Definition of Emotional Barriers to Communication
“Emotional barriers are defined as internal psychological factors that affect communication by creating emotional distress, tension, or anxiety, thereby impeding the free flow of information and understanding between individuals.” In the work “Communication in Everyday Life: A Survey of Communication,” Steve Duck and McMahan (2018)
What are the emotional barriers to communication?
Emotional barriers to communication refer to the emotional obstacles that prevent the productive interchange of information and emotions among individuals or groups. These barriers are typically rooted in the emotions, attitudes, and past experiences of individuals, and they can significantly impact the quality and clarity of communication.
Emotional barriers can appear in various ways, such as fear, anxiety, anger, lack of trust, and emotional insecurities. A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that emotional barriers are also associated with an increased risk of developing mental disorders.
Therefore these barriers often arise from personal biases, unresolved conflicts, past traumas, or negative perceptions of oneself or others. When these emotional barriers are present, they can interfere with open and honest expression, active listening, and understanding.
It’s important to note that emotional barriers can occur in both personal and professional relationships. In personal relationships, emotional barriers may hamper, trust-building, and conflict resolution. In professional settings, emotional barriers can obstruct effective collaboration, teamwork, and the ability to provide and receive constructive feedback.
Common types of emotional barriers to communication
Let’s explore some common types of emotional barriers to communication and gain insights into how they impact our interactions with others.
1/ Fear and anxiety:
Fear and anxiety can create significant obstacles to effective communication. When individuals experience fear, they may be hesitant to express themselves openly, fearing judgment, rejection, or negative consequences.
Anxiety, on the other hand, can lead to excessive worry and nervousness, which may interfere with clear thinking and articulation of thoughts. These emotional barriers can prevent individuals from actively participating in conversations, sharing their ideas, or asking questions, ultimately limiting effective communication.
2/ Anger and resentment:
Anger and resentment can significantly impede communication by clouding judgment, intensifying emotions, and fostering a defensive or hostile environment. When individuals are angry or resentful, they may become reactive, aggressive, or confrontational in their communication, hindering effective dialogue and understanding.
Anger can lead to impulsive and uncontrolled responses, while resentment can cause individuals to hold grudges or harbor negative feelings, making it difficult to engage in productive and empathetic communication. Resolving underlying anger and resentment is essential for creating a more open and constructive communication environment.
3/ Lack of trust:
Lack of trust poses a significant emotional barrier to communication. Without trust, individuals may be guarded, skeptical, or unwilling to share information openly. Suspicion or doubt about the intentions or reliability of others can hinder the development of meaningful and transparent communication.
When there is a lack of trust, individuals may withhold information, engage in secretive behavior, or doubt the authenticity of messages, which can lead to misunderstandings and breakdowns in communication. Building trust through consistent and honest communication is crucial for overcoming this barrier.
4/ Emotional insecurities:
Emotional insecurities refer to feelings of self-doubt, inadequacy, or uncertainty about one’s own abilities. These insecurities can create barriers to communication by impacting an individual’s confidence in expressing themselves openly and honestly. Fear of judgment or rejection may arise from these insecurities, causing individuals to hold back their thoughts, ideas, or emotions.
They may constantly seek validation or struggle with a fear of not being heard or understood. Addressing and overcoming emotional insecurities involves developing self-acceptance, building self-confidence, and practicing assertiveness in communication.
5/ Guilt and shame:
Guilt and shame are powerful emotions that can create potential barriers to effective communication. Guilt often arises when individuals believe they have done something wrong or violated their own moral or ethical standards. Shame, on the other hand, involves a deep-seated feeling of inadequacy or unworthiness.
Both emotions can prevent communication by causing individuals to feel embarrassed, defensive, or avoidant. They may struggle with expressing themselves honestly or discussing sensitive topics due to a fear of judgment or further humiliation. Overcoming guilt and shame involves self-compassion and creating a supportive and non-judgmental communication environment.
6/ Jealousy:
Jealousy is an emotional barrier that can arise when individuals feel threatened or insecure in comparison to others. It can lead to negative thoughts and feelings such as resentment, envy, or mistrust. In terms of communication, jealousy can hinder open and honest expression as individuals may struggle with acknowledging or celebrating the successes or achievements of others.
Jealousy may manifest as passive-aggressive behavior, possessiveness, or a tendency to undermine or devalue the contributions of others. Overcoming jealousy involves cultivating a mindset of abundance, practicing gratitude, and fostering supportive and collaborative communication.
