Definition of cultural barriers to communication
Cultural barriers to communication are the various factors, including language, behavior, values, and beliefs, that create differences in understanding and interpretation between individuals from different cultural backgrounds. Edward T. Hall
What are cultural barriers to communication?
Cultural barriers to communication refer to the challenges that arise from differences in cultural backgrounds, customs, values, and communication styles, which can brake effective understanding and interaction between individuals from different cultures. These barriers can slow down the flow of information and lead to misinterpretations, ultimately affecting the quality and efficiency of communication.
Cultural barriers can appear in various forms, including language differences, non-verbal communication variances, social customs and norms, and perception and interpretation disparities. Each of these types of communication barriers presents unique challenges that need to be recognized and addressed for successful cross-cultural communication.
What are socio-cultural barriers?
Socio-cultural barriers refer to the obstacles that arise in the process of communication due to differences in social backgrounds, norms, beliefs, and practices among individuals or groups. These barriers result from the diversity of cultural and social contexts and can affect the effective understanding, interpretation, and exchange of information.
Importance of understanding cultural barriers
Understanding cultural barriers to communication is crucial for achieving successful and effective communication in a multicultural environment. Here are key reasons why understanding these barriers is of utmost importance:
- Avoiding misunderstandings: Cultural barriers can often lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. By recognizing and understanding these barriers, individuals can proactively address potential pitfalls and prevent miscommunication.
- Enhancing mutual understanding: Cultural barriers can create gaps in understanding due to differences in language, communication styles, and cultural norms. By gaining insight into these barriers, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation and empathy for diverse perspectives.
- Facilitating effective communication: Effective communication relies on clear and accurate message transmission. Cultural barriers, such as language differences or non-verbal misinterpretations, can prevent the transmission of messages. By being aware of these barriers, individuals can adapt their communication strategies, clarify and ensure that messages are understood accurately.
Related Reading: What is effective communication discussed with an example
- Promoting cultural sensitivity and respect: Recognizing cultural barriers demonstrates respect for different cultural backgrounds and promotes cultural sensitivity. By appreciating the diversity of communication styles and norms, individuals can adapt their own communication approaches to accommodate others’ preferences.
Expert Comment: Milton Bennett established a robust framework for comprehending the different stages of cultural sensitivity, which he refers to as “intercultural sensitivity,” that individuals may go through.
What are the different types of cultural barriers to communication?
In the following section, we will explore the different types of cultural barriers that can negatively impact effective communication among individuals.
1/ Language Barriers:
Language barriers are one of the primary cultural barriers to communication. They arise when individuals from different linguistic backgrounds struggle to understand each other due to differences in language, vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, or idiomatic expressions. These barriers can significantly prevent effective communication and lead to misinterpretations. Let’s delve into the challenges posed by language differences and explore some examples of linguistic barriers and misinterpretations:
Vocabulary differences:
- Languages vary in their vocabularies, and specific words or ideas might lack direct equivalents in alternative languages. This can create difficulties when attempting to convey specific ideas or when translating between languages.
- For example, the English word “compromise” may not have an exact equivalent in another language, leading to challenges in expressing the concept concisely and accurately.
Pronunciation and accents:
- Pronunciation differences can pose challenges in understanding spoken language. Different languages have unique sounds and phonetic systems, making it difficult for non-native speakers to accurately reproduce certain sounds.
- Additionally, regional accents and dialects within a language can further complicate communication. Accents may influence the pronunciation and understanding of words, leading to potential misinterpretations.
Idiomatic expressions and cultural references:
- For individuals who are not native speakers, understanding idiomatic expressions, colloquialisms, and cultural references can pose difficulties. These linguistic variations often require cultural familiarity to fully grasp their intended meaning.
- For example, the English phrase “break a leg” is an idiomatic expression meaning “good luck” or “perform well” in the context of theater. However, if a non-native English speaker interprets it literally, they might be confused or concerned.
2/ Non-Verbal Communication Differences
Non-verbal communication includes a wide range of cues, including gestures, facial expressions, and body language, that convey meaning without the use of words. However, these non-verbal cues can vary significantly across different cultures, leading to potential misunderstandings. Let’s examine how gestures, facial expressions, and body language can differ across cultures and the implications this can have:
Gestures:
Across various cultures, gestures can convey diverse meanings and interpretations. What may be considered a positive or neutral gesture in one culture can be perceived as offensive or inappropriate in another culture. For example, the “OK” hand gesture, formed by joining the thumb and index finger in a circle, is widely recognized as a sign of approval or agreement in Western cultures. However, in some South American and European countries, it can be interpreted as an offensive gesture.
