In today’s complex business landscape, it is essential to grasp the different operational aspects of formal and informal organizations. These two distinct organizational structures significantly influence the way work is conducted and decisions are made within an organization.
In this blog post, we will begin a detailed exploration of formal and informal organizations, analyzing their defining characteristics and providing real-life examples to illustrate their practical applications.
What is a formal and informal organization?
Formal organization:
A formal organization refers to a structured and deliberately created system that operates within established rules, regulations, and hierarchical structures. The main aim of a formal organization is to accomplish specific objectives in a manner that is both efficient and effective.
It typically includes a hierarchical structure, with levels of management and various departments, each with its own functions and responsibilities. The formal organization provides a framework for individuals to work together towards common goals, enabling coordination, specialization, and the allocation of resources. It also establishes a system of communication and decision-making, ensuring information flows through proper channels and authority is appropriately delegated.
Informal organization:
The concept of an informal organization refers to the social structure and relationships that develop within a formal organization, but are not officially defined or governed by its formal structure. It is the network of personal interactions, communication channels, and social connections that emerge among employees beyond their assigned roles and responsibilities.
An informal organization can have a significant impact on how work is done, influencing communication patterns, decision-making processes, and the overall dynamics of the formal organization.
Characteristics of Formal and Informal Organizations
Characteristics of formal organizations
- The formal organization has an official structure defined by the organizational chart, job roles, and reporting relationships.
- Formal decision-making processes involve following established protocols and seeking approvals.
- Performance is evaluated based on predefined criteria and formal performance appraisal systems.
- The formal organization aims to provide stability, order, and predictability in how work is organized and executed.
Characteristics of informal organizations
- It is not officially defined or governed by the formal organizational structure.
- The informal organization is flexible and adaptive, allowing for quick response and problem-solving.
- The informal organization provides emotional support and fosters a sense of belonging.
- Informal communication channels, such as informal meetings, grapevine gossip, and social gatherings, play a significant role.
Importance of understanding the difference between formal and informal organization?
Understanding the difference between formal and informal organizations is crucial for individuals in managerial or leadership positions, as well as for overall organizational effectiveness. Here are the key reasons why it is important:
- Decision-Making: Understanding the interplay between formal and informal decision-making processes allows managers to make informed decisions. They can gather input from both formal structures and informal networks, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the organizational context and diverse perspectives.
