Communication enables us to connect, share ideas, and collaborate with one another. But have you ever wondered what exactly goes into the process of effective communication? How do our thoughts and intentions transform into meaningful messages that are understood by others?
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the communication process. We will explore its fundamental components, examine how messages are transmitted and received, and highlight the key factors that can influence successful communication.
Definition of the communication process?
“The systematic process in which individuals interact with and through symbols to create and interpret meanings in a particular context.” – Joseph A. DeVito
“The process by which people use signs, symbols, and behaviors to exchange information and create meaning.” – Kory Floyd
What is the communication process?
The communication process refers to the steps and elements involved in the successful transmission and understanding of a message between a sender and a receiver. It includes the exchange of information, ideas, opinions, or emotions through various channels or mediums. The communication process is cyclical, meaning it involves continuous feedback and adjustment.
Effective communication requires clarity, relevance, active listening, and consideration of the needs and perspectives of both the sender and the receiver. By understanding and utilizing the communication process, individuals and organizations can enhance their ability to convey messages, build relationships, and achieve their communication goals.
Process of communication with diagram
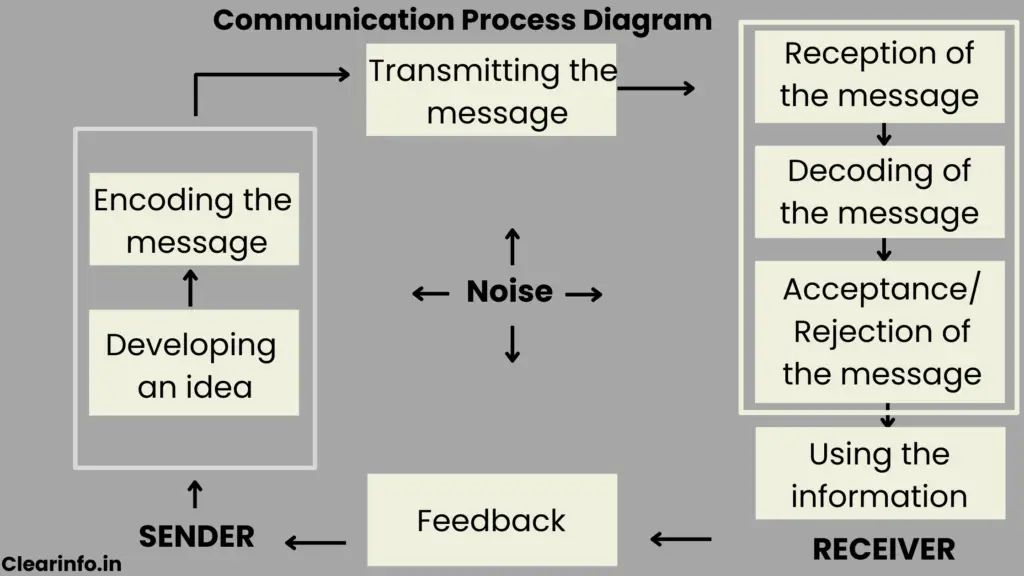
What is the communication process cycle?