Facial expressions:
Facial expressions are an essential part of non-verbal communication, conveying emotions and attitudes. However, the interpretation of facial expressions can vary across cultures, leading to misunderstandings. For instance, the display of emotions like happiness, sadness, or surprise may differ in intensity. Some cultures may express emotions more openly and vividly, while others may exhibit more subtle or restrained facial expressions.
Body language:
Body language, including posture, proximity, and gestures involving the entire body, can differ significantly across cultures. For example, handshakes, hugs, or bows are examples of culturally specific greetings that convey respect and social norms but may vary in appropriateness and frequency across cultures.
3/ Social customs and norms:
Social customs and norms play a significant role in shaping communication styles within different cultures. These norms reflect the shared values, beliefs, and traditions of a society, and they greatly influence how individuals interact and convey messages. Understanding the impact of hierarchy and formality is crucial in navigating cultural barriers to effective communication.
For instance, many cultures have hierarchical structures that define social relationships and power dynamics. These hierarchies can significantly influence communication styles. In cultures with high power distance, such as some Asian and Middle Eastern cultures, there is a greater emphasis on respecting authority and maintaining social hierarchy. Communication tends to be more formal and deferential to those in positions of power.
Similarly, the level of formality in communication can vary across cultures and influence the choice of language, and tone used. Some cultures place a strong emphasis on formal communication, particularly in professional or hierarchical settings.
This includes using respectful language, addressing individuals by their titles or surnames, and following prescribed etiquette. On the other hand, cultures that emphasize informal communication tend to express opinions and intentions explicitly, without relying heavily on indirect cues.
Overall the impact of these social customs and norms on communication styles is significant. Failure to recognize and adapt to these cultural influences can lead to misinterpretations and misunderstandings.
4/ Perception and interpretation:
Perception and interpretation are deeply influenced by an individual’s cultural background. Cultural norms, values, experiences, and beliefs shape how people perceive and interpret messages, leading to differences in understanding and potential communication barriers.
Cultural backgrounds and perception:
- Cultural backgrounds influence how individuals perceive and interpret messages by shaping their worldviews, attitudes, and values.
- Different cultures may prioritize different aspects of communication, such as directness, harmony, or context. These cultural lenses affect how individuals filter and interpret incoming information.
- For example, in cultures that emphasize collectivism, individuals may focus more on group dynamics and interpersonal relationships when interpreting messages, while in individualistic cultures, the emphasis might be on personal goals and autonomy.
Cultural backgrounds and interpretation:
- Cultural backgrounds also play a significant role in interpreting messages. Cultural frameworks, including language, symbols, and social norms, guide interpretation.
- Individuals from the same cultural background may share common interpretations and understandings of certain gestures, idioms, or non-verbal cues. However, these interpretations may differ across cultures, leading to misinterpretations.
5/ Communication Styles:
Communication styles refer to the unique patterns and approach individuals or cultures adopt when exchanging information, ideas, and emotions. It can be a strong cultural barrier to communication as differences in communication styles across cultures can lead to challenges in conveying and receiving messages.
Some cultures value direct and explicit communication, where messages are expressed straightforwardly. On the other hand, some cultures may lean towards indirect communication, relying on non-verbal cues, hints, or contextual signals to convey messages. When individuals from different communication styles interact, misunderstandings can occur.
In addition, communication styles can also be classified as high-context or low-context based on the amount of implicit information and context required to convey meaning.
High-context communication relies on shared understanding, cultural norms, and contextual cues. On the other hand, low-context communication places greater emphasis on explicit verbal communication and relies less on contextual information. When individuals from high-context and low-context communication cultures interact, high-context communicators may assume shared cultural understanding that low-context communicators do not possess, leading to confusion.
6/ Ethnocentrism:
Ethnocentrism involves considering one’s own culture as superior or the standard against which all other cultures should be assessed. This mindset can lead to biases, and a lack of openness when communicating with individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
The following elements of ethnocentrism can further create hurdles among groups while communicating::
Bias and Prejudice:
- Ethnocentrism often leads to biased and prejudiced views about other cultures. Individuals with ethnocentric attitudes may hold negative stereotypes or judgments based on their own cultural norms and values, which can slow down understanding and communication.