- Power Dynamics: Awareness of informal power structures within an organization helps management recognize sources of influence beyond formal positions. By understanding these dynamics, they can identify key stakeholders foster collaboration, and achieve organizational objectives more effectively.
- Employee Satisfaction and Retention: The informal organization contributes to employee satisfaction and retention. Recognizing and nurturing informal networks helps managers create a positive work environment.
- Organizational Agility: The informal organization is often more flexible and adaptable than the formal structure. Understanding the informal networks and their connections to the formal organization enables leaders to leverage this agility, making the organization more responsive to changes in the external environment and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Comparison table for formal Vs informal organization
Point of differentiation | Formal Organization | Informal Organization |
Structure and Authority | Well-defined hierarchical structure | Less rigid and more flexible structure |
Official roles and responsibilities | Clearly defined and documented roles | Roles may be adaptable or flexible |
Clear reporting relationships | Formal lines of reporting | Reporting relationships may be flexible |
Formal communication channels | Structured communication protocols | Informal and spontaneous communication |
Documented procedures and policies | Well-documented procedures and policies | Informal and ad hoc procedures |
Organizational charts | Formal organizational charts | Limited or no formal organizational charts |
Job titles and descriptions | Formal job titles and descriptions | Flexible job titles and descriptions |
Standard operating procedures | Established and documented procedures | Informal or unwritten procedures |
Top-down decision-making | Decisions made by those in authority | Collective decision-making |
Committees and decision-making bodies | Formal committees and decision-making bodies | Informal or ad hoc committees and decision-making bodies |
Formal Performance Evaluation | Structured performance evaluation process | Informal or less structured performance evaluation process |
Formal Training and Development Programs | Formal training programs and development opportunities | Informal or less formal training and development initiatives |
Organizational Culture | Cultivated and reinforced through formal policies and practices | Emerges organically based on group dynamics and interactions |
Conflict Resolution | Structured conflict resolution processes | Adaptive and flexible conflict resolution approaches |
Risk Management | Formal risk management processes and protocols | Adaptive and collective risk management approaches |
Diagram of formal and informal organization structure
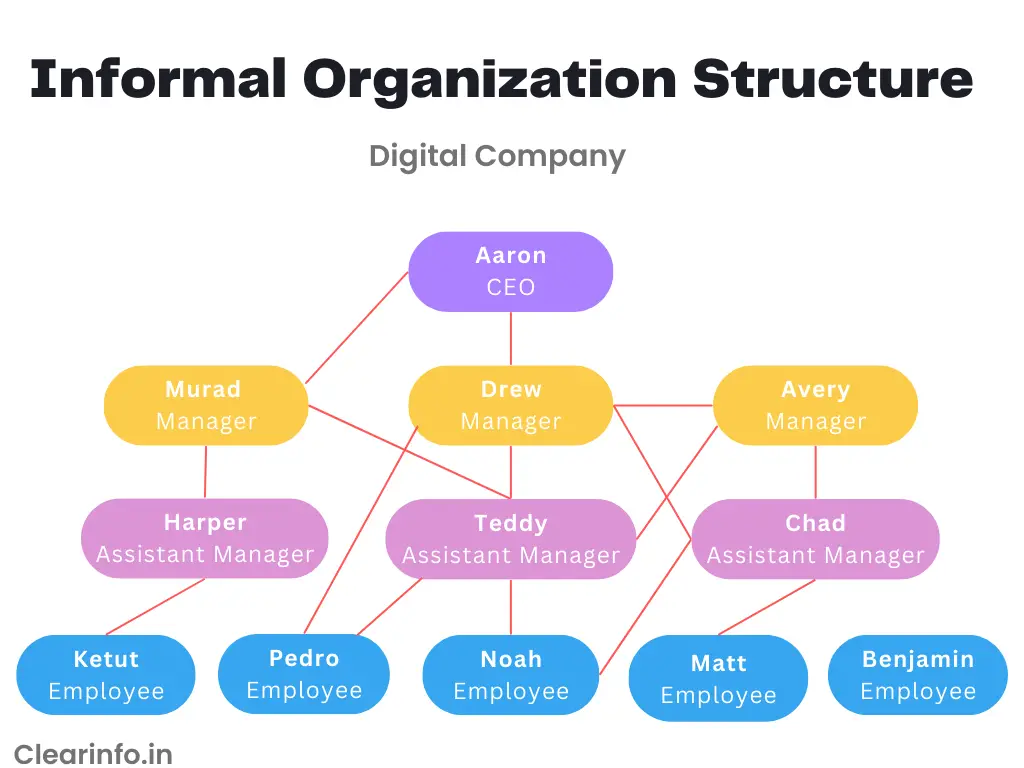
Formal and informal organizational systems have a significant influence on the dynamics within a workplace. To provide a clearer understanding, let’s explore two illustrations of these systems in two different digital companies. Through these examples, we can gain insights into how each type of organization structures communication, fosters culture, and influences overall operations.