7/ Pride and ego:
Pride and ego can create significant emotional barriers to communication. When individuals have an inflated sense of self-importance or an excessive need to be right or in control, they may struggle with active listening, accepting feedback, or considering alternative perspectives.
Pride can lead to defensiveness or a lack of receptiveness to different viewpoints. Ego-driven communication often prioritizes self-promotion and dominance rather than mutual understanding and cooperation. Overcoming pride and ego requires humility, openness to learning, and a willingness to prioritize the collective goals of effective communication over individual validation.
8/ Depression and sadness:
Depression and sadness can create emotional barriers to communication by affecting an individual’s overall mood, motivation, and energy levels. When someone is experiencing depression or deep sadness, they may have difficulty engaging in communication and may withdraw from social interactions.
They may feel emotionally drained, have trouble expressing themselves, or struggle to find the words to convey their thoughts and feelings. Depression can also lead to a pessimistic outlook, making it challenging to engage in positive and constructive communication. Overcoming these barriers involves seeking support, practicing self-care, and exploring counseling to address the underlying emotional issues.
9/ Low self-esteem and self-worth:
Low self-esteem and self-worth can significantly impact communication by influencing how individuals perceive themselves and how they believe others perceive them. When individuals have low self-esteem, they may struggle with self-confidence and doubt their own abilities, ideas, or contributions.
This can lead to hesitancy in expressing themselves assertively or fear of being judged or rejected. Low self-worth can also manifest as seeking constant approval or validation from others, making it difficult to engage in authentic and autonomous communication.
10/ Past Traumas and Unresolved Emotional Issues:
Past traumas and unresolved emotional issues can create significant barriers to communication. Traumatic experiences or unresolved emotional wounds from the past can affect an individual’s ability to engage in open and honest communication.
These experiences can result in emotional triggers or defensive reactions when certain topics or situations arise. Individuals may experience fear, anxiety, or emotional pain when attempting to discuss or address these sensitive areas. It can be challenging to express oneself fully or to trust others when past traumas or emotional issues remain unaddressed.
Expert Comment: Mental trauma emerges as one of the most prevalent psychological health conditions, with a significant impact on individuals’ well-being. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration highlights that a substantial portion of the population, specifically 61% of men and 51% of women, have reported experiencing at least one traumatic event throughout their lives.
How to Identify Emotional Barriers in Communication
Understanding and identifying emotional barriers in communication plays a crucial role in establishing meaningful connections and facilitating effective dialogue. Following are some of the techniques that can be used to identify them:
1/ Self-reflection and introspection: Self-reflection and introspection are crucial steps in identifying emotional barriers to communication. Taking the time to examine one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors allows individuals to gain insight into their own internal processes.
It involves asking oneself meaningful questions, such as “What emotions do I feel during communication?” or “What are my typical communication patterns?” Self-reflection helps individuals become aware of their emotional states, biases, and potential barriers that may impact their ability to communicate effectively.
2/ Recognizing common emotional patterns: Recognizing common emotional patterns involves becoming familiar with the recurring emotional responses and reactions that arise in communication. It requires paying attention to how certain emotions influence communication dynamics.
For example, some individuals may notice a tendency to become defensive or withdraw when feeling criticized. Others may have a pattern of becoming impatient or frustrated when they perceive a lack of understanding. By identifying these patterns, individuals can gain insight into the emotional barriers that hinder effective communication.
3/ Seeking feedback from trusted individuals: Seeking feedback from trusted individuals is incredibly valuable for identifying emotional barriers that one may struggle to recognize independently. Trusted friends or colleagues can provide honest insights and valuable perspectives on an individual’s communication habits.
Similarly, a mental health professional can offer objective advice to patients willing to examine their behaviors critically. They can help uncover blind spots or patterns that might be overlooked by the individual.
Additionally, feedback serves to uncover emotional barriers perceived by others, allowing individuals to gain deeper insights into their communication hurdles.