- These biases can manifest in communication through assumptions, generalizations, and judgments about others’ behaviors, beliefs, or communication styles. This can create a barrier to truly understanding and appreciating different perspectives.
Stereotyping and Misinterpretation:
- Ethnocentrism can result in the use of cultural stereotypes, where individuals assume that people from other cultures conform to a narrow set of characteristics or behaviors.
- Stereotyping blocks the accurate interpretation of messages and can lead to deep confusion. Individuals may attribute certain meanings or intentions to communication that are based on their biased assumptions rather than the actual message being conveyed.
What are the types of barriers to cultural diffusion?
Barriers to cultural diffusion refer to factors that restrict the spread or adoption of cultural traits, practices, or innovations from one society or culture to another. These barriers can vary in nature and impact. Here are some common types of barriers to cultural diffusion:
1/ Geographic Barriers: Distance and isolation between societies can prevent the diffusion of cultural elements as it becomes more challenging for interactions to occur.
2/ Technological Barriers: Technological limitations can act as barriers to cultural diffusion. Lack of access to technology or infrastructure can slow down the spread of cultural innovations or ideas that rely on technological advancements.
3/ Economic Barriers: Economic factors, such as poverty, resource constraints, or economic inequalities, can affect the diffusion of cultural elements.
4/ Religious or Ideological Barriers: Religious or ideological beliefs can create barriers to cultural diffusion when certain practices or ideas are considered incompatible.
It’s important to note that these barriers are not always absolute. Over time, advancements in transportation, communication, globalization, and changing attitudes can help overcome some of these barriers and facilitate cultural diffusion.
Cultural barriers examples
 Examples of cultural differences in communication?
Examples of cultural differences in communication?
Socio-cultural barriers examples
Cross-cultural barriers examples

How to overcome cultural barriers to communication
Strategies for overcoming cultural barriers to communication involve adopting proactive approaches to enhance understanding, adaptability, and sensitivity when interacting with individuals from different cultural backgrounds. Here are key strategies to overcome these barriers:
1/ Increase Cultural Awareness: Actively learn about different cultures, traditions, customs, and values. Educate yourself on the diversity of cultural practices and perspectives.
2/ Promote Sensitivity towards Cultural Differences: Recognize and appreciate cultural variations in communication styles, norms, and behaviors. Be cautious not to make assumptions or generalizations solely based on your own cultural viewpoint or perspective.
3/ Learn Basic Phrases: Make an effort to learn common phrases in different languages to facilitate communication and show respect for the other person’s language and culture.
For example, saying “Hello” in different languages would sound like this:
- Spanish: Hola
- French: Salut
- Portuguese: Olá
- German: Hallo
- Mandarin: 你好 (nǐ hǎo)
4/ Use Clear and Concise Language: Simplify complex concepts and prioritize clarity in your communication. Stay aware of possible language barriers and adapt your speech accordingly.
5/ Study Cultural Gestures and Body Language: Understand that gestures, hand moments, and body language can differ across cultures. Learn about specific nonverbal cues and their meanings to avoid misinterpretations.
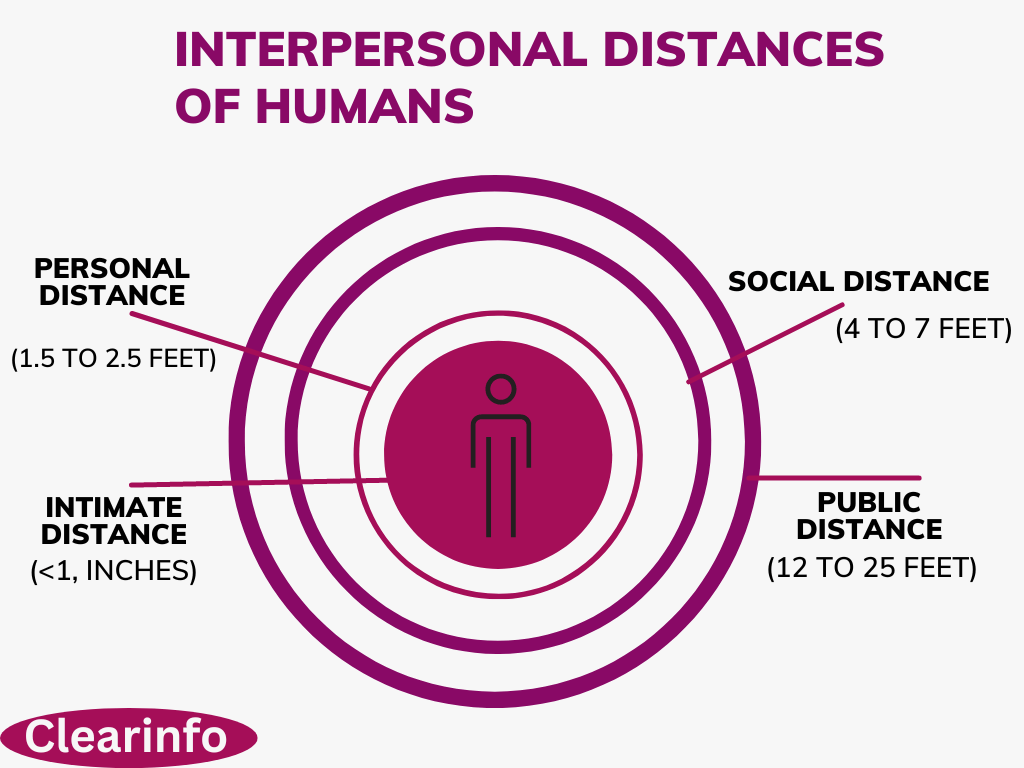
6/ Be Mindful of Personal Space: Recognize that cultural norms regarding personal space and physical contact differ. Respect personal boundaries and adjust your behavior accordingly to avoid discomfort or offense.