Diagram of formal organization structure:
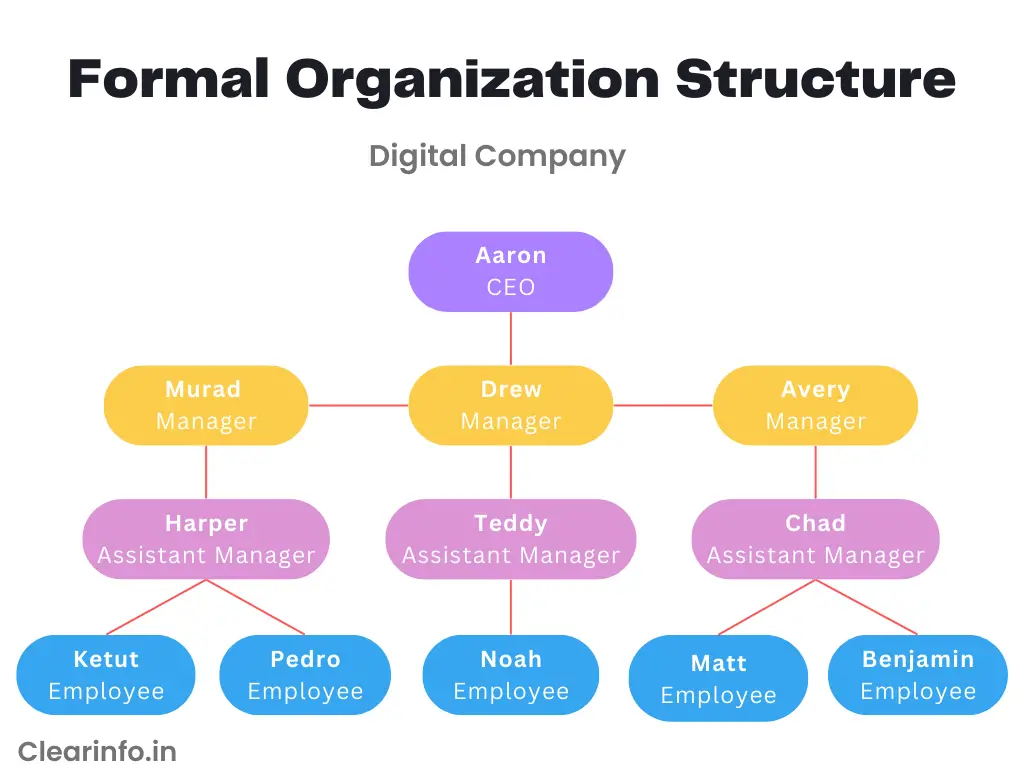
Diagram of informal organization structure:
15 Differences between formal and informal communication (Detailed explanation)
Understanding the differences between formal and informal communication is crucial for effective interaction and building professional relationships. Here, we will delve into 15 key differences between formal and informal communication, providing a detailed explanation of each aspect.
1/ Structure and Authority:
Formal Organization: A formal organization is characterized by a structured and hierarchical setup. It follows a predefined framework and establishes a clear chain of command. The organizational structure typically consists of various levels, such as top management, middle management, and frontline employees.
Each level has defined roles and responsibilities, and individuals report to their immediate superiors. This hierarchical structure helps maintain order, accountability, and efficient decision-making processes.
Informal Organization: In contrast, informal organizations lack a formalized structure and hierarchy. They are more spontaneous and emerge naturally based on social connections and shared interests among individuals.
The connections within an informal organization lack explicit definitions based on authority or reporting lines. Instead, they form through personal connections, friendships, or common goals. Informal organizations often arise as a result of informal networks and social interactions within a formal organization or a community.
2/ Official roles and responsibilities
Formal Organization: In a formal organization, official roles and responsibilities are clearly defined and assigned to individuals based on their position within the organizational structure.
Each role has specific duties, tasks, and areas of authority associated with it. Formal job descriptions outline the expectations and requirements of each position, providing employees with a clear understanding of their responsibilities. This clarity helps in establishing accountability, promoting efficiency, and ensuring that work is appropriately distributed within the organization.
Informal Organization: In an informal organization, roles, and responsibilities are not officially designated or explicitly defined. Instead, individuals often take on roles based on their interests, expertise, or influence within the group.
These roles are flexible and subject to change, as informal organizations rely on social dynamics rather than formal job descriptions. While informal leaders may emerge within the group, their authority is not derived from an official position or hierarchy.
3/ Clear reporting relationships
Formal Organization: In a formal organization, reporting relationships are well-defined and structured. Each employee has a designated supervisor or manager to whom they report directly. This hierarchical reporting system ensures a clear line of authority and accountability within the organization. Employees know who their superiors are and whom they should approach for guidance, feedback, or decision-making.
Informal Organization: In comparison, reporting relationships within an informal organization are not explicitly defined or based on a formal hierarchy. While individuals may seek guidance or advice from others within the informal group, there is no official reporting structure. Instead, influence and communication flow more organically through social connections and personal relationships.
4/ Formal communication channels
Formal Organization: Formal organizations have established channels of communication that are intended for official and professional purposes. These channels typically include formal meetings, emails, memos, reports, and other documented means of communication.
The use of these formal communication channels ensures that information flows in a structured and systematic manner throughout the organization. It helps in circulating important announcements, sharing updates, and facilitating collaboration among employees.
