In today’s highly competitive business environment, it is more important than ever for companies to communicate ethically and transparently with their stakeholders.
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful business relationships, but when ethical considerations are ignored, resulting in unethical communication in business, the consequences can be damaging to both the company and its stakeholders.
In this blog, we will explore what is ethics in communication in addition to key principles and real-world examples of ethical communication practices
Introduction of Ethics in business communication
Ethics in business communication refers to the principles and values that guide individuals and organizations in communicating in an honest, transparent, and responsible manner.
Business communication is a critical component of organizational success, and ethical communication practices are essential to building and maintaining trust with stakeholders such as customers, employees, partners, and the public.
What is ethics in business communication?
Ethics in business communication are a set of standards that govern the behavior of individuals and organizations in their interactions with stakeholders through various forms of communication, such as email, memos, reports, presentations, advertising, and sales letter in business communication.
It includes avoiding misleading or deceptive marketing tactics, being truthful in advertising and public relations efforts, and respecting the privacy and confidentiality of customer and employee information.
Additionally, ethical communication in business requires a commitment to truthfulness, confidentiality, and avoiding manipulative practices. Adhering to ethical standards in business communication helps to build trust, credibility, reputation, and long-term relationships with stakeholders. This ultimately contributes to the success and sustainability of the organization.
Types of Ethics in business communication
Below are just a few examples of the types of ethics that can guide business communication. It’s important for businesses to develop a strong ethical framework that encompasses all of these types of ethics in order to communicate effectively and ethically with all stakeholders.

1/ Professional Ethics: These are the ethical principles and standards that guide professional conduct in a particular industry or profession, such as journalism, public relations, or marketing.
2/ Corporate Ethics: This refers to the values and principles that guide the behavior of a company as a whole, including its communication practices. Corporate ethics might involve a commitment to transparency, accountability, and social responsibility.
3/ Social Ethics: This refers to the ethical principles that govern how a company interacts with society at large, including its customers, employees, and the broader community. Social ethics might involve treating all stakeholders fairly and with respect, avoiding harmful practices.
4/ Personal Ethics: This refers to the values and principles that guide an individual’s behavior in the workplace, including their communication practices. Personal ethics might involve a commitment to honesty, integrity, and treating others with respect.
5/ Cultural Ethics: This refers to the ethical principles that guide how a company communicates with individuals from different cultural backgrounds. Cultural ethics might involve being sensitive to cultural differences, avoiding stereotypes or prejudices, and respecting the beliefs and values of others.
Role of Ethics in business communication
Ethics plays a crucial role in business communication in several ways:
- Builds trust: Ethics in business helps to build trust between businesses and their stakeholders. When businesses communicate honestly, transparently, and respectfully, they demonstrate a commitment to integrity and build a reputation for trustworthiness.
- Maintains reputation: Ethical communication helps to maintain a positive reputation for the business. By communicating in an ethical and responsible way, businesses can avoid negative publicity, damage to their brand, and potential legal or regulatory issues.
- Enhances credibility: Ethical communication enhances the credibility of the business. When businesses communicate ethically and transparently, they demonstrate their commitment to accountability and responsibility, which can increase the credibility of their communication efforts.
- Foster’s employee morale: Ethical communication can also foster employee morale by creating a positive work environment based on trust and respect. When employees see that the business is committed to ethical behavior, they are more likely to feel valued and respected in their work.
- Ensures legal compliance: Ethical communication also helps to ensure that the business complies with legal and regulatory requirements. By communicating in an ethical and responsible way, businesses can avoid potential legal or regulatory issues and maintain compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Overall, ethics plays a vital role in business communication and its process by promoting trust, credibility, and responsibility, which are essential for building positive relationships with stakeholders and maintaining a strong reputation in the market.
Ethics in business communication examples
Some real examples of companies that follow ethics in business communication:
1/ Starbucks: Starbucks is committed to ethical business communication in several ways, including its commitment to fair trade coffee, its efforts to reduce waste and promote sustainability, and its commitment to diversity and inclusion in its workforce. They regularly communicate with their customers about their efforts to promote these values and to be a responsible corporate citizen.
2/ Zappos: Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, is committed to ethical communication with its customers. They are known for their exceptional customer service, which includes clear and transparent communication about their products, policies, and practices. They are also committed to being transparent about their pricing and shipping policies, which helps to build trust and loyalty with their customers.
3/ Airbnb: In 2020, Airbnb faced criticism for its handling of refunds and cancellations during the COVID-19 pandemic. The company responded by communicating more openly and transparently with its customers, including offering full refunds to guests who had to cancel due to COVID-19 restrictions.
7 Principles of Ethics in business communication
The following seven principles can ensure businesses that their communication efforts are ethical, responsible, and aligned with the broader values and principles of the organization.
1/ Honesty: Honesty means communicating truthfully and transparently in all communication efforts. This principle emphasizes the importance of avoiding deception, misrepresentation, and false claims in marketing, advertising, and public relations. Prioritizing honesty in business builds trust with stakeholders, which is crucial for sustaining positive relationships and reputations.