(Image of distance)
7/ Avoid Assumptions and Stereotypes: Refrain from making assumptions based on cultural stereotypes. Treat each individual as unique and evaluate them based on their own merits and characteristics.
8/ Seek Clarification and Feedback: Encourage open communication and create a safe space for individuals to seek clarification or provide feedback. Actively engage in dialogue to address any potential misunderstandings or cultural barriers.
What skills are needed to overcome cultural barriers
To overcome cultural barriers effectively, individuals should develop and refine the following skills:
- Open-Mindedness
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Active Listening
- Conflict Resolution
- Cultural Awareness
- Curiosity and Learning Mindset
What are cultural misunderstandings and how can they be avoided?
Cultural misunderstandings occur when individuals from different cultural backgrounds misinterpret or fail to understand each other’s intentions, messages, or behaviors due to differences in cultural norms, values, and communication styles. Such misunderstandings can result in confusion, conflicts, and communication breakdowns. However, there are several ways to avoid cultural misunderstandings:
- Practice Active Listening and Clarification: Listen attentively to others and seek clarification when needed. Paraphrase or repeat what you have understood to ensure accuracy and show that you genuinely want to understand their perspective.
- Foster Open and Respectful Communication: Create an environment that encourages open dialogue, where individuals feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and perspectives without fear of judgment or criticism. Respectful communication allows for greater understanding and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings.
- Develop Cross-Cultural Communication Skills: Enhance your cross-cultural communication skills through training, workshops, or intercultural experiences. These activities can equip you with the necessary tools to recognize and bridge cultural gaps effectively.
- Reflect and Learn from Mistakes: If misunderstandings occur, take the opportunity to reflect on the cultural factors that contributed to the confusion. Learn from these experiences and use them as opportunities for growth and improved cross-cultural communication.
Some examples of cultural misunderstandings
1/ Direct Feedback: In some cultures, providing direct and constructive feedback is considered valuable and necessary for improvement. However, in other cultures, direct feedback may be perceived as rude or confrontational.
2/ Personal Space: In crowded urban areas, people may be accustomed to standing close to each other, while in cultures that value larger personal space, such proximity can be uncomfortable.
3/ Humor and Jokes: Humor can vary greatly across cultures, and what may be considered funny in one culture may not translate well in another.
4/ The tone of Voice: The tone of voice used in communication can vary across cultures and convey different meanings. For instance, a raised voice may be perceived as a sign of anger or aggression in some cultures, while in others, it may indicate passion or emphasis.
How do cultural barriers influence communication in the workplace?
Cultural barriers in the workplace can significantly impact communication and create challenges in various ways. Here are some key ways in which cultural barriers influence communication in the workplace:
- Communication Styles: Cultural variations in communication styles, such as direct versus indirect communication, can create misunderstandings. Certain cultures place value on direct and assertive communication, whereas others favor a more indirect and polite approach. These differences can lead to confusion or perceived rudeness.
