Communication is a cornerstone of human interaction and shapes our connections, expressions, and understanding. In this blog, we explore the four fundamental types that influence our daily interactions.
TL;DR
Communication involves sharing thoughts, emotions, and information using words, expressions, and non-verbal cues.
There are 4 main types of communication: verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual.
Verbal communication uses spoken words, including face-to-face talks, phone calls, and public speaking.
Non-verbal communication includes body movements, eye contact, and personal space.
Written communication uses text, symbols, and graphics, providing a record and asynchronous communication.
Visual communication uses images, videos, and graphics to simplify complex ideas.
What are the types of communication with examples?
The four main types of communication are verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual communication. Each type plays a crucial role in how we interact and convey information in various situations. Let’s explore each type in detail:
1/ Verbal Communication:
Verbal communication is the process of conveying information, expressing ideas, and sharing emotions through the use of spoken words. It involves using language to convey messages between individuals or groups. This form of communication is an essential aspect of human interaction and is widely used in both personal and professional environments.
One significant importance of verbal communication is that it can be direct, allowing for real-time feedback and clarification, making it a dynamic and interactive mode of expression. It also incorporates elements such as tone of voice, volume, and intonation, which add meaning and emotional variations to the messages conveyed. Additionally, written and oral communication are two main components of verbal communication.
Types of Verbal Communication:
1/ Face-to-Face Communication: Face-to-face communication occurs when individuals interact in person, enabling immediate and direct interaction. There are several benefits of face-to-face communication such as, It allows for a deeper level of engagement, as participants can observe facial expressions and other non-verbal cues, enhancing understanding. Face-to-face communication is common in casual conversations, personal meetings, and various social settings.
2/ Phone Calls and Voicemails: Phone calls involve verbal communication over the telephone, allowing individuals to interact remotely. While not as expressive as face-to-face communication, phone calls still provide an opportunity for immediate responses and clear dialogue. Voicemails, on the other hand, allow individuals to leave recorded oral messages when the recipient is unavailable, facilitating communication even when direct interaction is not possible.
3/ Public Speaking and Presentations: Public speaking and presentations involve conveying information, ideas, or opinions to a larger audience. This form of verbal communication often takes place in professional or educational settings, where a speaker addresses a group of people.
4/ Meetings and Discussions: Meetings and discussions are formal or informal gatherings where participants exchange information, share ideas, and make decisions. Verbal communication plays a central role in these settings, as participants voice their thoughts, provide input, and collaborate to achieve common goals.
Check out our detailed guide on: Verbal communication definition and examples
2/ Non-verbal communication:
Non-verbal communication includes the transmission of information and intentions through means other than spoken or written words. It includes various cues and signals conveyed through, eye contact, personal space, and touch. According to psychologist Dr. Albert Mehrabian’s extensive research a significant 93% of our daily communication occurs through nonverbal means.
Therefore, recognizing the benefits of non-verbal communication is essential as it plays a vital role in human interaction by complementing and enhancing verbal communication. It provides additional layers of meaning and context to the spoken words, making it easier to understand the true intent behind the message.
Types of Non-Verbal Communication:
1/ Body Language and Gestures: Body language entails utilizing physical movements and postures to express messages. It includes gestures such as waving, pointing, and nodding, which can express agreement or disagreement. Additionally, body language includes stances, such as crossing arms (indicating defensiveness) or leaning in (indicating interest and engagement). Understanding body language can help interpret someone’s feelings and attitudes, even when they are not explicitly stating them.
2/ Facial Expressions: Facial expressions are a powerful form of non-verbal communication, reflecting emotions and reactions. Smiles frowns and Raised eyebrows, all convey distinct feelings like happiness, sadness, or surprise. Facial expressions can significantly impact how a message is perceived, as they often reveal the speaker’s genuine emotional state.
3/ Eye Contact: Eye contact is the fundamental act of directly looking into someone’s eyes while engaged in a conversation. It is a crucial aspect of non-verbal communication as it signals attentiveness, interest, and sincerity. Appropriate eye contact fosters connection and trust while avoiding eye contact might be interpreted as discomfort or lack of confidence. However, cultural norms can influence the significance of eye contact, and its interpretation may vary across different societies.