Informal Organization: Conversely, informal organizations depend primarily on informal communication channels. Informal communication channels are less structured and may include casual conversations, social gatherings, and informal networks within the organization. These channels often involve personal interactions and can be more flexible and spontaneous compared to formal communication channels.
Related Reading: Difference between formal and informal channels of communication
5/ Documented procedures and policies
Formal Organization: Formal organizations have well-defined and documented procedures and policies that govern various aspects of their operations. These procedures outline step-by-step guidelines for carrying out specific tasks or processes within the organization. Policies, on the other hand, establish rules, principles, and expectations for behavior, decision-making, and compliance. Documentation of procedures and policies ensures consistency, reduces ambiguity, and provides a reference for employees to follow.
Informal Organization: In contrast, informal organizations often lack formal documentation of procedures and policies. Since the structure and operations of informal organizations are more flexible, they rely less on written guidelines. Instead, informal organizations may have unwritten rules and norms that develop over time through shared understandings and informal communication among members.
6/ Organizational charts
Formal Organization: Formal organizations typically utilize organizational charts to visually represent the hierarchical structure of the organization. An organizational chart illustrates the relationships between different positions, departments, and levels of authority. It provides a clear overview of the reporting lines and shows how different roles are connected within the organization. Organizational charts help employees understand the structure and hierarchy of the organization and their position within it.
Informal Organization: Informal organizations typically do not have formal organizational charts since their structure is not based on a predetermined hierarchy. The relationships and connections within an informal organization are more fluid and based on personal interactions rather than a formal reporting structure. Informal organizations may have loose networks or clusters of individuals based on shared interests or social connections, but these relationships are not typically illustrated in a formal chart.
7/ Job titles and descriptions
Formal Organization: In formal organizations, job titles and descriptions are clearly defined and assigned to individuals based on their roles and responsibilities. Job titles serve as a formal designation for specific positions within the organization, indicating the level of authority and the scope of responsibilities associated with each role. Job descriptions provide a detailed outline of the tasks, duties, qualifications, and expectations for each position. These formal designations help in setting expectations, establishing career paths, and ensuring clarity in role assignments.
For professionals looking to create a well-structured and visually appealing resume, Online Resume Maker offers an easy-to-use platform to design standout resumes that align with their career goals.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, job titles and descriptions may be less formal or non-existent. Individuals may be recognized based on their contributions, expertise, or influence within the informal group, rather than holding specific job titles. The responsibilities and tasks within an informal organization are often distributed based on individuals’ strengths and interests, rather than predefined job descriptions.
8/ Standard operating procedures
Formal Organization: Formal organizations place a strong emphasis on developing and implementing standard operating procedures (SOPs). Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are documented guidelines that provide detailed instructions, specifying the steps for executing specific tasks or processes within an organization. These procedures ensure consistency, efficiency, and quality in the organization’s operations. SOPs serve as a reference point for employees to follow established protocols and best practices, promoting uniformity and reducing the likelihood of errors or inconsistencies.
Informal Organization: Informal organizations often do not have formalized standard operating procedures. Since the structure and operations of informal organizations are more flexible and spontaneous, they rely more on informal communication and personal interactions for carrying out tasks or processes. Informal organizations may develop their own informal guidelines or shared practices based on the group’s collective understanding and experiences.
9/ Top-down decision-making
Formal Organization: In formal organizations, decision-making typically follows a top-down approach. This means the decision-making authority is concentrated among the higher levels of the organizational hierarchy, primarily held by senior management or executives. Decisions are made by those in positions of authority and then communicated down to lower levels through a downward communication flow for implementation. This hierarchical decision-making structure ensures centralized control, accountability, and consistency in decision outcomes.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, decision-making is often more decentralized and participatory. The decision-making process may involve input and contributions from multiple individuals within the group. Decisions may emerge through collaboration or consultation with various stakeholders. In informal organizations, decision-making is often based on shared interests, expertise, or influence rather than strict hierarchical authority.