- Cultural Norms and Values: Cultural norms and values influence workplace communication. Differences in formal and informal hierarchical structures, power dynamics, and formality can affect how individuals communicate with each other. Varying norms can lead to clashes when expectations regarding authority, decision-making, or collaboration differ.
- Conflict Resolution Styles: Cultures have distinct approaches to resolving conflicts. Some cultures prefer direct confrontation and open discussion, while others emphasize harmony and avoiding confrontation. These differences in conflict resolution styles can create challenges in addressing and resolving workplace conflicts effectively.
How to overcome cultural barriers in the workplace
1/ Encourage Open Communication: Create an environment that values open communication and encourages employees to share their perspectives, ideas, and concerns. Foster a safe space for dialogue and ensure that diverse voices are heard and respected.
2/ Develop Cross-Cultural Communication Skills: Provide training and workshops on cross-cultural communication to enhance employees’ skills in understanding, interpreting, and adapting to different communication styles and cultural norms. This includes various aspects such as verbal and nonverbal communication, active listening, and the ability to empathize with others.
3/ Establish Clear Communication Channels: Implement clear and inclusive communication channels within the organization. Make sure that vital information is conveyed in a manner that is easily accessible and comprehensible to all employees, taking into account language and cultural variations.
4/ Provide Cultural Mentoring or Coaching: Pair employees from different cultural backgrounds as mentors or coaches to support mutual learning and understanding. This can help bridge cultural gaps, enhance communication, and promote cultural integration within the workplace.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can create a workplace culture that values diversity, fosters effective communication across cultures, and promotes collaboration among employees from different backgrounds.
Examples of cultural barriers in the workplace
- For example, if team members have different native languages or varying levels of fluency in a shared language, it can lead to difficulties in conveying ideas and instructions accurately.
- Certain cultures may place emphasis on strict adherence to schedules and value punctuality, while others may adopt a more flexible approach to time.
- In a hierarchical culture of an organization, junior team members may have a psychological barrier that makes them hesitant to express their opinions or challenge the ideas of senior colleagues, leading to a lack of open communication.
Difference between cultural barriers and semantic barriers
Cultural Barriers | Semantic Barriers |
Related to differences in cultural norms, values, and communication styles. | Related to differences in language, meaning, and interpretation of words and symbols. |
Arise from diverse cultural backgrounds and perspectives. | Arise from linguistic differences and language comprehension. |
Impact communication due to varying social customs, nonverbal cues, and communication norms. | Impact communication due to misunderstandings, ambiguity, and misinterpretation of words or symbols. |
Can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and conflicts. | Can lead to miscommunication, confusion, and barriers in conveying intended meaning. |
Require cultural awareness, sensitivity, and cross-cultural communication skills to overcome. | Require language proficiency, clarity in expression, and effective use of language to overcome. |
Can be addressed by promoting cultural understanding, open-mindedness, and empathy. | Can be addressed by using clear and concise language, seeking clarification, and promoting effective listening. |
Solutions involve building inclusive and diverse work environments, providing cultural training, and fostering open communication. | Solutions involve improving language skills, promoting effective translation and interpretation, and ensuring clarity in communication. |
Related Reading: How to overcome Semantic Barriers to Communication
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What are the cultural barriers?
Ans: Cultural barriers refer to the challenges that arise in communication and interaction due to differences in cultural norms, values, beliefs, and communication styles between individuals or groups from different cultures.
Q2) Why culture is one of the barriers to communication?
Ans: Culture acts as a barrier to communication due to its inherent influence on people’s communication styles, values, and norms. Each culture has its own unique way of expressing ideas, thoughts, and emotions, which may differ significantly from other cultures. These differences in communication styles can create obstacles when individuals from different cultural backgrounds interact.
Q3) What are examples of cultural issues?
Ans: Cultural issues include challenges arising from cultural differences and clashes. Examples include language barriers, nonverbal communication differences, social etiquette, conflicting values, and management differences.
Q4) What is cultural awareness in communication?
Ans: Cultural awareness in communication refers to having a deep understanding and sensitivity toward the cultural differences and nuances that influence communication. It involves recognizing and respecting diverse cultural backgrounds, norms, values, and communication styles.
Q5) Are time and distance cultural barriers to communication?
Ans: No, time and distance are not cultural barriers to communication. They are logistical factors that can challenge coordinating communication across different time zones or geographical locations.

 Examples of cultural differences in communication?
Examples of cultural differences in communication?