Related Reading: What is feedback communication
Emotional barriers to communication examples
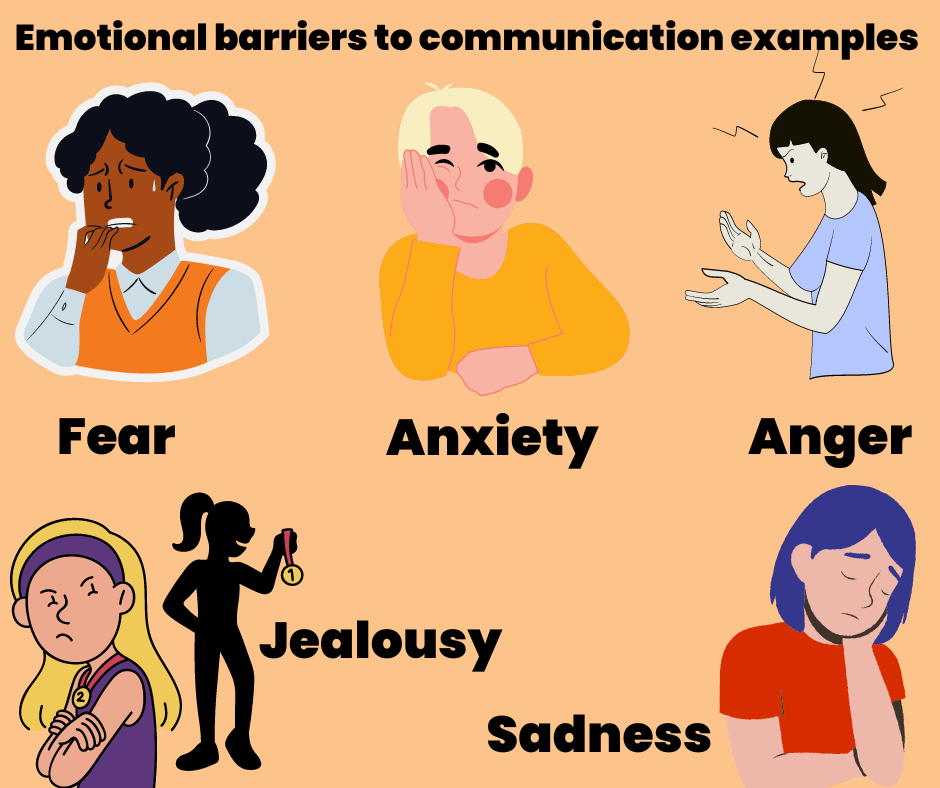
Examples of emotional behaviors
- Crying: Shedding tears as a response to sadness, frustration, or overwhelming emotions.
- Laughing: Expressing amusement, joy, or happiness through laughter.
- Yelling: Raising one’s voice in anger, frustration, or to convey strong emotion.
- Smiling: Displaying a facial expression that conveys happiness, friendliness, or contentment.
- Hugging: Engaging in a physical gesture of affection, comfort, or support.
- Holding hands: A gesture of affection, comfort, or connection between individuals.
How to overcome emotional barriers to communication
(A) Developing self-awareness:
Developing self-awareness is a fundamental step in overcoming emotional barriers to communication. It involves acquiring a profound understanding of one’s own emotions, biases, and reactions. By cultivating self-awareness, individuals can take ownership of their emotional states, as well as the attitudes that may prevent good communication.
Here are three key aspects of developing self-awareness:
- Identifying and understanding emotions: The first step is to identify and understand one’s own emotions. This involves being aware of the range of emotions experienced in different situations and recognizing how they influence communication. By becoming attuned to their emotions, individuals can make conscious choices about how to respond and express themselves effectively.
- Recognizing personal biases and prejudices: Self-awareness also entails recognizing personal biases and prejudices that may affect communication. Each individual possesses a unique assortment of biases influenced by their upbringing, experiences, and beliefs. By acknowledging and challenging these biases, individuals can strive for more objective and inclusive communication.
- Practicing mindfulness and emotional regulation techniques: Mindfulness and emotional regulation techniques can support the development of self-awareness. Mindfulness involves fully being present and attentive to one’s thoughts, emotions, and physical perceptions without judgment. Emotional regulation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, self-reflection, or seeking support, can help individuals manage and regulate their emotions in challenging communication situations.
(B) Building Trust and Rapport:
Building trust and rapport is essential for overcoming emotional barriers to communication. Trust forms the foundation of healthy and effective interpersonal interactions. Here are three key aspects of building trust and rapport:
- Active listening and validation: Active listening involves fully engaging with others during communication, paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues, and demonstrating genuine interest in understanding their perspective.
- Honesty and transparency: Honesty and transparency are vital for building trust in communication. Being honest involves expressing oneself truthfully and authentically, without withholding information. Transparency entails sharing relevant information openly and willingly. By consistently practicing honesty and transparency, individuals establish credibility and create an atmosphere of trust.