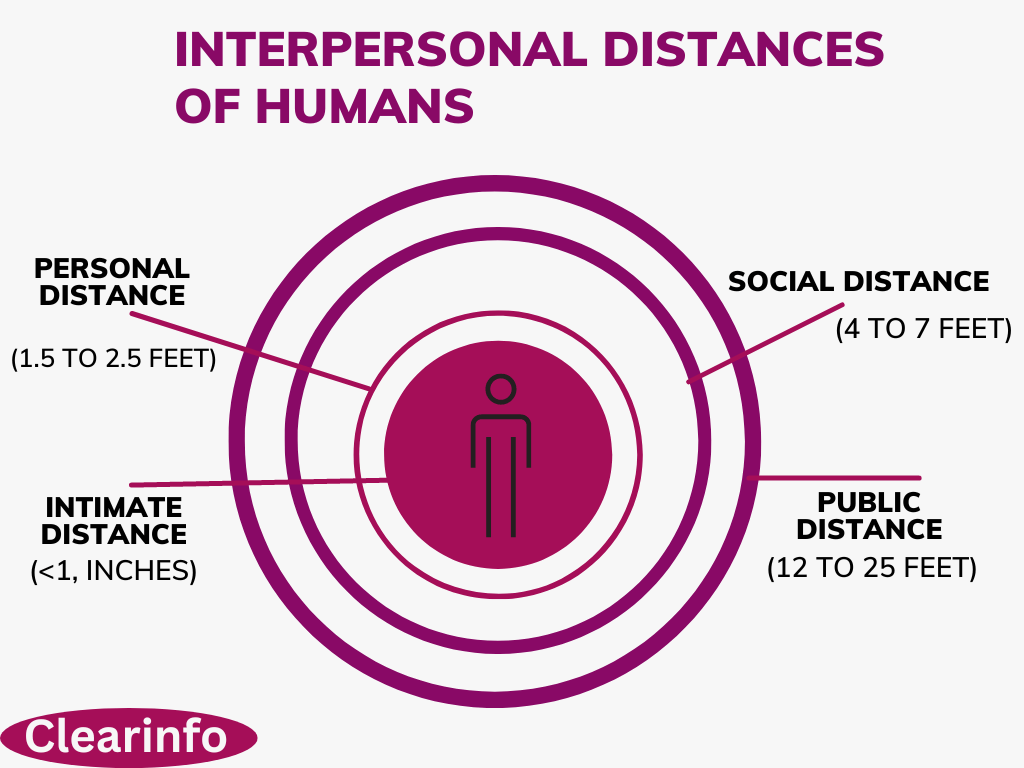
4/ Proxemics (Personal Space): Proxemics refers to the use and interpretation of personal space during interactions. Different cultures have varying norms about personal space, and individuals may feel comfortable with different degrees of proximity.
5/ Touch and Haptics: Touch, or haptics, is another form of non-verbal communication that is capable of conveying a wide variety of emotions and intentions. A comforting pat on the back, a firm handshake, or a gentle hug can communicate support or affection. However, it is crucial to consider cultural norms and personal preferences, as not everyone may be comfortable with touch during communication.
Further Reading:
3/ Written communication:
Written communication entails the act of conveying information and messages through the use of written words. It involves using text, symbols, or graphics to convey information and can be in the form of physical or digital documents. Written communication offers several advantages, including the ability to provide a permanent record of the message, making it easy to reference the written information later.
It allows for more thoughtful and structured expression as writers can carefully choose their words and organize their thoughts. Additionally, written communication enables asynchronous communication, meaning recipients can read and respond at their convenience, without the need for real-time interaction.
Types of Written Communication:
1/ Emails and Memos: Emails and memos are common forms of written communication used in business and professional environments. Emails are electronic messages exchanged via email platforms, allowing for quick and efficient communication between individuals and groups. Memos, on the other hand, are internal communications within an organization, typically used to inform employees about specific updates, policies, or announcements. Both emails and memos are effective for conveying detailed information to a targeted audience.
2/ Letters and Postcards: Letters and postcards are traditional written communication methods often used for personal and formal interaction. Letters are more detailed and formal, frequently used for professional purposes or resolving issues. Postcards, on the other hand, are concise messages on postcard-sized paper, often used for sharing brief greetings.
