Elements of Communication definition
“Elements of communication is the process of transmitting information from a sender to a receiver through a communication channel, with various elements involved in encoding and decoding the message.” Claude E. Shannon and Warren Weaver:
In their book “The Mathematical Theory of Communication”
Elements of the Communication Process
1) Sender: The sender is a fundamental element in the communication process. The communication is initiated by the sender who creates a message or information for sharing with others.
The sender’s role is to effectively encode their thoughts or information into a message that can be transmitted through a chosen communication channel to reach the intended recipient(s). The sender plays a crucial role in ensuring that the message is clear, purposeful, and appropriately customized to the audience.
The elements of the sender in communication include:
- Intention
- Knowledge
- Attitudes and Beliefs
- Communication Skills
- Non-verbal Cues
- Emotional State
- Cultural Background
- Perceptions and Assumptions
These elements shape how the sender formulates and delivers their message, impacting effective communication.
These elements shape how the sender formulates and delivers their message, impacting effective communication.
2) Encoding: Encoding is a process where the sender converts their messages into a format that can be transmitted to the receiver. It involves transforming concepts and mental images into language, symbols, or signals that the recipient can understand. The process of encoding is where the sender puts their thoughts into a structured and communicable form, allowing for effective transmission.
3) Message: The message is the informational content that the sender aims to communicate to the receiver. It serves as the core of the communication process, carrying the purpose and meaning that the sender wants to communicate. The role of the message is to effectively transfer thoughts, concepts, instructions, or emotions from the sender to the receiver, aiming to create mutual understanding and facilitate a specific response or action.
4) Channel: Within the framework of communication, channels serve as the pathways that help messages move from the sender to the receiver. These channels can be verbal or non-verbal and can include one-to-one conversations, voice calls, emails, business reports, social media, video conferences, and more. Each channel has its unique impact on the communication process, influencing factors such as clarity, and the emotional connection between the sender and the receiver.
Channels in the communication process are divided into three broad categories:
1. Oral
- In oral communication, the sender directly interacts with the receiver in a face-to-face conversation.
- For example, a sales executive directly deals with customers, allowing the sender greater control over the interaction.
=>Check out our detailed article on the merits and demerits of oral communication.
2. Written
- Messages are also transmitted in written format between sender and receiver.
- For example, letters, memos, business communication reports, emails, notices, manuals, etc.
=> Check out our detailed article on the merits and demerits of written communication.
3. Audio/Video: The audio channel involves video tapes, video conferences, video chats, etc.
5) Receiver: The receiver is a critical component of the communication process. The receiver is responsible for receiving and processing the message sent by the sender. The role of the receiver is to understand, analyze, and, where necessary, respond to the message in a way that aligns with the sender’s intent. Effective communication relies on the receiver’s ability to decode the message accurately and provide feedback or take necessary actions.
6) Decoding: Decoding is the process in the communication cycle where the receiver interprets and understands the message sent by the sender. This stage involves the receiver translating the encoded message (originally formulated by the sender) into their understanding and making sense of the information. Decoding is critical because it determines whether the intended message is accurately received or if misinterpretation occurs.
7) Response: The response element refers to the immediate reaction or action taken by the receiver based on the message received. It is the direct behavioral or verbal reply to the sender’s communication. The response can indicate whether the message was received, understood, and acted upon, but it may not necessarily provide in-depth insights or constructive criticism.
8) Feedback: Feedback in communication refers to the receiver’s response to the sender’s message. It gives the sender useful insights into how the message was received, understood, and explained. Feedback serves as a crucial tool for improving the effectiveness of future communication. It helps the sender evaluate the success of their message, adjust their approach if necessary, and ensure that the intended message aligns with the receiver’s interpretation.
Why is feedback important in communication?
-
- Feedback allows the sender to collect information about the message from the receiver.
-
- It completes the communication process as the sender and receiver interact with each other.
-
- Depending on positive or negative feedback from the receiver is a good way to measure the effectiveness of communication and make future improvements.
-
- Feedback helps in improving employee and management relations as it creates a congenial atmosphere in the workspace.
Must Read: What is Feedback In Communication: Examples & Importance
9) Noise: Communication noise means any disturbance or interruption that might happen while communicating, hampering the accurate transmission and reception of a message. Several types of communication noise can affect the clarity and effectiveness of communication.
Some common types of communication noise include:
1. Semantic Noise: This type of noise occurs when words and symbols used in communication are not understood in the same way by the sender and receiver.
2. Environmental Noise: Environmental noise includes any external factors that interfere with communication, such as loud background noises or physical barriers that disturb the communication process.