- Consistency and reliability: Consistency and reliability are crucial for building trust and rapport over time. Consistency refers to maintaining a predictable and dependable communication style, where individuals act in alignment with their words and values. Reliability involves following through on commitments, being punctual, and demonstrating consistency in behavior. When individuals consistently demonstrate trustworthiness and reliability, others feel secure in the relationship, knowing they can rely on them.
(C) Improving Empathy and Perspective-Taking:
Improving empathy and perspective-taking is essential for overcoming emotional barriers to communication. Empathy involves comprehending and experiencing the emotions and viewpoints of others, fostering a sense of shared understanding., while perspective-taking involves considering different viewpoints and understanding diverse experiences. Here are two key aspects of improving empathy and perspective-taking:
- Putting oneself in the other person’s shoes: Putting oneself in the other person’s shoes involves imagining oneself in their position and trying to understand their emotions, thoughts, and experiences. It necessitates putting aside personal biases and preconceptions in order to genuinely empathize with their viewpoint.
- Understanding diverse perspectives: Understanding diverse perspectives involves recognizing that people have different backgrounds, beliefs, and experiences that shape their worldviews. It requires acknowledging that there is no universal “right” or “wrong” perspective, but rather a range of valid viewpoints. By seeking to understand and appreciate diverse perspectives, individuals can broaden their own understanding and overcome biases or assumptions that may hinder effective communication.
Communication Techniques to Overcome Emotional Barriers
1/ Nonviolent communication:
Nonviolent communication, alternatively referred to as compassionate communication, is a method developed by Marshall Rosenberg. It focuses on expressing oneself honestly while also empathetically listening to others. This approach aims to create a non-judgmental and respectful communication environment. It involves using “I” statements to express feelings and needs, actively listening to other’s perspectives, and seeking mutual understanding. Nonviolent communication helps overcome emotional barriers by promoting empathy, understanding, and constructive dialogue.
2/ Assertiveness and active communication:
Assertiveness and active communication involve expressing thoughts, feelings and needs directly and respectfully. It is about clearly and confidently expressing oneself while also actively listening to others. Assertive communication enables individuals to set boundaries, express their opinions, and ask for what they need without being aggressive or passive. By practicing assertiveness and active communication, individuals can overcome emotional barriers by fostering clear and open communication.
3/ Empathetic listening and paraphrasing:
Empathetic listening involves actively listening to others with the intention to understand their emotions, perspectives, and needs. It requires setting aside one’s own judgments or agenda and fully focusing on the speaker. Paraphrasing is a technique used in empathetic listening where individuals restate or summarize what the speaker has said to ensure understanding.
These techniques promote understanding, empathy, and open dialogue, facilitating more meaningful and constructive interactions.
How do emotional barriers affect communication?
The impact of emotional barriers on communication is significant and can restrain the quality, depth, and effectiveness of interpersonal connections. Recognizing the impact of these barriers on communication is essential for fostering open, empathetic, and meaningful communication. Emotional barriers can affect communication in the following ways:
- Misinterpretation of messages: Emotional barriers can lead to the misinterpretation of messages during communication. When individuals are influenced by their emotions, they may filter information through their biases, insecurities, or fears. For example, someone who is experiencing fear may interpret a harmless comment as a personal attack.
- Reduced empathy and understanding: Emotional barriers can diminish empathy and understanding in communication. In instances where individuals find themselves overwhelmed by intense emotions such as anger, resentment, or defensiveness, it can become challenging for them to empathize with others and grasp their viewpoints. This lack of empathy can prevent effective listening and inhibit the ability to connect with others on an emotional level.
- Escalation of conflicts: Emotional barriers can contribute to the rise of conflicts during communication. When individuals are unable to manage their emotions effectively, conflicts can intensify and become more heated. Emotional barriers such as anger, resentment, or pride can prevent individuals from engaging in calm and rational discussions. Instead, arguments can become emotionally charged and reactive, with each party becoming defensive or aggressive.
- Strained relationships: Emotional barriers in communication can strain relationships over time. When emotional barriers persist, they can create a pattern of ineffective communication, and unresolved conflicts. Over time, this can spoil trust and connection between individuals. Strained relationships may experience a lack of open communication, reduced collaboration, and a decreased willingness to engage in honest and vulnerable conversations. Ultimately, emotional barriers can contribute to distance and dissatisfaction in relationships.
- Impacting decision-making processes: Emotional barriers can impair individuals’ ability to make rational decisions, leading to impulsive behavior and poor choices.