3/ Reports and Proposals: Reports and proposals are written documents commonly used in business and academic settings. Reports present information, findings, or data in a structured manner, aiming to inform or analyze a specific topic. Proposals, on the other hand, outline plans, and projects, or seek approval or funding from relevant stakeholders.
4/ Text Messages and Instant Messaging: Text messages and instant messaging are written communication methods facilitated by mobile devices and messaging apps. They allow for quick and real-time interactions between individuals, making them ideal for informal and casual conversations. Text messages are often used for personal communications, while instant messaging platforms cater to both personal and professional conversations.
Check out our detailed guide on: What is meant by written communication
4/ Visual communication:
Visual communication is the transmission of information and messages through visual elements, such as images, graphics, and videos. It plays a crucial role in modern communication due to its effectiveness in conveying complex concepts quickly and engagingly. As humans are highly responsive to visual stimuli, visual communication captures attention more effectively than pure text-based communication.
It simplifies information, making it easier to understand, remember, and share. Visual communication is widely used in various fields, including marketing, journalism, and business, to enhance understanding and overall communication impact.
Interesting Fact: Studies indicate that individuals typically retain approximately 20 percent of what they read and merely ten percent of what they hear. Conversely, these studies have revealed a remarkable 80 percent retention rate for what people see and do.(Source)
Types of Visual Communication:
1/ Infographics and Data Visualizations: Infographics and data visualizations showcase detailed data or statistics in a visually attractive and easily understandable format through graphical representations. They often include charts, graphs, icons, and illustrations to convey information concisely. Infographics are commonly used in reports, and presentations to help readers grasp key insights and trends at a glance.
2/ Charts and Graphs: Charts and graphs are visual tools used to illustrate numerical data and relationships between variables. Line graphs, bar charts, pie charts, and scatter plots are examples of commonly used visual aids for presenting quantitative data. These visuals allow viewers to analyze trends, patterns, and comparisons in data quickly and efficiently.
3/ Presentations with Visual Aids: Visual aids are an integral part of presentations, especially for business and educational purposes. Using slides with images, diagrams, and bullet points, improves the audience’s understanding and memory of the presented content. Visual aids provide visual reinforcement to the speaker’s verbal message, making the presentation more engaging and impactful.
4/ Photographs and Videos: Photographs and videos are powerful tools for visual communication, capturing real-life scenes, events, and emotions. They are widely used in marketing, storytelling, and journalism to evoke emotions and convey messages effectively.
Related Reading:
Why are different types of communication important?
Different types of communication are important because they serve specific purposes and are suitable for various situations.
- Verbal Communication: It allows us to exchange information and ideas through spoken words, helping build relationships and resolve conflicts effectively.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Non-verbal cues, like gestures, hand movement, and eye contact, convey emotions and add depth to communication beyond spoken words.
- Written Communication: It provides a clear and permanent record of information, making it ideal for formal correspondence, reports, and sharing detailed content.
- Visual Communication: Visual aids like infographics, diagrams, and videos simplify complex information, making it more accessible and improving retention.
Overall, by using different types of communication, we can connect with others, share knowledge, and convey messages more effectively, enriching our personal and professional interactions.
Which type of communication is best
The effectiveness of a communication type depends on the specific context, audience, and communication goals. Each type of communication (verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual) has its strengths and advantages, making it best suited for particular situations.
The “best” type of communication depends on the specific communication needs and objectives. For example, verbal communication may be best in face-to-face interactions or urgent situations where immediate feedback is essential. On the other hand, written communication might be preferred for detailed documentation and sharing information that requires careful consideration of words.
To determine the most effective communication type, it’s crucial to consider the context, the audience’s preferences and needs, the message’s complexity, and the desired outcome. Therefore, for communication to be successful it is important to use a combination of communication types and adapt their approach based on the specific circumstances to achieve the best results.
Types of Communication Skills
Communication skills refer to the capabilities that enable us to proficiently express and understand information when interacting with others. There are various types of communication skills:
1/ Verbal Communication Skills: Verbal communication skills revolve around using spoken words to express messages and ideas. These skills include speaking clearly and confidently, using appropriate tone and volume, and articulating thoughts effectively. Active listening is also essential for understanding others and responding appropriately in conversations.
