Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful interactions, whether in personal relationships or professional settings. Among the various forms of communication, two-way communication stands out as a crucial component for fostering meaningful dialogue.
In this blog, we will explore the essence of two-way communication, going deeper into its elements, examples, and benefits. By understanding the principles and practices of two-way communication, individuals and organizations can foster deeper connections and achieve greater mutual understanding.
Definition of two-way communication?
“Two-way communication is a process in which messages are exchanged between a sender and a receiver, allowing for feedback and mutual understanding. It involves active engagement, dialogue, and the exchange of information, ideas, and perspectives between the parties involved.” Source
What is two-way communication?
Two-way communication involves the mutual exchange of information between two or more parties. It involves an interactive process where participants not only send messages but also receive and respond to them in the form of feedback.
Unlike one-way communication, where information flows in a single direction (the Shannon–Weaver or linear model), two-way communication creates a dialogue and fosters active engagement between the parties involved.
In two-way communication, each participant has the opportunity to express their thoughts, ideas, and opinions while also actively listening and understanding the messages shared by others.
It involves a back-and-forth exchange of information, where both the sender and receiver play an essential role in the communication process. Additionally, the interactive nature of two-way communication allows for a deeper level of understanding and connection.
It enables individuals to clarify doubts, seek clarification, and ask questions to enhance comprehension. By actively participating in the communication process, individuals can exchange information and collaboratively arrive at solutions or decisions.
Two-way communication diagram
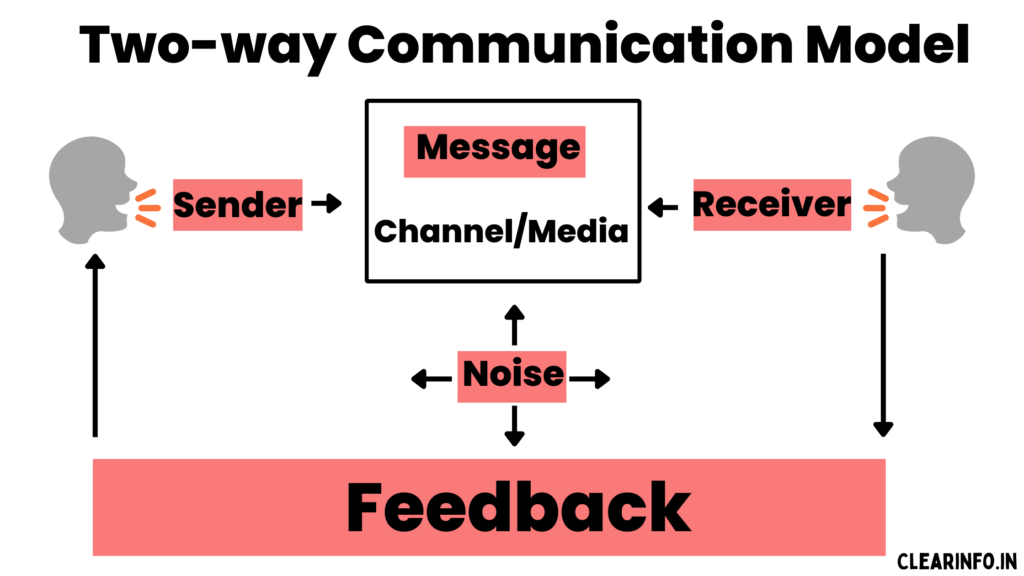
What is a two-way communication process?
Two-way communication is a process where the sender and receiver both send and receive information, allowing for a dynamic and engaged conversation. In a two-way communication process, individuals take turns as both speakers and listeners, actively engaging in the dialogue and responding to each other’s ideas and perspectives.
This process emphasizes the importance of active listening, feedback, and mutual understanding, as it aims to create a shared meaning between all participants involved. The two-way communication process is characterized by its interactivity, engagement, and the continuous exchange of information.
What is a two-way communication system?