Four components of emotion in communication
Understanding the components of emotion can help us navigate and effectively communicate our feelings. Here are the four components of emotion in communication:
1/ Physiological Response: The physiological response component of emotion refers to the physical transformations that take place within our bodies when we encounter an emotion. These changes can include increased heart rate, changes in breathing patterns, muscle tension, sweating, and other bodily sensations.
Related Reading: What are Physiological barriers to communication
2/ Cognitive Appraisal: Cognitive appraisal refers to the mental evaluation or interpretation of a situation that triggers an emotional response. It involves the conscious or unconscious assessment of the meaning and significance of an event or experience. The way we interpret, hold beliefs about and perceive a situation significantly shapes the emotions we encounter.
3/ Subjective Experience: The subjective experience component of emotion pertains to the individual’s personal and internal experience of an emotion. It involves the feelings and sensations we experience when we are in an emotional state. These subjective experiences can vary in intensity, duration, and quality.
4/ Expressive Behavior: Expressive behavior refers to the outward manifestation of emotions through facial expressions, body language, tone of voice, gestures, and other nonverbal cues. It involves how we communicate our emotions to others and how we interpret and respond to the emotional cues of others.
Why emotional communication is important
Emotional communication refers to the expression and understanding of emotions in the process of interpersonal interaction:
Here are the reasons why emotional communication is important:
1/ Connection and Relationship Building: Emotional communication forms the foundation for building strong connections and meaningful relationships. When individuals express their emotions authentically and listen empathetically to others’ emotions, it creates a sense of understanding, trust, and closeness.
2/ Effective Expression of Needs and Desires: Emotions provide important cues about our needs, desires, and values. By effectively communicating emotions, individuals can express their needs and desires more clearly, allowing others to understand and respond to them.
3/ Conflict Resolution: Emotions often arise during conflicts or disagreements. Emotional communication plays a crucial role in resolving conflicts by creating a safe space for individuals to express their emotions, concerns, and perspectives.
4/ Emotional Well-being: Emotional communication contributes to emotional well-being by allowing individuals to express and process their emotions. When emotions are acknowledged and validated through communication, it promotes emotional self-awareness, regulation, and growth.
What are emotional communication barriers in the workplace?
Emotional communication barriers in the workplace refer to obstacles that slow down the effective expression and understanding of emotions among employees and between employees and management. Here are some common emotional communication barriers in the workplace:
1/ Suppression of Emotions: In some workplaces, there is a cultural expectation or pressure to suppress or hide emotions. This can create a barrier to open and authentic communication, as employees may feel the need to hide their true feelings.
2/ Lack of Emotional Intelligence: Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. When individuals lack emotional intelligence, they may struggle to effectively communicate their emotions or empathize with the emotions of their colleagues
3/ Cultural and Language Barriers: In multicultural workplaces, cultural and language differences can present emotional communication barriers. Norms, values, and communication styles vary across cultures, and language barriers may prevent the accurate expression and understanding of emotions. These barriers can contribute to miscommunications in the workplace.
Further Reading: Cultural Barriers of communication definition
4/ Lack of Emotional Support: When individuals do not feel supported or heard in the workplace, it becomes challenging to communicate emotions effectively. A lack of emotional support can result in employees feeling isolated, unvalued, and reluctant to express their emotions.
What is an emotional blockage?
An emotional blockage, also known as an emotional block, refers to a psychological state or condition where an individual experiences difficulty in fully expressing, processing, or experiencing certain emotions. It is a state of emotional resistance or suppression that can impede the natural flow and healthy expression of emotions. Emotional blockages can arise due to various factors, such as past traumas, societal conditioning, or personal beliefs and experiences.
How to overcome emotional blockages
- Identify Triggers: Identify the triggers or underlying causes of your emotional blockages. Reflect on past experiences, traumas, or belief systems that may be contributing to the blockages. Understand how these factors have influenced your emotional responses and patterns.
- Create a Supportive Environment: Surround yourself with a supportive network of friends or like-minded individuals who encourage emotional expression and provide a safe space for you to share your feelings. Open and honest communication within your relationships can help overcome emotional blockages.
- Self-Awareness: Develop self-awareness by acknowledging and recognizing the presence of emotional blockages. Pay attention to your emotions, thoughts, and behavioral patterns to identify areas where you may be experiencing resistance or avoidance.
- Practice Emotional Release: Engage in activities that facilitate emotional release, such as journaling or physical exercise. Allow yourself the freedom to express your emotions openly and without self-judgment.