The communication process cycle is a continuous and dynamic sequence of stages involved in the successful exchange of messages between a sender and a receiver. The communication process cycle typically includes the following phases:
- Sender’s Input
- Message Transmission
- Message Reception
- Receiver’s Response
- Feedback Transmission
- Iteration and Adjustment
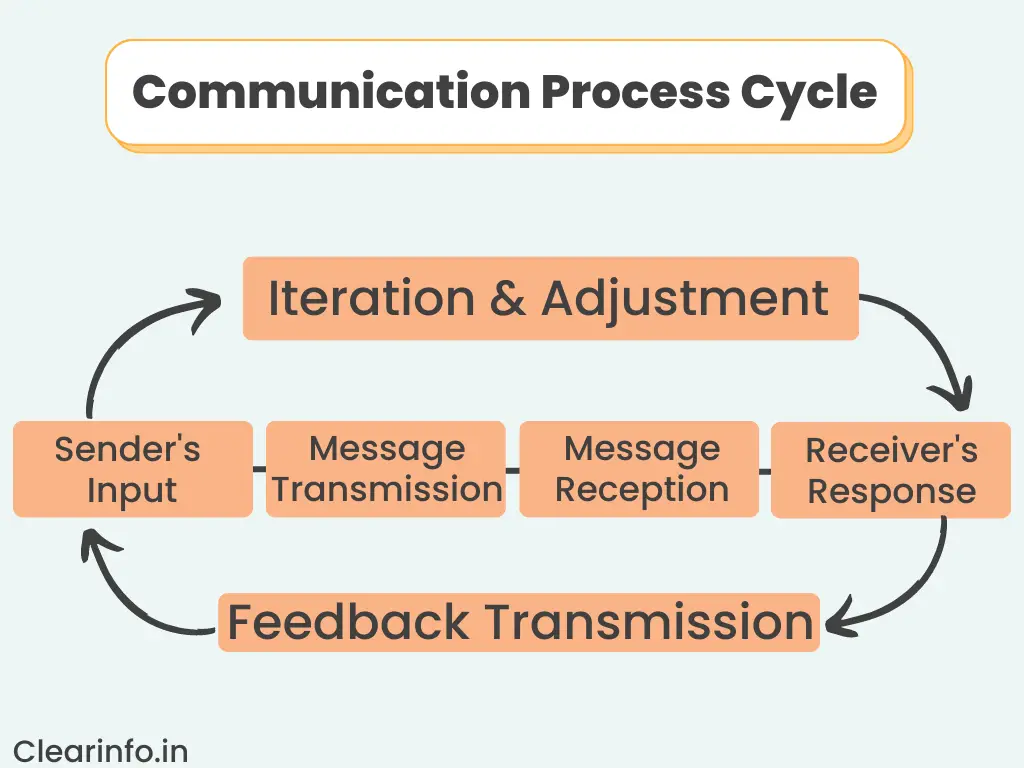
The communication process cycle is continuous, as it involves ongoing interactions and exchanges between the sender and the receiver.
Distinctive characteristics of the communication process?
The following characteristics help distinguish the communication process from other forms of human interaction and highlight its unique nature. The key characteristics of the communication process are as follows:
- Sender-Receiver Relationship: The communication process involves a relationship between the sender and the receiver. It requires both parties to participate actively and engage in the exchange of messages.
- Noise Effect: The communication process can be influenced by noise, which refers to any barriers or disruptions that affect the accurate transmission or reception of the message. Noise can be physical (e.g., background noise) or psychological (e.g., cultural differences).
Related Reading: Psychological barriers to effective communication
- Dynamic and Ongoing: Communication is a continuous process that involves ongoing interactions and exchanges between the sender and the receiver. It is not a one-time event but evolves.
- Subjectivity: The communication process is subject to interpretation and perception by both the sender and the receiver. Each individual may interpret and understand the message based on their own experiences, beliefs, and perspectives.
Components of the communication process
The communication process consists of several interconnected components that work together to facilitate effective communication.
1/ Sender: The sender takes the lead in initiating the communication process. They have a message or information to convey to the receiver. The sender’s role involves encoding the message, which means converting thoughts or ideas into a communicable format.
2/ Message: The message represents the ideas or informational content that the sender intends to convey. It can be expressed through different channels, including verbal, written, or non-verbal forms. Verbal elements include spoken or written words, while non-verbal elements encompass body language, facial expressions, and gestures.
3/ Channel: The channel serves as the pathway through which the message is conveyed from the sender to the receiver. Communication channels can include face-to-face conversations, phone calls, emails, text messages, video conferencing, or social media platforms.
4/ Receiver: The receiver is the person or group of people who are the intended target of the message. They play a crucial role in the communication process by decoding and interpreting the message received from the sender.
5/ Feedback: Feedback is the response or reaction given by the receiver in relation to the sender’s message. It serves as a vital component of the communication process, allowing the sender to gauge the effectiveness of their message and make necessary adjustments.