10/ Committees and decision-making bodies
Formal Organization: Formal organizations often establish committees and decision-making bodies to facilitate collective decision-making and governance processes. These committees are formed with specific objectives, and members are appointed or selected based on their expertise or representation within the organization. Committees can be permanent or temporary and may focus on areas such as strategic planning, project management, or policy development.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, the decision-making process may not involve formal committees or structured decision-making bodies. Instead, decisions are often made through informal discussions, consultations, or consensus-building among the group members. Informal leaders or influential individuals within the group may play a significant role in shaping decisions based on their expertise, experience, or persuasive abilities.
11/ Formal Performance Evaluation:
Formal Organization: In formal organizations, performance evaluation processes are typically established to assess and measure the performance of employees. These evaluations are conducted through structured procedures and frameworks, such as performance appraisal forms, metrics, and feedback sessions. Formal performance evaluations provide a systematic way to assess employee performance, provide feedback, identify areas for improvement, and make decisions regarding promotions, rewards, or disciplinary actions.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, performance evaluation may be less formalized or even nonexistent. Since the structure of informal organizations is more fluid and based on personal relationships and social dynamics, evaluations may rely more on informal feedback and recognition from peers or informal leaders within the group.
12/ Formal Training and Development Programs:
Formal Organization: Formal organizations typically have structured training and development programs in place. The purpose of these programs is to boost employees’ essential business communication skills, knowledge, and capabilities, aligning them with both organizational goals and job requirements. Formal training programs may include orientation for new employees, job-specific training, leadership development, and professional development opportunities.
Informal Organization: Informal organizations may have less formalized training and development programs. Learning and development within informal organizations often occur through informal means, such as on-the-job learning, mentorship, coaching, and peer-to-peer knowledge sharing.
13/ Organizational Culture:
Formal Organization: In formal organizations, organizational culture is often more defined and structured. The culture is influenced by the organization’s mission, values, and norms, which are typically communicated and reinforced through formal channels. Formal organizations often have well-established policies, procedures, and codes of conduct that shape the behavior and interactions of employees.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, the organizational culture tends to be more organic. The culture emerges from the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors of the group members. The culture is shaped through informal interactions, social dynamics, and collective experiences.
14/ Conflict Resolution:
Formal Organization: In formal organizations, conflict resolution processes follow established procedures. Formal organizations have policies and guidelines in place to address conflicts that arise among employees or teams. The conflict resolution process may involve identifying the parties involved, gathering relevant information, facilitating open communication, exploring potential solutions, and reaching a resolution. Formal organizations may have designated individuals or departments responsible for managing conflicts and ensuring fair outcomes.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, conflict resolution may be more dynamic. The resolution of conflicts is often driven by the individuals involved, and the process may vary depending on the situation and the group dynamics. Informal organizations may rely on open communication, active listening, and collaboration to address conflicts. Group members may engage in informal discussions or work together to find mutually acceptable solutions.
15/ Risk Management:
Formal Organization: Formal organizations have established procedures and protocols to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. They may have dedicated risk management departments or individuals responsible for monitoring and managing risks across different areas of the organization. Formal organizations may conduct risk assessments, implement risk control measures, and have contingency plans in place to mitigate the impact of potential risks.
Informal Organization: In informal organizations, risk management may be more flexible and adaptive. The approach to risk management is often driven by the collective efforts and shared responsibility of the group members. Informal organizations may rely on open communication, collaboration, and active problem-solving to identify and address risks.
Formal and informal organization examples
Examples of formal organizations:
1/ Corporations: Large multinational companies, such as Apple, Microsoft, or Coca-Cola, with a formal organizational structure and clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
2/ Educational Institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities that follow a formal organizational structure, including administrative departments, academic faculties, and support staff.
3/ Professional Associations: Formal organizations that represent professionals in a specific field, such as the American Medical Association or Engineers Without Borders.
Examples of Informal organizations:
1/ Online Communities: Informal groups that gather on social media platforms, forums, or online communities to discuss specific topics or share common interests.
2/ Hobby Clubs: Informal groups of people who come together based on shared hobbies or interests, such as photography clubs, book clubs, or sports clubs.
What is an example of a formal group?
1/ Board of Directors: A formal group consisting of individuals elected or appointed to oversee and make strategic decisions for an organization or company.
