hold individuals accountable for their actions. Without a formal reporting relationship, it might be unclear who is responsible for specific decisions or outcomes.
3/ Resistance to Change: Some employees or managers may resist diagonal communication due to concerns about losing control or power within their respective areas. This resistance can prevent effective collaboration.
4/ Lack of Formality: Diagonal communication channels may lack the formal structure of vertical communication, making it difficult to track and document important discussions or decisions.
5/ Information Overload: Employees may receive an overwhelming amount of information from various sources, leading to difficulties in prioritizing and processing the data effectively.
Why is a diagonal channel of communication not popular?
Diagonal communication implies the direction of communication in a crosswise direction. This reason results in the formation of grapevine information that cannot be effectively monitored by the organization.
A diagonal organizational structure may also give birth to gossip and the spread of biased opinions and misinformation. Information can flow freely from any individual of any rank, therefore sometimes, it can cause distortion of facts due to a lack of understanding, poor reporting skills, etc.
Difference between horizontal, vertical, and diagonal communication
Aspect | Horizontal Communication | Vertical Communication | Diagonal Communication |
Flow of Communication | Occurs between peers or individuals at the same level or department. | Flows between different hierarchical levels, such as superiors and subordinates. | Cuts across different levels and departments, connecting individuals not in a direct hierarchical relationship. |
Formality | Generally informal and less structured. | More formal and adheres to the formal chain of command. | Can be a mix of formal and informal, bypassing some formal channels. |
Purpose | Facilitates teamwork, coordination, and problem-solving within a department. | Ensures direction, delegation, and implementation of tasks and decisions. | Enhances collaboration, innovation, and flexibility across various parts of the organization. |
Speed of Information Flow | Typically fast, as it involves direct communication between peers. | Can be slower, as information moves up and down the hierarchical ladder. | Generally faster than vertical communication but may vary based on the organization's culture. |
Authority and Power | Power distribution is relatively equal, and decisions are often made collectively. | Power is concentrated at the top, and decisions are made by higher-ups. | Power dynamics may be less rigid, allowing for greater empowerment and shared decision-making. |
Common Examples | Team members collaborating on a project. | Manager providing instructions to subordinates. | Employees from different departments coordinating for a cross-functional initiative. |
Difference between horizontal and diagonal communication
The following table provides an insightful overview of the fundamental contrasts between these two communication approaches, offering valuable insights into their unique characteristics and their impact on organizational dynamics.
Point of Difference | Horizontal Communication | Diagonal Communication |
Level | It occurs between individuals or departments at the same hierarchical level. | It occurs between individuals or departments at different hierarchical levels and across different functional areas. |
Focus | It promotes collaboration, coordination, and teamwork within a department or team. | It facilitates coordination and collaboration across different departments or teams to achieve common organizational goals. |
Informality | It tends to be more informal and spontaneous, allowing for quick exchanges of information. | It can be both formal and informal, depending on the context, and often involves planned meetings or communication channels. |
Sharing | It focuses on sharing information, ideas, and feedback within a specific unit or team. | It emphasizes sharing information, ideas, and feedback across different units or teams, fostering cross-functional understanding. |
Hierarchy | It typically follows a traditional vertical hierarchy and chain of command. | It cuts across traditional hierarchical structures, promoting a more decentralized and flexible approach to communication. |
Similarities between diagonal and horizontal communication
Diagonal communication and horizontal communication share the following similarities:
- Both forms of communication can be oral or written in nature.
- Both horizontal and diagonal communication are forms of internal communication.
- They both achieve the common purpose of creating a system of effective communication in the workspace.
- Horizontal and diagonal communication use the same elements of communication to facilitate the flow of information.
What is horizontal communication?
Horizontal communication is also known as lateral communication. In this type of business communication, information flows between individuals on the same level in the organizational structure.
In this peer-to-peer form of communication, the channel of communication used is usually informal and is mostly free from distortion of information. Both lateral and diagonal communication encourages collaboration between employees who work in different areas of the organization
Check out our in-depth guide on what is horizontal communication to know more.
What is vertical communication?
Vertical communication in an organization follows the hierarchical chain of command. It refers to communication that flows either upward or downward. Upward communication implies communication from down to top (subordinates to superiors) and downward communication implies the transmission of information from top to bottom (superiors to subordinates).
Managers giving instructions and tasks to subordinates and receiving feedback from them comes under the banner of vertical communication.
Must Read: Check out our detailed guide on what is Vertical Communication: Examples, Types & Importance
What are the 7 C’s of Communication?
The 7 C’s of communication are a set of principles that are applied to oral and written forms of communication to achieve maximum efficiency. They are:
- Completeness: The information provided in the communication process should be complete and contain all required facts and figures.
- Conciseness: The content should not be wordy and should only be communicated in as few words as possible.
- Consideration: The communicator must factor in the audience’s background, point of view, education level, etc. while communicating information to them.
- Clarity: The information communicated should be clear and specific to the context of the information.
- Concreteness: The message exchanged from sender to receiver must not be confusing and hazy. It should be to the point.
- Courtesy: The tone in which the information is conveyed should be polite and courteous to the listener/reader.
- Correctness: The content should be free from grammatical errors and spelling mistakes.
Must Read: 10 Principles of Effective Business Communication With Examples & 7C’s
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is diagonal communication in business communication
Ans: Diagonal communication in business communication refers to the exchange of information and messages between individuals who are not directly connected through the formal hierarchy or chain of command in an organization.
Q2) Can letters be used for diagonal communication within an organization?
Ans: Yes, letters can be used for diagonal communication within an organization. While letters are often thought of as a more traditional form of communication, they can still be a useful tool for communicating with employees who are at different levels or departments within an organization.
Q3) Is diagonal communication formal?
Ans: Diagonal communication can be both formal and informal depending on the channel of communication the sender uses to contact the receiver. It can happen in an informal manner in the form of a face-to-face conversation at lunch or by use of formal means such as the communication section in the company portal.
Q4) What is the other name for diagonal communication?
Ans: Crosswise communication and Cross-functional communication are the two other names for diagonal communication.