To know more check out our detailed article on: What are the components of the communication process
Types of the communication process
Communication processes can be broadly categorized into four main types:
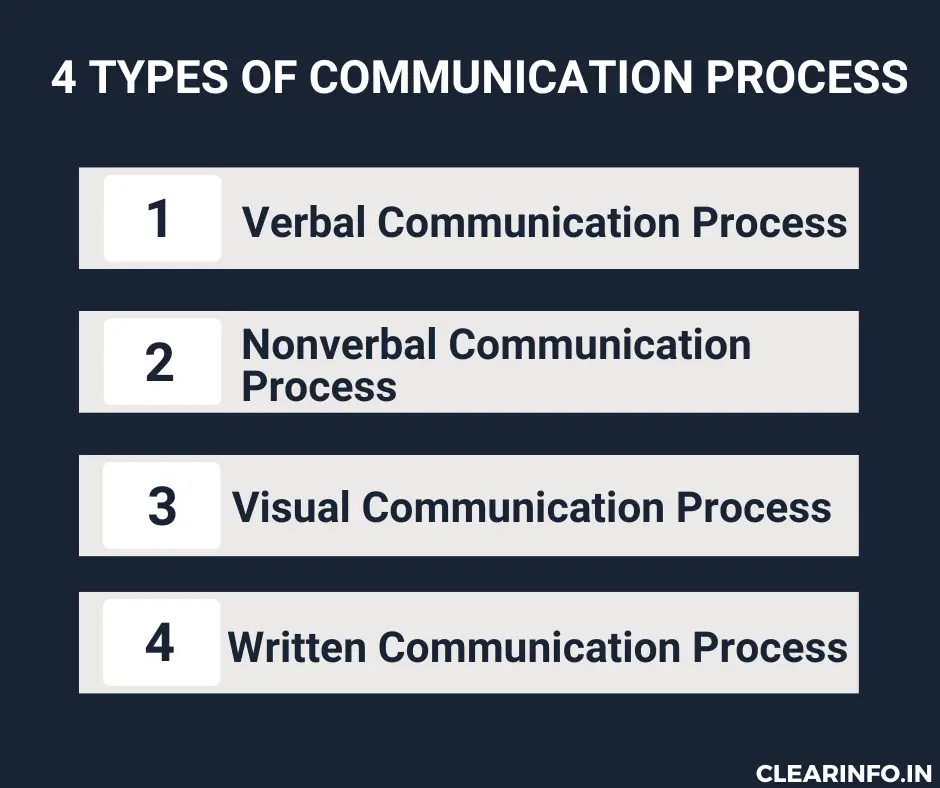
1/ Verbal Communication Process: Verbal communication involves the usage of spoken or written language to express and convey messages. It allows for immediate feedback and clarification, promoting interactive and real-time exchanges.
Further Reading: What is verbal communication
2/ Nonverbal Communication Process: Nonverbal communication involves the transmission of messages without the use of words. It incorporates a range of nonverbal cues such as physical movements, hand gestures, vocal intonation, interpersonal distance, and other forms of nonverbal expression.
Further Reading: What is nonverbal communication
3/ Visual Communication Process: Visual communication relies on visual elements to convey messages. It involves the use of images, graphics, charts, diagrams, videos, presentations, and other visual aids. Visual communication is effective in simplifying complex information, enhancing understanding, and appealing to visual learners.
Further Reading: What are the advantages and disadvantages of visual communication
4/ Written Communication Process: Written communication includes the utilization of written words or text as a means to convey information. It includes letters, memos, reports, articles, emails, text messages, social media posts, and other forms of written communication.
Further Reading: What is written communication with example
How does the communication process work?
The communication process involves 8 interconnected stages that facilitate the exchange of information, ideas, or messages between a sender and a receiver. Here’s a simplified explanation of how the communication process works:
8 stages of the communication process
1/ Sender’s Input: The communication process begins with the sender, who initiates the communication by having a message to convey. The sender identifies the purpose of the communication and formulates the message accordingly. This involves determining what information, ideas, or emotions need to be conveyed and what outcome the sender hopes to achieve through the communication.
2/ Encoding the message: After formulating the message, the sender encodes it by selecting appropriate symbols, language, or means of expression. Encoding involves converting thoughts or ideas into a form that can be understood by the receiver. This could include:
- Selecting specific words
- Using nonverbal cues such as gestures or facial expressions
- Utilizing visual or auditory elements to enhance the message’s meaning.
3/ Message Transmission: Once the message is encoded, the sender transmits it through a chosen communication medium or channel. The medium can vary depending on the nature of the communication and the available options, such as:
- Face-to-face conversations
- Written communication
- Telephone calls or emails,
- Social media platforms
The sender selects the most suitable medium to effectively deliver the message to the receiver.