A two-way communication system refers to a method or infrastructure that enables the exchange of information between two or more parties in a bidirectional manner. It involves the transmission and reception of messages, allowing for interactive communication between senders and receivers.
A two-way communication system typically includes channels or mediums through which information can be conveyed, such as face-to-face conversations, telephone calls, video conferences, or digital platforms. Two-way communication systems can be found in various settings, including interpersonal interactions, organizational communications, educational environments, and technological platforms.
Examples of two-way communication?
1/ Live Chat: Many businesses and websites offer live chat support, where customers can interact with a representative in real-time. Customers can ask questions or seek assistance, while the representative can provide immediate responses and address any concerns or issues.
2/ Interactive workshops or seminars: In interactive workshops or seminars, participants have the opportunity to engage in two-way communication. They can ask questions, participate in discussions, share their perspectives, and provide feedback to the speaker or facilitator.
3/ Phone or video call: Two-way communication can also occur remotely through phone or video calls. People can exchange information, ideas, and opinions while receiving immediate responses and feedback.
4/ Employee feedback sessions: Organizations often conduct feedback sessions to promote two-way communication between management and employees. These sessions create a platform where employees can freely express their opinions, concerns, and suggestions while providing an opportunity for management to respond and effectively address any raised issues.
A real-life example of two-way communication
Below is a live representation of an employee feedback session involving two-way communication
Example of two-way communication strategies
Online Surveys: An organization conducts online surveys to gather feedback from customers or employees. The surveys are designed to be interactive, allowing respondents to provide detailed responses and suggestions. The organization then analyzes the survey results and shares the findings with the participants, demonstrating that their input has been valued. This strategy encourages two-way communication by providing an avenue for individuals to express their opinions and for the organization to gain valuable insights.
Here is a live example of how we use online surveys in our organization for two-way interaction We value your feedback! Please take a few minutes to complete our online survey. Your responses will help us improve our services and understand your needs better. Thank you for your honest input!
- Rate your satisfaction with our products/services from 1 to 10.
- What aspects of our products/services do you find most valuable?
- How can we improve? Any specific suggestions?
- Rate the effectiveness of our customer support team.
- Any challenges or difficulties you encountered? How can we resolve them?
- How likely are you to recommend us? Why?
- Additional comments or feedback?
Thank you for participating! Your input is invaluable.
Example of using two-way communication in a sentence
During the team meeting, the project manager encouraged two-way communication by actively listening to each team member’s input, addressing their concerns, and facilitating a constructive dialogue to ensure everyone’s perspectives were heard. In this sentence, the phrase “two-way communication” highlights the interaction and exchange of information happening between the project manager and the team members.
Elements of two-way communication
In the following section, we will explore the key elements that contribute to successful two-way communication within an organizational context.”
1/ Active listening
Active listening plays a crucial role in facilitating effective two-way communication. It involves fully engaging with the speaker’s message, both verbally and non-verbally, to demonstrate attentiveness, understanding, and empathy. Here are some key points to consider:
Importance of active listening in two-way communication: Active listening is vital because it shows respect for the speaker, encourages them to express themselves openly, and creates an atmosphere of trust and support. It enables a deeper understanding of the speaker’s perspective and helps build a solid foundation for meaningful dialogue.
Techniques for Active Listening in two-way communication:
- Maintaining eye contact: In two-way communication, maintaining eye contact establishes a connection and signals your genuine interest in the speaker’s words. It demonstrates that you are fully present and actively engaged in the conversation.
- Non-Verbal Cues of Agreement and Understanding: Using non-verbal cues, such as nodding, encourages the speaker to continue sharing their thoughts and ideas. Nodding signifies your active processing of the information and conveys agreement or understanding.
- Reflective Listening and Summarizing: In two-way communication, paraphrasing and summarizing the speaker’s message in your own words helps ensure accurate understanding. It demonstrates your active engagement and shows the speaker that their message has been heard and comprehended.
- Asking clarifying questions: Seeking further information or clarification through questions shows your engagement and ensures that you clearly understand the message.