3. Psychological Noise: Psychological noise relates to the mental and emotional state of both the sender and receiver. It can include stress or emotional reactions that impact the ability to process and understand the message.
4. Physical Noise: Physical noise refers to tangible obstructions, such as a poor-quality phone line or written text that is difficult to read.
Related Reading: Sender and Receiver oriented barriers to communication
Example of elements in communication with diagram
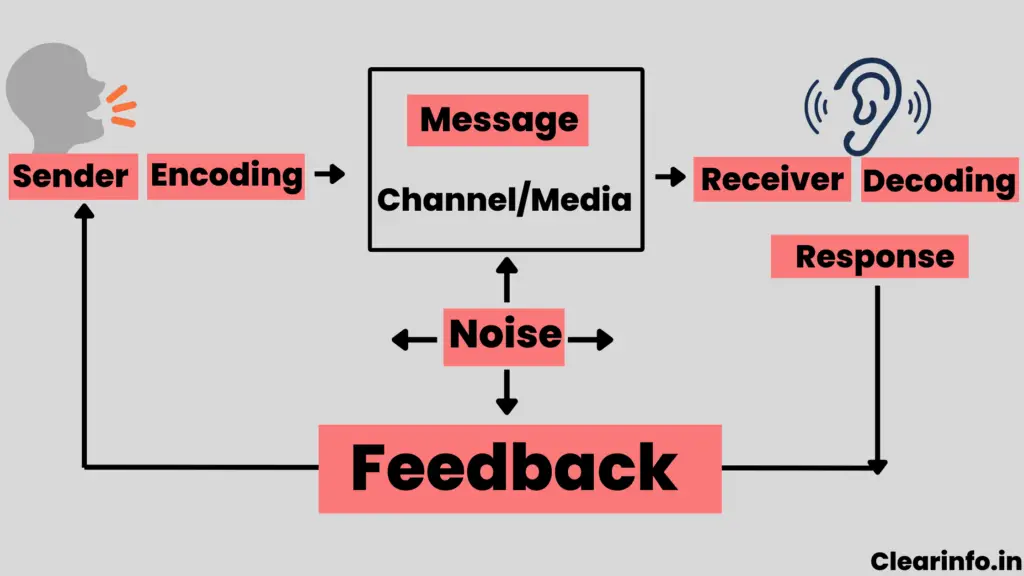
Importance of elements of communication
The elements of communication are fundamental components that collectively contribute to the success and effectiveness of the communication process. Each element fulfills a distinctive and crucial role in enabling the transfer of information among individuals or groups. Here is the importance of these elements:
1/ Effective Message Delivery: The clarity and accuracy of the message are essential for successful communication. The sender’s ability to encode the message appropriately ensures that the intended information is conveyed clearly and without ambiguity to the receiver.
2/ Building Relationships: Effective communication establishes the cornerstone for building strong relationships, in both personal and professional environments. When messages are conveyed accurately and understood well, it fosters trust and mutual understanding between individuals or groups.
3/ Feedback and Confirmation: Feedback from the receiver allows the sender to confirm whether the message was received and understood as intended. It helps in identifying any misunderstandings and provides an opportunity for clarification and improvement.
4/ Problem-Solving: Clear communication facilitates problem-solving by ensuring that instructions, suggestions, or ideas are effectively transmitted and comprehended, leading to better outcomes.
5/ Enhancing Collaboration: Proper communication enhances collaboration and teamwork. When messages are delivered effectively, it promotes open communication and encourages individuals to share ideas, opinions, and feedback.
How elements of the communication process are used for the marketing communication process?
Businesses and organizations utilize communication processes to effectively convey their marketing messages to their intended audience. Subsequently, the consumer responds to these messages by providing feedback and expressing their likes or dislikes towards the products or services being offered.
The process begins with the organization, acting as the sender, formulating a marketing message specifically tailored for their target audience. This message is then converted into understandable symbols, a process known as encoding. These symbols are closely aligned with the marketing messages developed by the organization.
The encoded message is transmitted to the target consumer through a channel or medium. This enables organizations to effectively deliver their marketing message to potential customers. The medium used can be direct, such as sales executives making phone calls to prospects, or indirect, utilizing various forms of media like newspapers, magazines, brochures, television, and radio.
The next stage involves the consumer’s response to the organization’s message. This feedback stage provides the organization with valuable insights regarding the perception of its product or service directly from consumers. Feedback can be positive or negative, depending on how the consumers perceive the product.
The process concludes with the element of “Noise.” In this context, noise refers to cultural differences that exist between the targeted region and the organization’s marketing message. Such differences can hinder the acceptance of the product in the market, leading to lower levels of success.
Explanation of communication cycle with diagram
- The communication cycle involves different elements working together to transmit a message.