4/ Receptioning the Message: The receiver, who is the intended recipient of the message, receives the transmitted message through the selected medium or channel. The receiver perceives the message using their senses (e.g., hearing or reading) or through technological devices (e.g., listening to an audio recording or reading a text on a screen). The receiver’s attention and focus on the message play a crucial role in this stage.
5/ Decoding the Message: Upon receiving the message, the receiver decodes it by interpreting and extracting meaning from the information received. Decoding involves understanding the encoded symbols, language, or context used by the sender to derive the intended message. The receiver applies their knowledge, experiences, cultural background, and perceptual filters to make sense of the message and derive meaning from it.
6/ Receiver’s Response: After decoding the message, the receiver formulates a response or feedback based on their understanding and interpretation. This response can take various forms, such as verbal or written communication, actions, or nonverbal cues. The response allows the receiver to provide:
- Feedback,
- Seek clarification,
- Ask questions,
- Express agreement or disagreement,
- Contribute additional information related to the message.
7/ Feedback Transmission: The receiver’s response is transmitted back to the sender through the same or a different communication medium or channel. Feedback serves as an essential component of the communication process, as it provides valuable information to the sender. It helps the sender gauge the effectiveness, understanding, and impact of the message on the receiver. Feedback allows for adjustments, clarification, and improvement of future communications, ensuring the accuracy and clarity of the message.
Related Reading: What is feedback in the communication cycle
8/ Noise: Throughout the communication process, various factors can influence the effectiveness of communication. These factors include noise, which can be
- External Noise: (e.g., Environmental distractions or technical issues)
- Internal Noise: (e.g., Preconceived notions or biases)
Noise can disrupt message transmission or reception. The communication context, such as the physical environment, cultural norms, relationship dynamics, and power dynamics between the sender and receiver, can also impact the communication process.
Example of the communication process?
Sarah, a project manager, wants to inform her team about a change in project deadlines, so she sends an email.
1/ Sender: Sarah, the project manager
- Sarah, as the project manager, is the sender of the message. She initiates communication by composing and sending emails.
2/ Message: Change in project deadlines
- The message is about the change in project deadlines. Sarah wants to inform her team members about this important update.
3/ Encoding: Composing the email
- Sarah encodes her message by composing an email. She chooses the appropriate words, tone, and structure to effectively convey the information regarding the change in project deadlines.
4/ Medium: Email
- The medium used for communication in this scenario is email. Sarah sends the message through the company’s email system.
5/ Channel: Company’s email server
- The channel refers to the means through which the message is transmitted. In this case, the email is transmitted through the company’s email server to reach the team members’ inboxes.
6/ Receivers: Sarah’s team members
- Sarah’s team members are the intended receivers of the message. They will receive and interpret the email sent by Sarah.
7/ Decoding: Reading and understanding the email
- The team members decode the email by reading it and interpreting the content. They understand that there has been a change in project deadlines based on the information provided by Sarah.
8/ Feedback: Team members’ response or clarification
- After decoding the message, the team members may provide feedback to Sarah by replying to the email. They might seek clarification, acknowledge the change, or ask questions related to the new deadlines.
9/ Noise: Distractions or communication barriers
- Noise can refer to technical issues with the email server, language barriers, or even conflicting priorities that could negatively affect the effective transmission or reception of the message.
10/ Context: Project management and deadlines
- The context of the communication is the project management and the change in deadlines. It provides the background and relevance for Sarah’s message to her team members.
The example highlights how the communication process functions within a business, specifically in the scenario of Sarah communicating changes in project deadlines to her team members via email.
Examples of communication models:
Communication models provide frameworks for understanding the complexities of the communication process. Two well-known models are the Shannon-Weaver model and the Transactional model. The Shannon-Weaver model focuses on the transmission of information from the sender to the receiver through a linear process.
The Transactional model emphasizes the dynamic nature of communication, where both the sender and receiver actively participate in encoding, decoding, and exchanging messages.
Why communication process is important?
The communication process serves as the foundation for effective and meaningful interactions between individuals, groups, and organizations. Here are some key reasons why the communication process is vital:
- Enhancing Decision-Making: Effective communication is essential for informed decision-making. Through the communication process, individuals can gather insights, weigh different options, and collectively arrive at well-informed decisions that consider multiple factors and stakeholder interests.