What are the emotional barriers in the exit barrier?
Emotional barriers in exit barriers refer to the emotional factors that can complicate the process of leaving a particular situation, relationship, or organization. These barriers can arise when individuals face emotional attachments, fears, or uncertainties related to the decision to exit. Emotional barriers in exit barriers can include:
1/ Attachment and Loyalty: Emotional attachments and loyalty to a person, organization, or project can create barriers to leaving. Individuals may feel a sense of loyalty or obligation, making it difficult to detach emotionally and make the necessary exit.
2/ Fear of Change and Unknown: Exiting a familiar situation often involves stepping into the unknown, which can evoke fear and uncertainty. The fear of change, potential risks, or the unfamiliar can act as emotional barriers, causing individuals to hesitate or resist the exit process.
3/ Emotional Investment: If an individual has invested significant time, effort, or emotions into a situation or relationship, it can create emotional barriers. The fear of losing the emotional investment or the sense of identity associated with it can make the exit challenging.
4/ Guilt and Obligation: Feelings of guilt or obligation towards others involved in the situation can be emotional barriers to exit. Individuals may struggle with the guilt of disappointing or hurting others, making it difficult to make the decision to exit.
What are emotional intelligent barriers?
Emotional intelligence barriers refer to factors or obstacles that slow down the development or application of emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence involves the capacity to identify, regulate, and articulate emotions in a proficient manner, both within oneself and in others.
Here are some common emotional intelligence barriers:
1/ Difficulty Recognizing Emotions in Others: Some individuals may find it challenging to accurately perceive and understand the emotions of others. This barrier can prevent effective interpersonal communication and empathy, as they may struggle to pick up on nonverbal cues, facial expressions, or vocal tones that convey emotions.
2/ Lack of Emotional Regulation: Emotional intelligence requires the ability to effectively control and handle one’s own emotions in different circumstances. A barrier arises when individuals struggle to effectively manage or express their emotions in a suitable manner. This may lead to impulsive reactions or difficulty maintaining composure in challenging or stressful situations.
3/ Negative Self-Talk and Self-Criticism: Internal barriers to emotional intelligence include negative self-talk and self-criticism. Individuals who engage in harsh self-judgment or have a negative self-image may struggle to effectively manage their emotions. This can impact their ability to connect with others and engage in healthy emotional interactions.
How do positive emotions become barriers to communication?
Positive emotions can become barriers to communication in various ways. Over-optimism can lead to overlooking challenges or dismissing others’ concerns, while excessive enthusiasm may dominate conversations and disregard balanced input. Ignoring negative feedback due to a focus on maintaining positive emotions can be a perceptual problem that restrains growth and improvement. Minimizing problems and glossing over negative emotions can all prevent open and honest communication.
However, it’s important to note that positive emotions themselves aren’t barriers, but the lack of balance, open-mindedness, and addressing challenges can create communication obstacles. Striving for a balanced approach that embraces both positive and negative emotions and encourages respectful dialogue helps overcome these barriers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is an example of an emotional barrier?
Ans: An example of an emotional barrier is when fear and anxiety prevent someone from expressing their thoughts or feelings openly in a conversation or discussion. Overcoming this barrier requires addressing and managing the underlying fears and anxieties and creating a supportive and non-judgmental communication environment.
Q2) What is an example of emotional communication?
Ans: An example of emotional communication is when two individuals engage in a conversation where they openly express their emotions and connect on a deep level. This type of communication involves the genuine sharing of feelings, thoughts, and experiences in a vulnerable and authentic manner.
Q3) What is emotional communication?
Ans: Emotional communication is the process of conveying and understanding information, thoughts, and feelings through the expression of emotions. It involves more than just using words, as it encompasses the use of nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions, body language, tone of voice, and gestures, to effectively convey emotions and intentions.
Q4) What are the emotional barriers to learning?
Ans: Emotional barriers to learning are internal factors that can create challenges and obstacles in the learning process, potentially limiting educational progress. These barriers arise from individuals’ emotional experiences and can significantly affect their ability to actively engage, comprehend information, and retain knowledge.
Q5) Is stress an emotional barrier?
Ans: Yes, stress can be considered an emotional barrier. When individuals experience high levels of stress, it can impact their ability to effectively engage in communication, learning, and other tasks.
Q6) Mostly emotional barriers are faced by?
Ans: Emotional barriers to communication can be faced by anyone who experiences emotions and engages in interpersonal communication.