2/ Non-Verbal Communication Skills: Non-verbal communication skills are about using body language and facial expressions to complement spoken words. These skills help convey emotions, intentions, and attitudes. Maintaining eye contact, using gestures, and having an open body posture are vital components of effective non-verbal communication.
3/ Written Communication Skills: Written communication skills focus on expressing thoughts and information through written words. This includes crafting well-structured and logical sentences, using proper grammar and punctuation, and tailoring messages to the audience. Written communication is crucial for emails, reports, and other written forms of interaction.
4/ Listening Skills: Listening skills require actively focusing on others’ spoken words and understanding their viewpoints. Effective listeners avoid interrupting, show interest through nods and responses, and ask clarifying questions to ensure understanding.
5/ Interpersonal Skills: Interpersonal skills involve how we interact and connect with others on a personal level. These skills include emotional intelligence, and the ability to build rapport and positive relationships with others.
Types of communication styles
Communication styles refer to the distinct ways individuals express themselves and interact with others during communication. The main types of communication styles are
1/ Assertive Communication Style: Individuals with an assertive communication style confidently express their thoughts, feelings, and needs while respecting the rights and opinions of others. They are direct and clear in their communication, which helps them stand up for themselves without being overly aggressive.
2/ Passive Communication Style: People with a passive communication style tend to avoid conflicts and disagreements. They may struggle to express their thoughts or feelings, leading them to comply with others’ opinions or decisions even when they disagree. Passive communicators may find it challenging to assert their needs and may end up feeling unheard or taken advantage of in some situations.
3/ Aggressive Communication Style: Those with an aggressive communication style are forceful in expressing their thoughts and feelings, often without considering the feelings or needs of others. They may use harsh language, and interrupt others to get their point across. This style of communication can lead to tense relationships and increase conflicts.
4/ Submissive Communication Style: A submissive communicator tends to avoid expressing their own needs and desires, often agreeing with others to maintain peace or avoid conflict. They may have difficulty saying no and tend to be accommodating to others’ requests, even when it is not in their best interest.
How do we differentiate the types of communication in relation to mode, context, and style?
Differentiating the types of communication in relation to mode and context involves understanding the various ways information is conveyed, the specific environment or situations in which communication occurs, and the manner or approach used to express messages. Let’s explore each aspect:
(A) Mode of Communication:
The mode of communication refers to the specific way or channel through which information is conveyed. It includes the practical means of transmitting the message. Different modes of communication include verbal, non-verbal, written, visual, and digital communication.
- Verbal Communication: Using spoken or written words to convey messages.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Conveying information through body language, facial expressions, gestures, etc.
- Written Communication: Expressing ideas and information in written form, such as emails, letters, and reports.
- Visual Communication: Conveying information through visual elements like images, charts, graphs, etc.
- Digital Communication: Communication facilitated through electronic devices and online platforms.
(B) Context of Communication:
The context of communication refers to the specific circumstances or environment in which communication takes place. It influences the way messages are delivered and received. Different contexts of communication include interpersonal, group, mass, intrapersonal, public, cross-cultural, and business communication.
- Interpersonal Communication: Communication between individuals during face-to-face interactions or small group discussions.
- Group Communication: Communication that occurs within small or large groups of people.
- Mass Communication: Spreading of information to a large audience through mass media channels like TV, radio, and social media.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Communication that occurs within one’s mind, involving self-reflection and thoughts.
- Public Communication: Addressing a larger audience through public speaking or presentations.
- Cross-Cultural Communication: Communication involves individuals from different cultural backgrounds interacting with each other.
- Business Communication: Communication within an organization among employees and with external stakeholders.
By understanding the distinctions between mode and context of communication, individuals can adapt their communication strategies appropriately to different situations and effectively convey their messages while building positive and constructive relationships with others.
Difference between human communication and other types of communication
The following comparison explores seven key differences between human communication and other types, emphasizing the unique qualities of human interactions.