2/ Quality Control Team: A formal group within a manufacturing or production setting that is responsible for ensuring product quality, adhering to quality standards, and implementing quality improvement initiatives.
The interplay between formal and informal organization
Coexistence and overlap in most organizations
Formal and informal organizations coexist and overlap in most organizations. This means that alongside the official structure, there are informal networks and relationships among employees.
These informal interactions can lead to social bonds, friendships, and networks outside of the formal structure. The coexistence allows employees to participate in various social structures simultaneously.
It can foster collaboration and innovation, but also create challenges like exclusion or conflicts with formal rules. Recognizing this coexistence helps leaders understand and leverage the strengths of both structures for a productive work environment.
Potential challenges and conflict between formal and informal organizations?
The interaction between formal and informal organizations can present several challenges and conflicts within an organizational context. These challenges arise due to the differing nature and dynamics of these two structures. Some key points to consider include:
- Power struggles and resistance: Informal networks may challenge formal authority, leading to power struggles and resistance to change.
- Communication breakdown: Different communication styles between formal and informal groups can result in miscommunication and information gaps.
- Conflicting goals and priorities: Formal organizations typically have defined missions and objectives. Informal organizations, however, are driven by shared interests and personal connections. These differing priorities can result in conflicts between formal and informal groups.
- Misalignment: Formal and informal organizations may operate with different sets of rules, norms, and expectations. Conflicts may arise when there is a lack of alignment between these two structures. For example, informal networks might prioritize personal relationships or informal agreements over formal policies.
How informal networks can shape formal organizations?
Informal networks, formed through personal relationships and social connections, possess a significant influence on formal organizations. These networks shape formal organizations in several ways. First, they serve as alternative communication channels, facilitating the flow of information and knowledge outside the boundaries of formal structures.
Informal networks encourage collaboration and innovation by offering a platform for employees to exchange ideas, collaborate efficiently, and discover creative solutions. Moreover, informal networks can impact formal decision-making processes by influencing opinions and guiding the thinking of decision-makers.
Balancing between a formal and informal organization
Finding the balance between formal and informal organizations is crucial for organizational success. Formal structures provide stability, defined roles, and efficient processes, while informal networks foster creativity, collaboration, and innovation.
To strike the right balance, organizations should encourage open communication, transparency, and collaboration between the two. Leaders play a key role in recognizing and valuing the contributions of informal networks while aligning them with formal objectives.
Effective communication is essential to ensure seamless integration and coordination plays a vital role in this process. By managing this interplay, organizations can leverage the strengths of both structures and drive long-term success.
Advantages and disadvantages of informal and formal organizations
Advantages of formal organizations:
- Clear structure and roles: Formal organizations provide clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines, which enhance clarity and efficiency in decision-making and task allocation.
- Standardization and consistency: Formal structures establish standardized procedures and practices, ensuring consistency and reducing variability in operations.
- Accountability and oversight: Formal organizations have mechanisms in place to ensure accountability and monitor performance, promoting fairness and transparency.
Disadvantages of formal organizations:
- Bureaucracy and rigidity: Formal organizations can become bureaucratic and inflexible, slowing down decision-making and stifling creativity and innovation.
- Communication barriers: Hierarchical structures in formal organizations can hinder effective communication, leading to delays, misunderstandings, and reduced collaboration.
- Resistance to change: Formal structures may be resistant to change, making it difficult to adapt to evolving market conditions or embrace new ideas.
Advantages of informal organizations:
- Flexibility and adaptability: Informal organizations can quickly respond to changing circumstances and adapt to new challenges due to their flexible nature.
- Efficient communication: Informal networks often have faster and more efficient communication channels that can bypass bureaucratic hurdles and facilitate information sharing.
Disadvantages of informal organizations:
- Lack of accountability: Informal networks may lack formal mechanisms for accountability and oversight, leading to potential misuse of power or unethical behavior.
- Information silos: Informal networks may create information silos where critical knowledge or insights are shared within the network but not disseminated throughout the entire organization.
Differences between formal, informal, and hybrid structures in an organization?