2/ Integrity: Integrity means upholding ethical values and principles in all communication efforts. The principle of integrity emphasizes the significance of doing the right thing, even when it may be challenging. When businesses prioritize integrity, they display their dedication to ethical conduct, thereby building trust with their stakeholders.
3/ Respect: Respect means treating all stakeholders with dignity and courtesy in business communication interactions. This principle emphasizes the importance of cultural sensitivity, inclusivity, and diversity in business communication. Businesses that prioritize respect promote a positive workplace culture, attract a diverse customer base, and build trust with stakeholders.
4/ Fairness: Fairness means treating all stakeholders equitably and without bias in all communication interactions. This principle emphasizes the importance of avoiding discrimination, exploitation, or any unfair treatment of stakeholders. Businesses that prioritize fairness build trust with stakeholders, promote a positive workplace culture, and improve their reputation.
5/ Responsibility: Responsibility means taking ownership of one’s actions and being accountable for the consequences of communication efforts. This principle emphasizes the importance of considering the impact of communication on all stakeholders, including the environment and society. Prioritizing responsibility in business not only builds trust with stakeholders but also displays a dedication to ethical conduct, thus enhancing their reputation.
6/ Confidentiality: Confidentiality means respecting the privacy and confidentiality of customer and employee information. This principle emphasizes the importance of protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust with stakeholders. Businesses that prioritize confidentiality demonstrate a commitment to protecting stakeholders’ privacy and maintaining their trust.
7/ Compliance: Compliance means adhering to legal and regulatory requirements in all communication efforts. This principle emphasizes the importance of ensuring that all communication is ethical, legal, and responsible. Businesses that prioritize compliance avoid legal and regulatory penalties, build trust with stakeholders, and improve their reputation.
Importance of Ethics in business communication
Ethical business communication involves being honest, transparent, and respectful in all communications, while also considering the impact of communication on stakeholders and society as a whole.
By adhering to ethical principles in business communication, businesses can demonstrate a commitment to doing what is right, which can help them establish a positive reputation. Ultimately, businesses that prioritize ethical communication observe the following signs in their business:
- Promotes Positive Workplace Culture: Ethical business communication promotes a positive workplace culture. When businesses treat employees with respect and fairness, they create a work environment that values ethical behavior and fosters trust, respect, and cooperation among colleagues.
- Enhances Customer Loyalty: Ethical business communication enhances customer loyalty. When businesses communicate honestly and transparently, they build trust with customers, which can lead to increased loyalty and repeat business.
- Mitigates Risk: Ethical business communication mitigates risk by helping businesses avoid legal and regulatory penalties, and damage to their reputation. By adhering to ethical principles, businesses can minimize the risk of negative consequences resulting from unethical communication practices.
- Improves Decision-Making: Ethical business communication improves decision-making by encouraging businesses to consider the impact of their communication on stakeholders, including the environment and society. By doing so, businesses can make well-informed decisions that take into account the long-term effects of their communication strategies.
- Enhances Financial Performance: Ethical business communication can enhance financial performance by improving the reputation of the business and building trust with stakeholders. This can lead to increased customer loyalty, higher employee productivity and retention, and improved investor confidence.
Ethical issues in business communication
J.O. Cherrington and D. J. Cherrington identified twelve specific ethical issues that most organizations will face. These twelve ethical issues are
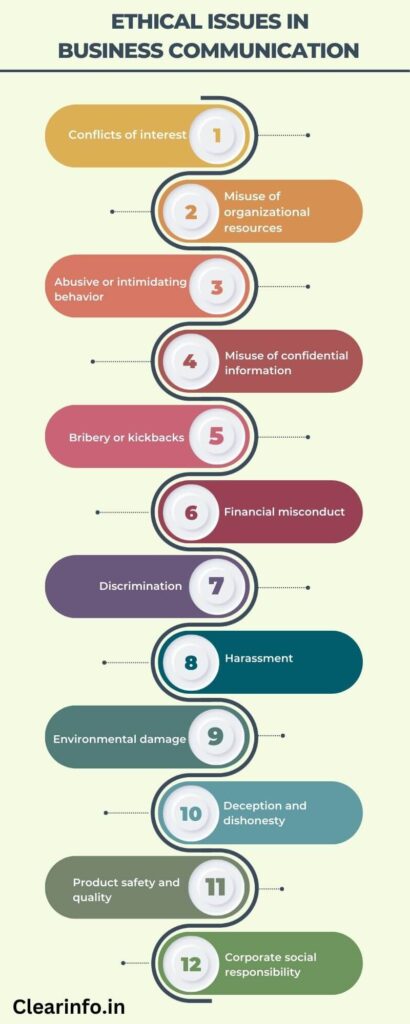
1/ Conflicts of interest: This ethical issue arises when an employee or organization has a competing interest that may interfere with their ability to act in the best interests of the company or its stakeholders. For example, an employee who owns stock in a competing company may be motivated to act in the interests of the competitor rather than their own employer.