- It starts with a sender acting as the source, encoding information into words or pictures.
- The encoded information forms a message transmitted through a channel to the receiver.
- The receiver decodes the information and responds with a reply, action, or inaction.
- Feedback from the receiver completes the stages of the communication cycle.
Communication cycle diagram
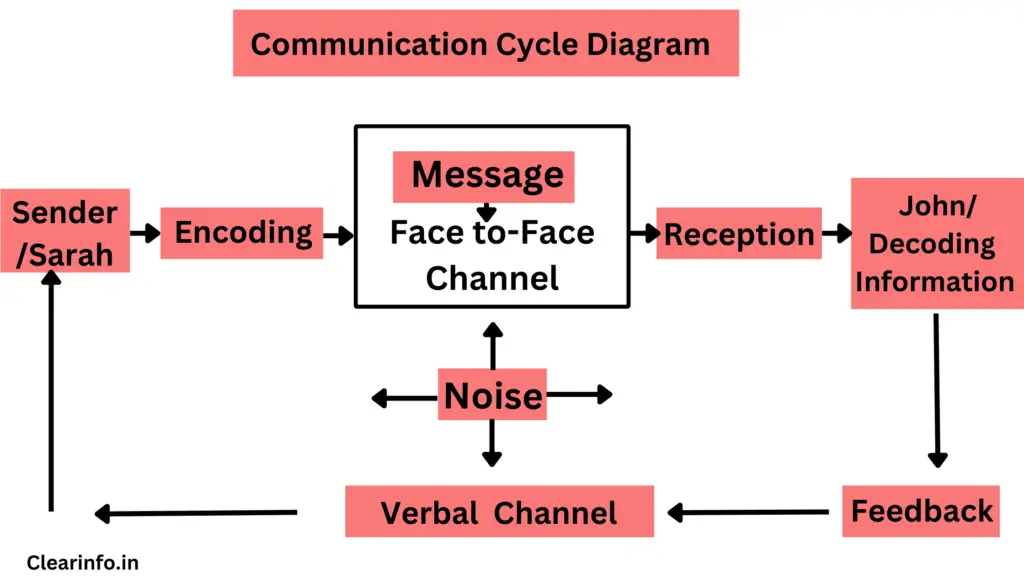
Communication cycle example
The communication cycle starts with the sender and ends with the receiver. Similarly, the above diagram shown can be explained with the following example:
- Sender: Sarah wants to share information about an upcoming project with her colleague, John.
- Encoding: Sarah processes the information in her mind and translates it into a message using words, tone of voice, and body language.
- Message: Sarah verbally communicates the details of the project to John, explaining its objectives, timeline, and tasks involved.
- Channel: Sarah delivers the message through a face-to-face conversation with John.
- Reception: John receives the message, paying attention to Sarah’s words, tone of voice, and nonverbal cues.
- Decoding: John mentally processes the message, interpreting its meaning based on his own knowledge and experiences.
- Feedback: John responds to Sarah, asking clarifying questions or providing his thoughts and suggestions on the project.
- Channel: John conveys his feedback through verbal communication, continuing the conversation.
- Reception: Sarah receives John’s feedback, paying attention to his words, tone, and nonverbal cues.
- Decoding: Sarah mentally processes John’s feedback, understanding his perspective and incorporating his suggestions, if applicable.
- Response: Sarah replies to John’s feedback, addressing any queries or concerns and discussing further steps.
Feedback elements of the communication cycle:
In the communication cycle, the element of feedback refers to the receiver’s response or reaction to the message sent by the sender. Here are the key elements of feedback in the communication cycle:
- Receiver’s Response: Feedback involves the receiver providing a response or reaction to the message they have received.
- Understanding: Feedback indicates whether the receiver has understood the message correctly.
- Clarity: If the receiver provides feedback that they found the message unclear or confusing, it prompts the sender to reconsider their communication approach and improve the clarity of the message.
- Confirmation: Positive feedback or confirmation from the recipient indicates successful reception and comprehension of the message.
- Questions and Queries: Feedback can include questions or queries from the receiver seeking clarification or more information.
- Action or Response: In certain situations, feedback may involve the receiver taking specific actions or responding to the message in some way, indicating engagement with the communication.
- Improvement and Adaptation: Feedback helps the sender to improve future communication by learning from the receiver’s response.
Types of the Communication Cycle
There are several types of communication cycles that are commonly recognized in the field of communication studies. Here are brief descriptions of some of the key types:
1/ Linear Communication Cycle: This is a basic communication model that involves a one-way flow of communication, starting from the sender and ending with the receiver.