Differences | Formal Structure | Informal Structure | Hybrid Structure |
Authority | Formal authority is clearly defined and hierarchical. | Authority is decentralized, and influence is based on personal relationships and expertise. | Authority is a combination of formal positions and personal networks. |
Communication | Formal communication channels follow established protocols and flows. | Communication is more fluid, with informal networks facilitating information exchange. | Communication combines formal channels with informal networks for a balanced approach. |
Decision-making | Decision-making is centralized and follows predefined processes. | Decision-making is decentralized, relying on consensus and informal influence. | Decision-making combines formal processes with input from informal networks. |
Flexibility | Formal structures may be less flexible and slow to adapt to changes. | Informal structures are more flexible and adaptable to evolving circumstances. | Hybrid structures aim to combine flexibility with the benefits of formalization. |
Culture | Formal structures often have more rigid and rule-driven cultures. | Informal structures foster a more relaxed and collaborative culture. | Hybrid structures seek to blend formal culture with elements of informality. |
Accountability | Accountability is clearly defined and tied to formal roles and responsibilities. | Accountability relies on personal relationships and informal norms. | Hybrid structures establish accountability mechanisms that balance formal and informal aspects. |
Collaboration | Collaboration is based on assigned roles and formalized processes. | Collaboration occurs organically through personal connections and shared interests. | Hybrid structures promote collaboration through a mix of formal and informal approaches. |
Difference between formal group and informal organization
Formal Groups | Informal Organizations |
Established by the organization's structure, policies, and objectives. | Emerges spontaneously based on social relationships and common interests among individuals. |
Roles, responsibilities, and tasks are clearly defined and assigned. | Roles and responsibilities evolve organically within the group based on individual skills, interests, and influence. |
Communication follows formal channels and is governed by organizational protocols. | Communication is more fluid, and informal, and often occurs through informal networks and social interactions. |
Accountability and performance are measured and enforced through formal mechanisms. | Accountability is primarily maintained through social norms, personal relationships, and reputation within the informal network. |
Typically focuses on achieving specific organizational goals and tasks. | Emphasizes social connections, shared interests, and mutual support among members. |
Difference between informal rule and formal rule in business organization
Point of differentiation | Informal Rules | Formal Rules |
Definition | Unwritten, implicit guidelines and norms | Written, explicit policies and procedures |
Origin | Arise naturally from interactions and culture within the organization | Established and communicated by management or governing bodies |
Flexibility | Flexible and adaptable to specific situations | Generally inflexible and must be followed consistently |
Enforcement | Self-enforced through social norms and peer pressure | Enforced through disciplinary measures and consequences |
Documentation | Typically not documented or formally recorded | Documented in written policies, manuals, or contracts |
Formal Vs informal system
These differences highlight key distinctions between formal and informal systems in terms of their structure, rules, communication, decision-making processes, and documentation practices.
Point of differentiation | Formal System | Informal System |
Structure | Well-defined structure and hierarchy | Lack of defined structure or hierarchy |
Rules | Explicit rules and procedures | Flexible and adaptable |
Communication | Official channels and protocols | Informal and spontaneous |
Decision-making | Centralized decision-making | Decisions made collectively or individually |
Documentation | Extensive documentation and records | Minimal documentation |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What are the three types of formal organization?
Formal organizations can be classified into three main types: coercive organizations, utilitarian organizations, and normative organizations. Coercive organizations use control and force to maintain discipline. Utilitarian organizations focus on efficiency and profit. Normative organizations strive for social change, including activist groups and human rights organizations.
Q2) What are the 4 types of informal organizations?
The four types of informal organization include vertical informal organization, horizontal informal organization, mixed informal organization, and cliques informal organization. These types of informal organizations demonstrate various informal structures and relationships within an organization.
Q3) What is the difference between formal and informal letters?
Formal and informal letters differ in tone, purpose, language, and structure. Formal letters are utilized for professional or official communication and are governed by specific rules and conventions. Informal letters are casual and personal, allowing for a relaxed tone and conversational language.
Q4) What is the difference between formal and informal communication channels in business organizations?
Formal and informal communication channels in a business organization differ in structure, purpose, and adherence to protocols. Formal channels follow a hierarchical, rule-based approach through written documentation and established channels of authority. They convey official information. Informal channels go beyond hierarchy, encourage personal interactions, and foster creativity, innovation, and team spirit among employees. Balancing both is crucial for productive communication.