2/ Feedback and Response:
Providing feedback and responding to the speaker’s message is another crucial component of two-way communication. It enhances the quality of the exchange and promotes active participation.
Significance of Feedback in two-way communication: Feedback communication serves multiple purposes in two-way communication. It validates the speaker’s message and acknowledges their effort to communicate. It also encourages the speaker to continue sharing, as they feel heard and valued. Feedback provides an opportunity for the speaker to gain insights into how their message is being received, leading to improved understanding and connection.
Role of Feedback in Promoting Involvement: Feedback promotes a sense of involvement and engagement by showing that you are actively processing and reflecting on the speaker’s message. It encourages the speaker to participate further and contributes to a dynamic and interactive conversation.
Importance of Constructive and Meaningful Responses in Two-Way Communication: Offering constructive and meaningful responses is crucial to maintaining the quality of communication. Constructive feedback focuses on the message rather than personal criticism, highlighting areas for improvement or clarification. Meaningful responses show genuine interest, empathy, and understanding, further strengthening the connection between participants.
3/ Clarity and Articulation:
Clarity and articulation are essential elements of effective two-way communication. They involve expressing ideas, thoughts, and messages concisely and understandably. It covers the following aspect:
- Clear and Concise Expression: Clear communication involves organizing thoughts and ideas coherently, using basic principles of communication, and avoiding jargon or complex terminology that may prevent understanding. It is important to express ideas in a concise manner, focusing on the key points to avoid confusion and information overload.
- Active Clarification: In two-way communication, both the speaker and the listener have a responsibility to ensure clarity. The listener should actively seek clarification when faced with ambiguous or unclear messages, and the speaker should be open to providing further explanations or examples to enhance understanding. Active clarification helps eliminate misunderstandings and promotes effective communication.
Importance of two-way communication
Two-way communication is vital for a smooth reciprocal exchange of information. It allows individuals and organizations to create an environment that fosters collaboration and effective communication outcomes. Here are some primary reasons why two-way communication is important.
1/ Problem-Solving and Conflict Resolution: Two-way communication allows for effective problem-solving and conflict resolution. By encouraging open dialogue and the exchange of ideas, participants can share their perspectives, identify common ground, and work together to find mutually agreeable solutions.
2/ Improved Decision-Making: Two-way communication enhances the quality of decision-making. By allowing different viewpoints, diverse expertise, and critical analysis, it helps gather a broader range of information and insights. This leads to well-informed decisions that consider multiple perspectives, resulting in better outcomes and increased acceptance of the decisions made.
3/ Customer Satisfaction: In customer service and business contexts, two-way communication is essential for achieving high levels of customer satisfaction. Businesses can build trust, loyalty, and long-lasting relationships with customers by actively listening to customer feedback, addressing concerns, and providing timely and relevant responses.
4/ Increases Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: Two-way communication plays a significant role in the workplace by fostering employee engagement and satisfaction. When employees have opportunities to share their ideas, provide feedback, and actively participate in discussions, they feel valued and connected to the organization. This leads to higher levels of motivation, productivity, and overall job satisfaction.
5/ Effective Feedback and Growth: Two-way communication facilitates the provision of constructive feedback. By engaging in open and honest discussions, participants can offer feedback that focuses on improving performance and refining ideas.
In fact, according to the Harvard Business Review, a substantial 72% of employees believe that their performance would enhance if their managers were to offer corrective feedback, often referred to as “negative” feedback. Therefore feedback promotes personal and professional growth, supporting continuous learning and development.
What is two-way communication in the workplace?
Two-way communication in the workplace refers to an interactive exchange of information between employees, teams, and management. It involves a dynamic process where individuals both send and receive information, feedback, and suggestions, fostering a collaborative and engaging work environment.
Two-way communication within an organization can take place in two directions: horizontally or vertically. Vertical two-way communication refers to the exchange of information between superiors and subordinates. In contrast, horizontal two-way communication occurs among individuals who hold the same rank or position.
Additionally, in a two-way communication model, employees are not only recipients of information but active participants in the communication process.