Aspect | Human Communication | Other Types of Communication |
Participants | Involve human beings as both senders and receivers. | May involve machines or devices as senders or receivers. |
Complexity | Utilizes complex and diverse languages. | Other types may be more straightforward and limited in expression. |
Emotional Expression | Emotions are often conveyed through expressions. | In other types, emotions are not typically expressed. |
Adaptability | Can adapt communication based on social cues. | Other types may have fixed patterns and responses. |
Feedback | Real-time feedback is common in face-to-face interactions. | In other types of communication, feedback may be limited or delayed. |
Non-Verbal Cues | Relies on extensive non-verbal cues for expression. | In other types of communication, non-verbal cues may not play a role. |
Cultural Influence | Influenced by cultural norms, customs, and values. | Other types may not be influenced by culture or context. |
Difference between models of communication and types of communication
Here are seven key differences between communication models and types, exploring both theoretical and practical aspects of effective communication.
Aspect | Models of Communication | Types of Communication |
Definition | Represent abstract frameworks of the communication process. | Categorize communication based on forms or contexts. |
Purpose | Describe how communication works in theoretical terms. | Classify communication based on specific characteristics. |
Focus | Emphasize the components and stages of communication. | Focus on the ways or modes of expression. |
Application | Used for research, analysis, and understanding of communication. | Used for practical communication purposes. |
Examples | Shannon-Weaver Model, Transactional Model, etc. | Verbal, non-verbal, written, mass communication, etc. |
Nature | Theoretical and abstract representation of communication. | Concrete classification of communication types. |
Use in Practice | Offers insights into the communication process. | Guides the selection of appropriate communication methods. |
What are formal types of communication?
Formal types of communication refer to official or structured methods of exchanging information within an organizational setting. These types of communication follow established rules, and protocols, and they are typically used for official business. Formal communication is essential in maintaining order, clarity, and consistency within an organization, as it helps convey important information accurately and efficiently. The main purpose of formal communication is to ensure that crucial decisions and announcements are communicated effectively.
Here are some common examples of formal types of communication:
- Formal Meetings: Scheduled and structured meetings where participants follow a set agenda to discuss important matters, make decisions, and address issues.
- Memos and Reports: Written documents used to convey information, instructions, or updates within an organization. Memos are usually brief and used for internal communication, while reports are more detailed and may be distributed externally.
- Official Letters and Emails: Written communications used for formal interaction with clients, customers, partners, or government agencies.
- Policies and Procedures: Formal documentation outlining rules, guidelines, and processes within an organization.
- Annual Reports: Comprehensive reports detailing an organization’s financial performance, achievements, and future plans.
Check out our detailed guide on: What is meant by formal communication
Different types of business communication
Different types of business communication refer to the various methods and channels through which information is exchanged within a business or organizational context. Effective business communication is vital for seamless operations and maintaining positive relationships with employees, customers, and other stakeholders. Here are some key types of business communication:
Internal Communication:
- Upward Communication: Flow of information from lower-level employees to higher-level management, such as sharing feedback, suggestions, and progress updates.
- Downward Communication: Flow of information from higher-level management to lower-level employees, including directives, policies, and organizational goals.
- Horizontal Communication: Exchange of information between colleagues or departments at the same hierarchical level, facilitating collaboration and coordination.
External Communication:
- Business to Customer (B2C): Communication between a business and its customers, including marketing messages, customer support, and product/service information.
- Business to Business (B2B): Communication between two or more businesses, such as negotiating contracts, placing orders, and collaborating on projects.
- Business to Supplier (B2S): Communication between a business and its suppliers, involving orders, shipments, and supply chain management.
Formal Communication:
- Memos and Reports: Written communication used for formal documentation, policies, and performance evaluations.
- Official Letters and Emails: Official written communication with clients, customers, and external stakeholders.
- Policies and Procedures: Formal documentation outlining rules, guidelines, and processes within the organization.
Informal Communication:
- Watercooler Talk: Informal conversations that occur between colleagues during breaks or informal gatherings.
- Grapevine Communication: Informal communication that spreads through social networks within the organization.