2/ Misuse of organizational resources: This ethical issue occurs when an employee or organization uses company resources, such as equipment or time, for personal gain or non-work-related activities. For example, an employee who uses their company computer to conduct personal business during work hours.
3/ Abusive or intimidating behavior: This ethical issue involves behaviors that are aggressive or intimidating towards other employees or stakeholders. Examples of abusive behavior include bullying, harassment, and discrimination.
4/ Misuse of confidential information: This ethical issue arises when an employee or organization fails to maintain the confidentiality of sensitive information, such as personal data or trade secrets. For example, an employee who shares confidential information with a competitor for personal gain.
5/ Bribery or kickbacks: This ethical issue involves offering or accepting bribes or kickbacks in exchange for personal gain. Examples of bribery and kickbacks include accepting gifts in exchange for awarding a contract to a vendor or offering money to a government official to expedite a permit application.
6/ Financial misconduct: This ethical issue involves fraudulent or unethical financial practices, such as embezzlement or insider trading. For example, an employee who misuses company funds for personal gain or an executive who uses insider information to profit in the stock market.
7/ Discrimination: This ethical issue involves treating employees or stakeholders unfairly based on factors such as race, gender, age, or religion. Examples of discrimination include denying job opportunities or promotions based on these factors.
8/ Harassment: This ethical issue involves unwanted or unwelcome behavior, such as sexual harassment or workplace bullying. Instances of harassment comprise unwanted physical contact, verbal abuse, or threats.
9/ Environmental damage: This ethical issue arises when an organization’s activities harm the environment, such as through pollution or the destruction of natural habitats. For example, a manufacturing company releases harmful chemicals into the air or water.
10/ Deception and dishonesty: This ethical issue involves misleading or deceiving stakeholders through false information or misrepresentation. Examples of deception and dishonesty include false advertising, misrepresenting product features, or falsifying data.
11/ Product safety and quality: This ethical issue involves ensuring that products are safe and of high quality for consumers. Examples of product safety and quality issues include manufacturing defects that could harm consumers or failing to disclose potential risks or side effects of a product.
12/ Corporate social responsibility: This ethical concern relates to an organization’s obligation to act in the best interest of society and the environment, rather than solely focusing on financial gain. Examples of corporate social responsibility include charitable giving, environmental sustainability initiatives, and fair labor practices.
What purpose do ethical and legal issues in business communication serve?
Ethical and legal issues are critical components of business communication as they serve several essential purposes. One of the primary purposes of ethical and legal standards is to protect the interests of stakeholders, including employees, customers, shareholders, and the general public
Moreover, ethical and legal issues also play a crucial role in establishing trust and credibility for businesses. Organizations that operate within the boundaries of the law and uphold high ethical standards are more likely to be trusted and respected by their stakeholders. In contrast, businesses that engage in unethical or illegal practices risk damaging their reputation and eroding trust with their stakeholders.
Therefore, businesses that prioritize ethical and legal considerations in their communication strategies are more likely to attain long-term success and sustainability.
How do the 7C’s of ethical communication lead to effective business and organization communication?
When crafting a business message, it is important to keep in mind the objectives of a good business message. The 7 C’s of ethical communication – completeness, conciseness, clarity, consideration, concreteness, courtesy, and correctness – provide a set of guidelines that help ensure that a business message is effective while also upholding ethical standards.
By adhering to these principles, businesses can create messages that are not only clear and concise but also respectful, truthful, and empathetic toward the receiver. This, in turn, helps to achieve the objectives of a good business message, which are to convey information clearly and effectively while also promoting the organization’s goals.
Would Habermasian theory on discourse ethics be applicable to business communication?
Habermasian theory on discourse ethics can be applied to business communication. Habermas’s discourse ethics proposes that ethical decision-making should be based on communicative action, which involves free and open dialogue among all affected parties. This approach emphasizes the importance of mutual understanding, respect, and equal participation in the decision-making process.
In the context of business communication, discourse ethics can be applied in several ways. For instance, when making decisions that impact stakeholders, businesses can engage in open and transparent communication to ensure that all affected parties are heard and understood.
Moreover, discourse ethics can also be applied in the context of organizational culture. By fostering a culture of open and respectful communication, businesses can create an environment where ethical decision-making is prioritized, and employees are encouraged to speak up about ethical concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What are the 5 ethics of communication?
Ans: The five ethics of communication are honesty, fairness, responsibility, respect, and integrity. These ethics serve as a foundation for effective communication, as they promote trust, transparency, and accountability in all forms of communication.
Q3: What are the 4 principles of ethical communication?
Ans: The four principles of ethical communication are respect, honesty, fairness, and responsibility. These principles serve as a guide for communicators to ensure that their messages are truthful, respectful, fair, and responsible towards the receiver. By following these principles, communicators can create messages that are not only effective but also ethical and responsible.