- Conflict Resolution: Communication plays a vital role in resolving conflicts and addressing differences. By encouraging open dialogue, active listening, and empathy, the communication process allows individuals to express their concerns, and find mutually acceptable solutions.
- Achieving Organizational Objectives: In the organizational context, the communication process is vital for achieving goals and objectives. It ensures that employees understand the organization’s vision, mission, and strategies.
- Influencing and Persuasion: Communication is a powerful tool for influencing and persuading others. The communication process allows for the delivery of persuasive messages that can shape opinions, change behaviors, and motivate individuals or groups to take desired actions.
- Social and Cultural Cohesion: Communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction and societal cohesion. The communication process helps bridge gaps, promote understanding across diverse cultures, and foster inclusive and harmonious relationships within communities and societies.
Importance of the communication process in real life?
Effective communication serves as a cornerstone for building and nurturing relationships in personal, and social life. By actively engaging in the communication process, individuals establish connections and build trust, which forms the foundation of healthy and meaningful relationships.
Moreover, the communication process provides a platform for individuals to express their thoughts, emotions, and experiences. It serves as a medium for self-expression, enabling individuals to share their perspectives and joys with others.
Additionally, engaging in the communication process contributes to personal growth and development. It enhances self-awareness and interpersonal skills. Through active participation in communication, individuals can refine their communication abilities, become more adaptable, and strengthen their relationships, both personally and professionally.
What are the common problems in the process of communication?
There are several common problems that can arise in the process of communication. These problems can hinder effective communication and lead to misunderstandings or breakdowns in the exchange of information. Here are some common communication problems:
1/ Misunderstandings: Misunderstandings can arise when the receiver does not accurately grasp the intended meaning of a message, leading to misinterpretations. This can happen due to differences in language or individual interpretations. Misunderstandings can result in misinformation and ineffective communication.
2/ Encoding and Decoding Errors: Encoding involves transforming thoughts or ideas into a communicable format, while decoding refers to the interpretation of the received message. Errors can occur during encoding or decoding, leading to misinterpretation or distortion of the intended message.
3/ Channel Selection: Choosing the appropriate communication channel is crucial for effective message transmission. Using an incorrect or inefficient channel can lead to message loss, distortion, or delayed communication. Selecting the right channel based on the nature of the message and the target audience is essential.
4/ Lack of Adaptability: Communication processes need to be adaptable to different contexts, audiences, and communication styles. Failing to adapt the communication approach can result in resistance or a lack of engagement from the intended recipients.
How does intercultural communication affect the communication process?
Intercultural communication refers to the exchange of information and ideas between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds. It plays a significant role in today’s globalized world where people with diverse cultural identities interact and collaborate. Intercultural communication can have a profound impact on the communication process in several ways:
- Language Barriers: Different cultures have distinct languages or variations of languages. When individuals from different cultures communicate, language barriers may arise, making it challenging to convey ideas accurately.
- Nonverbal Communication Differences: Nonverbal communication, such as eye contact and body movements can reflect cultural variations. Various cultures may attribute different interpretations to specific nonverbal cues, resulting in differences in meaning and understanding.
- Cultural Context: Cultural context significantly influences the communication process. Social norms, customs, and historical backgrounds shape how messages are constructed and interpreted. Without an understanding of the cultural context, messages may be misunderstood.
Related Reading: Cultural Barriers To Communication: Examples & How to Overcome it
Communication process in the workplace
In the workplace, the communication process refers to the series of interactions through which information, feedback, and instructions are exchanged between employees or teams to achieve common goals and facilitate effective work dynamics.
It involves both verbal and non-verbal communication, utilizing various channels and methods to ensure clear and meaningful understanding among employees and across different levels of the organization.
Communication process in advertising
In advertising, the communication process refers to the strategic and systematic approach of developing and delivering persuasive messages to target audiences with the goal of promoting products, services, or ideas. It involves a series of interconnected stages that aim to capture attention, generate interest, and elicit desired actions from the audience.