They have the chance to ask questions, seek clarification, and provide feedback to enhance understanding. Management and leaders play a crucial role in facilitating this communication by creating channels and platforms that encourage open discussions and feedback loops.
Furthermore, two-way communication in the workplace can take various forms, such as team meetings, one-on-one conversations, feedback sessions, and employee surveys. And it supports effective change management, as it allows for open dialogue and understanding during times of transition.
Example of two-way communication in the workplace
Below is a live representation of how two-way communication can be used for giving feedback to supervisors at the workplace.
What is the two-way communication model in business
The two-way communication model in the business allows for a better exchange of ideas and feedback between managers, employees, and teams.
In fact, organizations that foster strong employee connections experience a significant boost in productivity, with increases ranging from 20% to 25%. Having said that, below is a graphical representation of the two-way communication model in the business context:
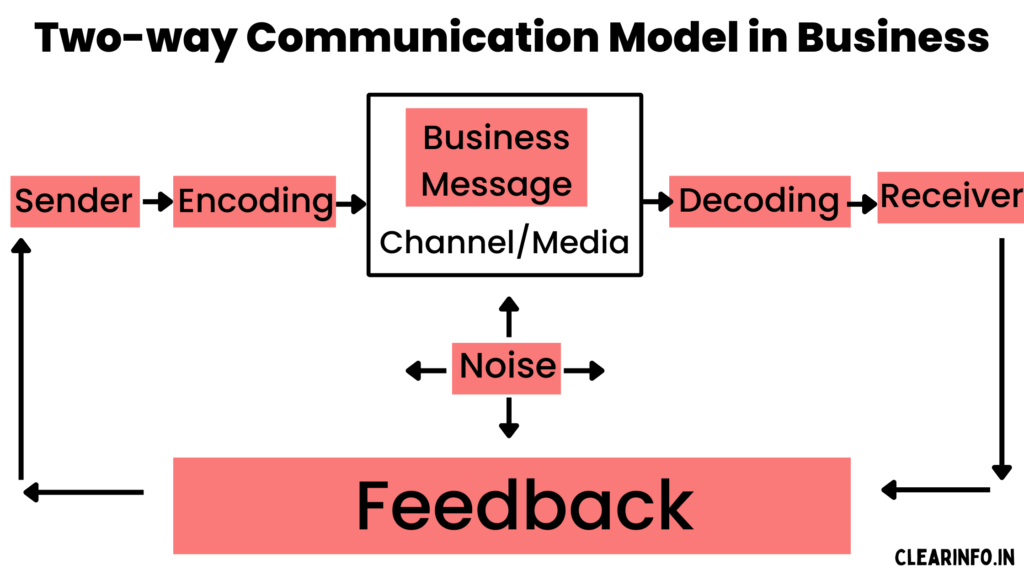
The above two-way communication model in business represents a sender initiating the communication by encoding a message and transmitting it through a chosen medium such as face-to-face conversations, phone calls, emails, or live video conferences.
The receiver then decodes the message, interprets its meaning, and provides a response or feedback. This response may involve asking questions, seeking clarification, offering input, or expressing opinions.
Two-way marketing communication
Two-way marketing communication refers to an interactive exchange of information between a company or brand and its target audience. It involves both sending marketing messages to the audience and receiving feedback or responses from them.
Unlike traditional one-way marketing communication, where companies primarily focus on broadcasting their messages to the audience, two-way marketing communication recognizes the importance of engaging in a dialogue with customers. It emphasizes the active participation of the audience and provides opportunities for them to express their opinions, preferences, and concerns.
Two-way marketing communication can take various forms, including social media interactions, customer surveys, focus groups, customer service interactions, and online reviews. It allows companies to gather valuable insights and feedback directly from their customers, enabling them better to understand their needs, preferences, and expectations.
Furthermore, two-way marketing communication enables companies to address customer concerns, provide personalized experiences, and create a positive brand image. It helps establish trust, credibility, and transparency, which are essential factors in today’s customer-centric marketing landscape.