2/ Interactive Communication Cycle: This type of communication cycle incorporates feedback and interaction between the sender and receiver. It recognizes that communication is a two-way process, where the receiver’s feedback influences subsequent messages from the sender, creating a back-and-forth exchange.
3/ Transactional Communication Cycle: This cycle emphasizes the continuous nature of communication. In this model, communication is seen as a dynamic and ongoing process where both the sender and receiver play active roles. It highlights that both parties are constantly sending and receiving messages, influencing and being influenced by each other.
4/ Organizational Communication Cycle: This communication cycle focuses on communication within organizations. It includes various levels of communication, including three main directions, upward communication (from lower authority subordinates to higher authority superiors), downward communication (from higher authority superiors to lower authority subordinates), and horizontal communication (between colleagues or departments). It recognizes the formal and informal channels of communication within an organizational structure.
What is the Communication Process?
Communication is the exchange of information between individuals through a sender-receiver model. The sender transmits ideas, opinions, or facts to the receiver, who responds with feedback.
This interactive exchange allows understanding and engagement with each other’s perspectives. The communication process is vital for coordination, teamwork, and relationship building in business.
Elements in the communication cycle include sender, receiver, message, channel, encoding, decoding, feedback, response, and noise.
Sender-receiver communication in a company occurs orally (meetings, calls) and in writing (reports, emails). Communication may involve more than two parties, with multiple groups participating in the process.
Check out our detailed guide on: What is Communication Process: Examples, Stages & Types
Example of the communication process
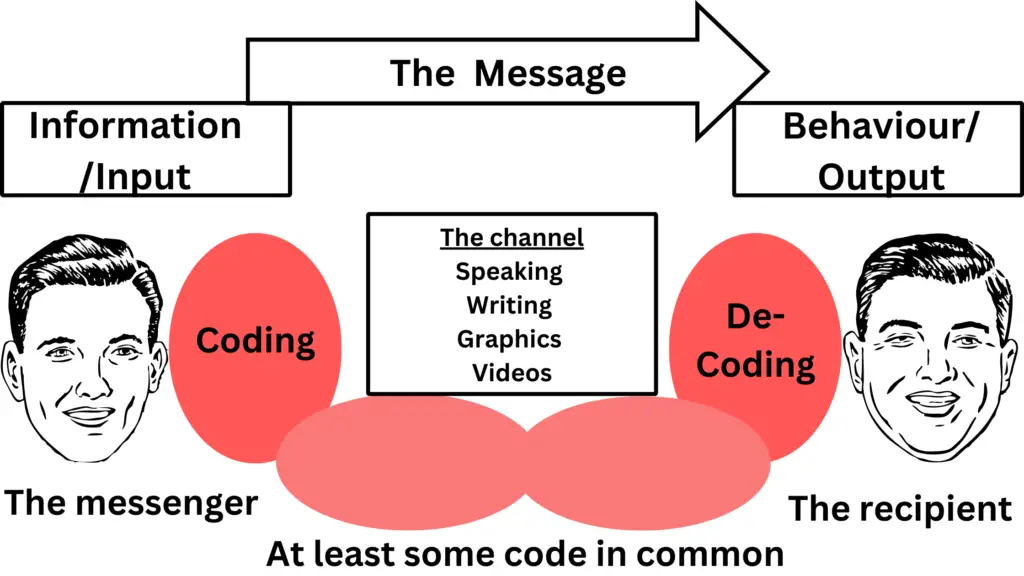
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) What is communication?
Ans: Communication refers to the transmission of thoughts, ideas, and messages between a sender and a receiver. This is done through a channel of communication which can be oral, written, symbolic, picturized, etc. For communication to be effective, certain principles of effective communication should be followed by the sender and receiver.
Q2) What are the 7 elements of communication?
Ans: The seven elements of communication are: sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. These seven elements facilitate understanding and successful interactions between individuals or groups.
Q3) What are the four elements of communication?
Ans: The four elements of communication are sender/source, message, channel, and receiver. These four elements work together in the communication for the successful transmission and reception of the intended message.
Q4) What are the major elements of a communication process?
Ans: The essential components of communication are Sender, Encoding, Message, Channel, Receiver, Decoding, Response, Feedback, and Noise.
Q5) What are the 5 elements of communication?
Ans: The five elements of communication are sender, message, channel, receiver, and feedback. These five elements work together to ensure an effective and meaningful exchange of information between individuals or groups.
Q6) Definition of the sender in communication?
Ans: In communication, the term “sender” refers to the individual, group, or entity that initiates the process of transmitting information or a message to one or more recipients, known as receivers. The sender is the source of the communication and plays a crucial role in conveying a thought, idea, feeling, fact, or any other form of information through various communication channels.