What types of communication are commonly used in the workplace
In the workplace, various types of communication are commonly used to facilitate daily operations, ensure effective teamwork, and maintain a balanced work environment. These communication methods help convey information, share ideas, and build relationships among employees and external stakeholders. Here are some of the most commonly used types of communication in the workplace:
1/ Verbal Communication:
- Face-to-Face Conversations: Direct interaction between individuals for discussions, feedback, and problem-solving.
- Phone Calls: Real-time communication for quick updates or resolving urgent matters.
- Team Meetings: Regular gatherings of team members to discuss progress, plans, and project-related issues.
- Presentations: Delivering information or proposals to a group using visual aids.
2/ Written Communication:
- Emails: Common mode for official communication, sharing information, and exchanging documents.
- Reports and Memos: Formal written documents used for documentation, updates, and policies.
- Letters: Written communication for external correspondence with clients, partners, or stakeholders.
- Text Messages: Quick and informal messages for brief communication.
3/ Non-Verbal Communication:
- Body Language: Conveying emotions, attitudes, and reactions through facial expressions and gestures.
- Eye Contact: Indicating attentiveness, interest, or authenticity during conversations.
4/ Digital Communication:
- Instant Messaging: Real-time text communication for quick queries and team coordination.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings with audio and video capabilities for remote collaboration.
- Social Media: Engaging with customers, sharing updates, and promoting the organization.
5/ Formal Communication:
- Policies and Procedures: Formal documents outlining rules and guidelines for employees.
- Official Announcements: Communicating important updates, events, or changes in the organization.
6/ Informal Communication:
- Watercooler Conversations: Informal chats among colleagues during breaks.
- Grapevine Communication: Informal sharing of information through informal networks.
7/ Customer Communication:
- Customer Support: Addressing customer inquiries, and complaints, and resolving issues.
- Sales Communication: Interacting with potential customers, providing product information, and closing deals.
What are the different levels of communication?
The different levels of communication refer to the hierarchical structure or scope of communication within an organization or social setting. The common levels of communication include
1/ Intrapersonal Communication:
Intrapersonal communication refers to internal communication happening within an individual’s mind. It involves self-talk and the processing of thoughts, emotions, and ideas. This level of communication is essential for self-reflection, decision-making, and understanding one’s own feelings and motivations.
2/ Interpersonal Communication:
Interpersonal communication happens when two or more individuals interact directly, either face-to-face or virtually. It entails sharing information and ideas and is essential for fostering relationships, resolving conflicts, and expressing thoughts and feelings.
3/ Small Group Communication:
Small group communication involves interactions among a limited number of individuals (usually 3 to 12 people) who come together for a specific purpose or task. This level of communication facilitates collaboration, problem-solving, and decision-making within the group.
4/ Public Communication:
Public communication is communication that occurs when an individual or a few individuals address a larger audience. Examples include public speaking, delivering presentations, and addressing an audience during conferences or events. This level of communication requires effective message delivery to engage and inform the audience.
5/ Organizational Communication:
Organizational communication takes place within an organization, involving various hierarchical levels, departments, and teams. It includes communication between employees, managers, and executives and is essential for coordinating activities and ensuring smooth operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1/ What are the 6 types of communication?
Ans: The six types of communication are verbal communication (spoken or written words), non-verbal communication (body language and gestures), written communication (emails, letters), visual communication (images, charts), digital communication (online platforms), and interpersonal communication (face-to-face interactions). Each type serves a specific purpose and is essential for effective communication in various contexts.
2/ What are the 3 main types of communication?
Ans: The three main types of communication are verbal communication, non-verbal communication, and written communication. They play crucial roles in personal and professional interactions, facilitating effective understanding and exchange of information.
3/ What are the 4 main communication methods?
Ans: The four main communication methods are verbal communication (spoken words), written communication (emails, memos), non-verbal communication (body language), and visual communication (charts, images). They complement each other to ensure effective information exchange in various interactions.
4/ What is the most common type of communication?
Ans: The most common type of communication includes verbal communication (spoken and written). It facilitates effective exchanges of information through spoken words.
5/ What is 3-way communication?
Ans: Three-way communication, also known as triangular communication, is a form of communication that involves three participants or parties engaging in a conversation. Unlike traditional two-way communication, where information flows between two individuals, three-way communication adds a third person or entity to the interaction.