What is two-way communication in public relations?
Two-way communication in public relations refers to a reciprocal exchange of information between an organization and its public, including stakeholders, customers, media, and the general public.
In this context, two-way communication in public relations can take various forms, such as media interviews, press conferences, social media interactions, surveys, and community engagement initiatives.
It allows organizations to receive feedback, address issues or crises, and gather insights that can inform their decision-making and strategic planning.
By engaging in two-way communication in public relations, organizations can achieve several objectives:
- It helps in building trust and credibility by demonstrating openness, responsiveness, and a willingness to listen to publics’ concerns.
- It allows organizations to gather valuable information about public sentiment and preferences, enabling them to adapt their messages accordingly.
- Thirdly, two-way communication in public relations helps in managing and resolving crises or issues effectively.
The difference between one-way communication, two-way communication, and Broadcast communication
The following table provides a comparison of the key aspects that differentiate one-way communication, two-way communication, and broadcast communication. It highlights the differences in information flow, interaction, feedback, dialogue, engagement, and relationship building, and provides examples of each type of communication.
Aspect | One-Way Communication | Two-Way Communication | Broadcast Communication |
Information Flow | One-directional: Information flows from sender to receiver. | Bi-directional: Information flows between sender and receiver(s). | One-directional: Information flows from sender to a large audience. |
Interaction | Limited or no interaction between sender and receiver. | Active interaction and engagement between sender and receiver. | Limited or no direct interaction between sender and audience. |
Feedback | Limited or no provision for feedback or response from receiver. | Feedback and response are encouraged and expected from receiver. | Limited or no opportunity for immediate feedback from the audience. |
Dialogue | Communication is primarily a monologue with little or no dialogue. | Dialogue and conversation are essential components of communication. | Communication is mainly a monologue without direct dialogue. |
Engagement | Passive engagement of the receiver with limited participation. | Active engagement of both sender and receiver in the communication process. | Passive engagement of the audience with limited opportunity for participation. |
Relationship Building | Minimal focus on building relationships between sender and receiver. | Emphasizes building relationships and rapport through open dialogue. | Limited focus on building individual relationships with the audience. |
Examples | Traditional advertising, speeches, announcements, mass media broadcasts. | Face-to-face conversations, interviews, feedback sessions, online chats. | Television and radio broadcasts, webinars, podcasts, social media live streams. |
Two-way communication system vs one-way communication system
Aspect | Two-Way Communication System | One-Way Communication System |
Information Flow | Bi-directional: Information flows both ways between sender and receiver. | One-directional: Information flows from sender to receiver. |
Interaction | Active interaction and engagement between sender and receiver. | Limited or no interaction between sender and receiver. |
Feedback | Feedback and response are encouraged and expected from receiver. | Limited or no provision for feedback or response from receiver. |
Dialogue | Dialogue and conversation are essential components of communication. | Communication is primarily a monologue with little or no dialogue. |
Examples | Face-to-face conversations, video conferences, instant messaging, interactive workshops. | Traditional advertising, speeches, announcements, mass media broadcasts. |
One-way communication vs two-way communication examples
One-Way Communication Examples | Two-Way Communication Examples |
In a television advertisement, the company broadcasts a message to the viewers without any opportunity for immediate feedback or interaction. The audience passively receives the information without engaging in a dialogue with the company. | In a team meeting, team members engage in a two-way communication process. They actively participate by sharing ideas, discussing issues, and providing feedback to each other. The communication is bi-directional, allowing for dialogue, collaboration, and problem-solving. |
A press release is a written communication issued by a company or organization to provide information to the media. It is a one-way communication where the company disseminates news or announcements without actively engaging in a conversation with the recipients. | In a customer service call, the customer interacts with a representative of the company to address their concerns or seek assistance. The conversation involves active listening, problem resolution, and feedback exchange, creating a two-way communication experience. |
Advantages and disadvantages of two-way communication
Advantages of two-way communication:
- Effective Feedback Loops: Two-way communication enables effective feedback loops, enhancing performance and growth.