Impact of Technology on the communication process
The impact of technology on the communication process refers to the changes and transformations that technology has brought to the way people exchange information, connect with others, and engage in communication. It has revolutionized various aspects of communication, including speed, accessibility, reach, and modes of interaction. Here are some key impacts of technology on the communication process:
- Speed and Efficiency: Technology has drastically increased the speed and efficiency of communication. Messages can be sent and received instantly through various digital platforms, reducing the time required for information exchange and decision-making processes.
- Global Connectivity: The internet and digital communication technologies have facilitated global connectivity, bringing together individuals from diverse regions of the world. Geographic barriers no longer limit communication, allowing individuals to connect, collaborate, and engage with others regardless of their physical location.
- Expanded Communication Channels: Technology has expanded the range of communication channels available. In addition to face-to-face conversations, people can communicate through emails, instant messaging, video calls, social media platforms, and other digital tools. This variety of channels provides flexibility and choice in how people interact and exchange information.
In addition, the impact of technology on the communication process also comes with challenges. Misinterpretation, miscommunication, and information overload are limitations of digital communication. Balancing virtual interactions with maintaining personal connections and non-verbal cues can also be a challenge. It is important to be mindful of these challenges and adapt communication strategies accordingly.
What makes the communication process effective and ineffective?
Key factors that make the communication process effective:
1/ Clarity: Clearly articulating ideas and messages using concise and understandable language helps ensure that the intended meaning is easily comprehended by the audience.
2/ Active Listening: Actively engaging in the communication process by attentively listening to the speaker, seeking clarification when needed, and demonstrating genuine interest in their message.
3/ Empathy and Understanding: Showing empathy towards others’ perspectives, being open-minded, and seeking to understand their viewpoints fosters a positive and inclusive communication environment.
4/ Feedback and Confirmation: Providing feedback to the speaker to confirm understanding, asking questions, and actively seeking clarification when necessary to ensure accurate comprehension.
5/ Contextual Awareness: Being mindful of the context and situation in which the communication takes place, including cultural norms, social dynamics, and any relevant background information.
6/ Timeliness: Communicating information in a timely manner, providing updates and responses promptly, and avoiding unnecessary delays to maintain the relevance and effectiveness of the communication.
By incorporating these factors into the communication process, individuals can enhance their ability to convey messages clearly and promote meaningful and effective interactions.
Key factors that can make the communication process ineffective:
1/ Non-Verbal Inconsistency: Sending conflicting non-verbal cues, such as mismatched facial expressions or body language, can create confusion and mistrust.
2/ Information Overload: Overwhelming the audience with excessive or irrelevant information can lead to disengagement and hinder understanding.
3/ Assumptions and Stereotyping: Making assumptions about others’ knowledge, beliefs, or experiences based on stereotypes can lead to miscommunication and misunderstandings.
4/ Emotional Barriers: Allowing strong emotions, such as anger, frustration, or fear, to dominate the communication process can prevent effective dialogue and problem-solving.
Awareness of these factors can help individuals identify and address potential barriers to effective communication and fostering productive interactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What are the 7 steps of the communication process?
Ans: The communication process involves seven key steps: sender, message, channel, encoding, decoding, receiver, and feedback. The sender initiates the process by encoding a message, which is transmitted through a chosen channel. The receiver decodes the message and provides feedback, completing the communication loop. Following these steps enhances communication effectiveness.
Q2) What are the 5 stages of communication?
Ans: The communication process involves five stages: sender, message, channel, receiver, and feedback. The sender encodes and delivers the message through a chosen channel, which is then received, decoded, and responded to by the receiver.
Q3) What is most important in the communication process?
Ans: The most important aspects of effective communication are clarity and active listening. Clarity involves using clear and concise language, while active listening refers to actively engaging with the speaker during a conversation or communication exchange. Other important elements include feedback, non-verbal communication, empathy, emotional intelligence, and adaptability.
Q4) What are the basics of the communication process?
Ans: The basics of the communication process include a sender who encodes a clear message, a chosen channel for transmission, an engaged receiver who decodes the message, and feedback for effective communication. Minimizing noise and considering the context is important.
Q5) What is a two-way communication process?
Ans: Two-way communication is an interactive process where information is exchanged between a sender and receiver. It involves active participation from both sides, with the sender transmitting a message and the receiver providing feedback. This promotes understanding, collaboration, and effective communication.