- Stronger Relationships: Two-way communication strengthens relationships between individuals and groups.
- Higher Customer Loyalty: Engaging in two-way communication with customers fosters loyalty and enhances customer relationships.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Two-way communication enhances collaboration among team members or departments.
- Accurate and Relevant Information: Two-way communication ensures the accuracy and relevance of information shared. Through feedback and clarification, participants can verify the accuracy of the message and address any misunderstandings.
Disadvantages of two-way communication:
- Time-Consuming: Two-way communication often involves active engagement, dialogue, and feedback exchange, which can be time-consuming.
- Resistance to Feedback: Some individuals or organizations may resist feedback or constructive criticism, leading to a breakdown in the communication process.
- Information Overload: In interactive communication, there is a risk of information overload, especially in group settings or when dealing with a large volume of feedback.
- Privacy and Confidentiality Concerns: Open dialogue and active engagement in two-way communication may raise privacy or confidentiality concerns, particularly when sensitive or confidential information is shared.
Tips for enhancing two-way communication
Two-way communication enables individuals to express their thoughts and concerns while fostering understanding and collaboration. To enhance your ability to engage in effective two-way communication, here are some valuable tips to consider.
1/ Cultivating a Safe and Respectful Environment: Creating an atmosphere of trust, respect, and non-judgment is vital for effective two-way communication. This involves valuing diverse perspectives, practicing empathy, and displaying emotional intelligence to foster an open dialogue and create a safe space for participants to express themselves freely.
2/ Active Engagement and Non-Verbal Communication: To actively engage in two-way communication, maintain eye contact, use open and welcoming body language, and minimize distractions to show genuine interest and attentiveness. Pay attention to non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions and gestures, to convey empathy, interest, and understanding.
3/ Effective Questioning and Feedback: By using open-ended questions that prompt deeper conversation and reflection, you can encourage meaningful dialogue. This approach facilitates the generation of detailed and reflective responses, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the interaction. When providing feedback, focus on the message and offer constructive suggestions for improvement or clarification. Deliver feedback with empathy, respect, and the intention to help the speaker improve their communication skills.
4/ Encouraging Equal Participation: Strive for equal participation and balanced conversation in two-way communication. Make sure that every participant has a chance to express their thoughts, ideas, and opinions. Facilitate turn-taking and actively invite input from all individuals involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is meant by two-way communication?
Ans: Two-way communication refers to a form of interaction where information is exchanged between two or more parties in a reciprocal manner. It involves both sending and receiving messages, allowing for an active exchange of ideas, thoughts, and feedback.
Q2) What is a two-way communication example?
Ans: An example of two-way communication could be a team meeting where team members share their ideas, discuss issues, and provide feedback to each other. Other examples include customer service calls, interactive workshops, and social media interactions where individuals can engage in a back-and-forth exchange of messages and responses.
Q3) Who introduced two-way communication?
Ans: Grunig and Hunt (1984) initially introduced the concept of two-way symmetric communication as a form of public relations.
Q4) What is 3-way communication?
Ans: Three-way communication refers to a communication process involving three participants or parties. It involves three individuals or groups exchanging information, ideas, and feedback with one another.
Q5) Two-way communication is also called?
Ans: Two-way communication is also called interactive communication. This concept emphasizes the mutual exchange of information and the active participation of both the sender and receiver in the communication process.
Q6) When was two-way communication invented?
Ans: Grunig and Hunt (1984) initially invented two-way symmetric communication as a form of public relations, but Stacks and Watson (2007) expanded its application to encompass communication in various contexts. They further clarify that the two-way model is frequently employed in the field of public relations.
Q7) What is two-way audio communication?
Ans: Two-way audio communication refers to a form of interactive communication where individuals or parties can both transmit and receive audio signals. It enables a reciprocal exchange of information, allowing participants to engage in real-time conversations, discussions, or dialogues.



